
- •Instructor: Sara Osman
- •Introduction
- •Literature review
- •General Family Policy in Kazakhstan: Past (Soviet time) and now
- •Family diversity: Recent changes
- •Specific Family Policies in different countries and people’s attitude on it
- •Methodology
- •Results
- •Discussion
- •Conclusion
- •Bolas, d. (n.D.). Feminist family law rooted in ussr Marxist Law, 1974. Retrieved on the 17th of February from http://www.Equalparenting-bc.Ca/
Methodology
To analyze these issues, primary research was done. The research was designed as descriptive. Survey is easy to conduct and requires little time from respondents to respond and from me to survey. Thus, I created a survey on surveymonkey.com and it consisted of 10 questions. There were some open ended questions. At the beginning respondents asked to write down general information about them: age, gender, and social class. Then they were asked to describe their family and, finally, their position in some issues about family. Respondents may skip some questions or make multiple choice when answering not open ended questions.
The population of the survey is KIMEP university students. The link to the survey questions was sent to group of students with note that responses are voluntary. The primary sample consisted of 30 people and they were chosen randomly from subscribers’ list of KIMEP’s official forum on vk.com. After a day only 11 students volunteered and because of that I expanded the sample. Another 10 KIMEP students were chosen from friends’ list of my vk.com page. In whole, the sample for the questionnaire study comprised students from all courses, but many of them were freshmen. Then, there were only 4 male respondents of general 18. On the next day 10 male respondents were chosen randomly from groups of KIMEP students’ organizations to make a balance between genders.
The survey was created and started on 6th of March. It lasted till evening of 10th of March. The survey link was sent to 50 people and was answered by 24 students, 11 male and 13 female. The results were analyzed by the help of surveymonkey.com site and described in the next section. For better understanding figures for the main findings were created.
The survey was intended to answer what family structure respondents have and what family structure they are planning or likely to build. The family structure was considered in relation to parents’ role and its cultures’ modernization or, vice verse, conservation.
Results
The purpose of this part is to count results and show or describe the main findings by visual aids. More than three quarters of the respondents were freshmen from 17 to 19 and more than half of general sample were girls.
The results of the survey were analyzed and the major parts of it will be shown here. Half of the respondents were from the middle class, a single respondent answered that he or she from lower class, and other major group preferred not to answer this question. The majority, 19 students, answered that their families are modern and many of them described “modern families” as tolerant to new youth culture and creative, also. Other respondents described “conservative ones” as families with old lifestyles, concepts, traditions, and religious views. Interestingly, there is one female respondent, from her respond in their family mother dominates on everything. There are other results of the survey. It is predictable that on issues related to child upbringing mother has more authority and on issues related to different kinds of problem solving father has more controll. The next major points will be shown with figures.

Figure 1
Figure 1 describes how structured the respondents’ families are in relation to parents’ role related to finance and work. The first colored column shows the number of families that have equality on specific issue, the second one shows the number of mother-headed families, and the last third one shows the father-headed families’ number. There are two tables to compare. The first is related to earning or working and the second is related to how to spending or budget regulating. The families where parents are equal on these issues are greater in both, but mother-dominating families on spending money are more, but not on earning. On the other hand, families with fathers as breadwinners are more common than as budget regulators. It shows how different parents treat financial issues.
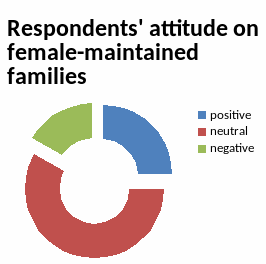
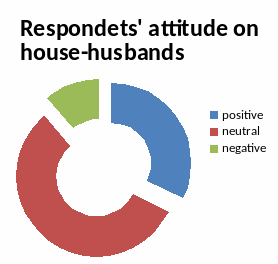
Figure 2a Figure 2b
There are the results that show the respondents position related to role reversal. The Figure 2a shows respondents’ attitude on families where females dominate and the second one, Figure 2b, shows respondents’ attitude to families where fathers, sit at home and do all house works instead of housewives. There are 3 variants on each for the respondents when answering: positive, it means that they are not against it and support; neutral, means that they do not care or have no idea about; negative, means that they are against it and do not support the idea. It is apparent that in the Figure 2a more than half of the respondents have neutral attitude to women-maintained families and only few number of respondents do not support this idea. Men and women have same responses to this question. However, almost half of the respondents are against families (9 females and 3 males) with fathers doing house works in the Figure 2b. Only four respondents have positive attitude to it (1 female and 3 males). The two tables are absolutely different.
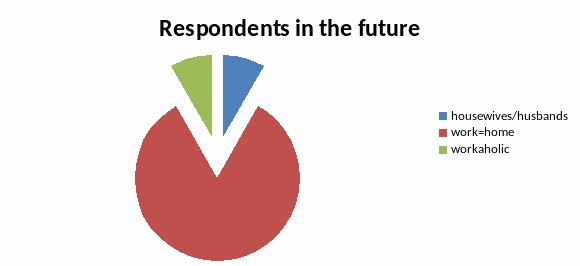
Figure 3
The data from the third figure describes respondents’ willingness or plans for their future life. There are three parts of the circle: first, for people seating at home; second, for the ones who prefer to combine family with work; and third part, which shows the number of future workaholics. There are only a pair on first piece of a circle and another pair on the third piece. 2 women responded that they are planning to be housewives and one man and 1 woman responded that they are planning to be workaholics. The remaining majority plans to hold on to both, work and home.
As it is mentioned many findings are similar to predictions. However, there are some points to be discussed and clarified. There is an interesting trend between parents’ role on financial issues.
