
- •Contents
- •Введение
- •Introduction
- •In groups of two or three discuss the following points and report back to the class on your major conclusions.
- •Vocabulary enrichment
- •Vocabulary practice
- •If you are looking for a career that will … and excite you. If you want to make a real difference in the lives of children. If you are ready to make an … on the future. Then New York needs you!
- •In groups of two or three discuss the following points and report back to the class on your major conclusions.
- •Vocabulary enrichment
- •Teacher certification from start to finish
- •In groups of two or three read the following texts, discuss them, and report back to the class on your major conclusions in order to make a procedure of teacher certification complete.
- •Applicants for Certification
- •II. Certification Summary: Types of Certificates and Licenses
- •Requirements for Certification in Specific Subject Titles
- •IV. Ways to Obtain Teacher Certification. Applying for a certificate
- •1. Say what you’ve learned from the texts about:
- •2. Decide if the following statements are true or false, and circle either the t or f. If the statement is false, write the correct answer in the space provided.
- •Vocabulary practice
- •In groups of two or three discuss the following points and report back to the class on your major conclusions.
- •Vocabulary enrichment
- •I. About the nystce
- •II. Teacher Certification Examinations: Program Overview
- •III. Citizenship/Residency Requirement
- •Say what you’ve learned from the texts about:
- •Vocabulary practice
- •In groups of two or three discuss the following points and report back to the class on your major conclusions.
- •Vocabulary enrichment
- •Vocabulary practice
- •In groups of two or three discuss the following points and report back to the class on your major conclusions.
- •Vocabulary enrichment
- •I. Last Framework & Objective
- •II. Last Preparation Techniques & Test-Taking Strategies
- •Vocabulary practice
- •In groups of two or three discuss the following points and report back to the class on your major conclusions.
- •Vocabulary enrichment
- •I. Reading Review
- •II. Writing Review. Written Analysis and Expression
- •Vocabulary practice
- •In groups of two or three discuss the following points and report back to the class on your major conclusions.
- •Vocabulary enrichment
- •I. Mathematics Test Strategies
- •II. Mathematics Review
- •Integers
- •Vocabulary practice
- •In groups of two or three discuss the following points and report back to the class on your major conclusions.
- •Vocabulary enrichment
- •I. Biology Review
- •Vocabulary practice
- •Vocabulary enrichment
- •II. Geosciences Review
- •Vocabulary practice
- •Vocabulary enrichment
- •III. Physical Sciences Review
- •Vocabulary practice
- •In groups of two or three discuss the following points and report back to the class on your major conclusions.
- •Vocabulary enrichment
- •Industrialization of America
- •I. United States History and Humanities Review
- •Industrialization of america
- •Vocabulary practice
- •Vocabulary enrichment
- •II. World History Review
- •Vocabulary practice
- •In groups of two or three discuss the following points and report back to the class on your major conclusions.
- •Visual and performing arts
- •Vocabulary enrichment
- •Visual and Performing Arts Terms Review
- •I. Visual Arts Review
- •II. Performing Arts Review
- •Vocabulary practice
- •Visual and performing arts practice items
- •In groups of two or three discuss the following points and report back to the class on your major conclusions.
- •Vocabulary enrichment
- •Interpretation
- •I. Literature Review
- •II. Communication Review
- •Information sources
- •Vocabulary practice
- •Assessment of teaching skills-written (ats-w)
- •01 Understand human developmental processes and variations, and use this understanding to foster student learning.
- •02 Understand how factors in the home, the school, and the community may affect learners; and use this knowledge to create a classroom environment within which all students can grow and learn.
- •05 Understand learning processes and apply strategies that foster student learning and promote students' active engagement in learning.
- •06 Understand curriculum development and apply knowledge of factors and processes in curricular decision making.
- •07 Understand instructional planning and apply knowledge of planning processes to design effective instruction.
- •08 Understand how to use formal and informal assessment to learn about students, plan instruction, monitor student understanding, and make instructional adjustments.
- •09 Understand principles and procedures for organizing and implementing lessons, and use this knowledge to help learners construct meaning and achieve intended outcomes.
- •10 Understand multiple approaches to instruction, and use this knowledge to facilitate learning in various situations.
- •11 Understand how motivational principles and practices can be used to promote student achievement and active engagement in learning.
- •12 Understand how to use a variety of communication modes to promote student learning and to foster a climate of trust and support in the classroom.
- •13 Understand how to structure and manage a classroom to create a climate that fosters a safe and productive learning environment.
- •14 Understand how to reflect productively on one's own practice and take advantage of various resources and opportunities for enhancing professional development and effectiveness.
- •15 Understand how to foster effective home-school relationships and school-community interactions that support student learning.
- •17 Understand the structure and organization of the New York State educational system and the role of education in the broader society.
- •Liberal arts and sciences test (last)
- •01 Use mathematical reasoning in problem-solving situations to arrive at logical conclusions and to analyze the problem-solving process.
- •02 Understand connections between mathematical representations and ideas; and use mathematical terms and representations to organize, interpret, and communicate information.
- •03 Apply knowledge of numerical, geometric, and algebraic relationships in real-world and mathematical contexts.
- •06 Understand and apply skills, principles, and procedures associated with inquiry and problem solving in the sciences.
- •07 Understand the interrelatedness of historical, geographic, cultural, economic, political, and social issues and factors.
- •08 Understand principles and assumptions underlying historical or contemporary arguments, interpretations, explanations, or developments.
- •09 Understand different perspectives and priorities underlying historical or contemporary arguments, interpretations, explanations, or developments.
- •10 Understand and apply skills, principles, and procedures associated with inquiry, problem solving, and decision making in history and the social sciences.
- •11 Understand and interpret visual representations of historical and social scientific information.
- •12 Understand elements of form and content in representations of works from the visual and performing arts from different periods and cultures.
- •21 Prepare an organized, developed composition in Edited American English in response to instructions regarding content, purpose, and audience.
- •Reading practice items
- •Mathematics practice items
- •Science practice items
- •History, humanities, and social science practice items
- •Visual and performing arts practice items
- •Literature and communication practice items
- •References
- •2 25404, Г. Барановичи, ул. Войкова, 21.
History, humanities, and social science practice items
1. Which of the following has the least significant impact on the culture of a group?
(A) Material conditions of life.
(B) Geography.
(C) Climate.
(D) Physical appearance.
2. Which of the following forms of government is least used in the countries of today's world?
(A) Democracy.
(B) Aristocracy.
(C) Monarchy.
(D) Federal states.
3. In the United States, the power to declare war is given to the
(A) president.
(B) Congress.
(C) Supreme Court.
(D) Senate.
4. Which of the following limits the powers of the federal government?
(A) Judicial branch.
(B) The Bill of Rights.
(C) Constitution.
(D) Executive branch.
5. Social psychologists study
(A) people as individuals.
(B) animals in interactive settings.
(C) children at play.
(D) people's behavior in groups.
6. The Ming, Chou, Sung, and Manchu Dynasties were
(A) Indian.
(B) Taiwanese.
(C) Japanese.
(D) Chinese.
7. Sigmund Freud's psychosexual stages of development listed below are organized into which sequence?
(A) Oral, genital, anal, latency.
(B) Genital, anal, oral, latency.
(C) Oral, anal, genital, latency.
(D) Oral, anal, latency, genital.
8. All the following would be considered the job of an anthropologist EXCEPT:
(A) Studying the genetic make up of a fossil.
(B) Living with a community of Aborigines.
(C) Testing a rock sample with carbon 14.
(D) Organizing a dig at a burial site.
9. Who coined the term “iron curtain”?
(A) Churchill.
(B) Truman.
(C) Lenin.
(D) Stalin.
10. A U. S. Army officer describes any victory over Native American groups as a triumph, but any defeat as a massacre. What is this an example of?
(A) Authoritarianism.
(B) Ethnocentrism.
(C) Righteousness.
(D) An inferiority complex.
11. Which of the following is not a reason why early civilization began in these shaded areas?
(A) Comfortable climate.
(B) Fertile land.
(C) Fresh water supply.
(D) Potential commerce opportunities.

(A) The steam engine.
(B) The cotton gin.
(C) Standard parts.
(D) The conveyor belt.
13. Why do multinational corporations produce goods in countries such as Mexico and the Philippines?
(A) To increase cash flow in these countries.
(B) To widen the marketing area.
(C) To lower the cost of labor.
(D) To lower the price of the product.
14. During one of the Lincoln-Douglas debates, Abraham Lincoln acknowledged that the Southern people were no more responsible for the existence of slavery than those in the North. He went on to say that he understood and appreciated the position of those in the South who said that it was very difficult to get rid of the institution of slavery in an acceptable way. He concluded, however, that these arguments were no more a basis for extending slavery into the free territories of the United States, than they were a basis for legalizing the importation of African slaves. During this debate, Lincoln conveyed the notion
(A) existence doesn't justify expansion.
(B) hate the sin but not the sinner.
(C) do unto others as they would do unto you.
(D) let sleeping dogs lie.
15. Those who validly criticize the workings of the electoral college do so for which of the following reasons?
(A) The system is not direct democracy.
(B) It is not a true representative democracy.
(C) There is not an equal number of votes for each state.
(D) The electors are influenced by their party affiliation only.
16. All these statements were advice given by George Washington in his farewell address. EXCEPT:
(A) Avoid permanent alliances with any foreign powers.
(B) Avoid political parties based on geographic boundaries.
(C) The ability of America to pay its national debts must be safeguarded.
(D) Avoid supplying monetary aid to foreign countries.
17. Karl Marx's Communist Manifesto wished for what result for an economic revolution?
(A) A society where the proletariat ruled.
(B) A democratic society.
(C) Authoritarian society.
D) A classless society.
18. What reason was given to Japanese Americans when they were put in internment can during World War П?
(A) They were told that their lives were in danger.
(B) They were thought to be plotting a sneak attack on home soil.
(C) They were considered a threat to n security.
(D) They were being shipped back to, as soon as possible.
Use this map to answer questions 19 and 20.
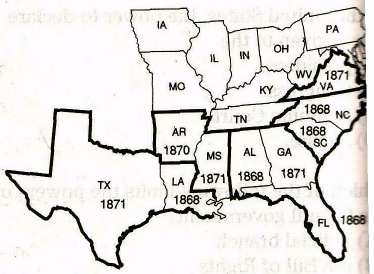
Military Districts During Reconstruction Date State Readmitted to the Union
19. Which of the states listed below was under federal rule for the longest period of tin
(A) Texas.
(B) Arkansas.
(C) Alabama.
(D) South Carolina.
20. Florida was part of a military district i which two other states?
(A) Mississippi and Arkansas.
(B) Texas and Louisiana.
(C) North Carolina and South Carolina.
(D) Georgia and Alabama.
21. Which of the following is NOT an example of a self-evident truth found in the Declaration of Independence?
(A) Being treated as equal to someone else.
(B) Being free from taxation without representation.
(C) Being able to have a say in the government.
(D) Being able to change a government that is hurting society.
22. What 1957 event justified a massive increase in spending for science programs in U. S. schools and research institutions?
(A) The detonation of a hydrogen bomb by the Soviet Union.
(B) The launching of Sputnik by the Soviet Union.
(C) The development of the microprocessor by the Soviet Union.
(D) The revelation of huge Soviet stockpiles of deadly chemical weapons.
23. The Bill of Rights guarantees all of the following EXCEPT:
(A) the right to free speech.
(B) the right to a fair trial.
(C) the right to bear arms.
(D) the right to vote.
24. Which situation described here illustrates the constitutional principle of checks and balances?
(A) The President vetoes a bill passed by Congress.
(B) The President criticizes a decision of the Supreme Court.
(C) The President delivers a State of Union address.
(D) The President appoints a cabinet.

APPENDIX G
