
- •V. Index method
- •Solution:
- •Solution:
- •I. Index analysis of the loan repayment
- •II. Analysis of the index variable and the constant compositions and the structural shifts
- •III. Factor analysis of absolute increases of the amount of turnover of the loan repayment
- •Solution:
- •Effect of changes in prices (tariffs)
- •Effect of changes in cost of sales
- •Effect of changes in the volume of sales
- •Effect of changes in the structure of goods sold
V. Index method
The educational purpose of solving the problems using the index method consists of the following:
- to seize the techniques of calculating individual and summary indices; average indices; indices of variable, constant composition and structural shifts; to learn how to conduct a factorial analysis of the absolute and relative increases of the studied features; to study the technique of the factorial analysis of the sales profit from such factors, as the price (tariffs) of sold production, the cost price of sold output, volume of sales, change of structure of sold production;
- to give economic interpretation of the received numerical characteristics;
- to formulate the conclusions derived from the received data.
Indices are generalizing parameters of comparison in time and in space for not only the same phenomena, but also for sets consisting of incommensurable elements.
Techniques of construction and calculation for time and spatial comparisons are identical.
Dynamics of the same phenomena is studied by means of individual indices (i). Changes of the sets consisting of elements, which are not directly comparable, we can study by means of the general (summary) indices (I). Summary indices are subdivided into aggregate indices and weighted average of individual indices.
The general indices are performed in the form of the aggregate indices. The aggregate index is a complex relative parameter in which the sums of products of two values are directly compared. One value changes, and it is the indexed value. Other value remains constant, and it is the weight of the index.
The average index is the index calculated as the average size from individual indices.
T he
arithmetic-mean index of the physical volume of production is:
he
arithmetic-mean index of the physical volume of production is:
T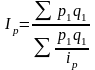 he
harmonic-mean index of prices is:
he
harmonic-mean index of prices is:
The index expressed as the ratio of average levels of the studied phenomenon, related to the different periods of time, is named the index of variable composition. The index of variable composition shows simultaneous change of the indexed value and the structure of set.
Index of variable composition of the cost of production of the same kinds at the several enterprises is:

The index showing change of average value of the studied phenomenon only due to the change of the indexed value is named the index of constant composition.
The index of constant composition of the cost of production is:

The index describing influence of change of structure of the studied phenomenon on the dynamics of the average level of this phenomenon is named the index of structural shifts (structure).
T he
index of structural shifts at studying the change of the average
level of the cost is:
he
index of structural shifts at studying the change of the average
level of the cost is:
Task # 5. There are data on the tax rates and the tax bases for the base and the reporting years for two types of taxes:
-
Tax
Tax rate
Tax base,
thousand tenge
Base year

Reporting year

Base year

Reporting year

А
1
2
3
4
1
0,2
0,1
250
400
2
0,16
0,2
95
100
Total:
-
-
345
500
• Calculate:
1) The aggregate index of the tax revenues - the total change in the tax revenue for two types of taxes together, which is accounted for changes of two factors: the tax base and the tax rates;
2) The general index of the tax base - the change of the tax revenue only by changing the tax base;
3) The general index of the tax rates - the change of the tax revenue only by changing the tax rates;
4) Check the correlation between the indices.
• Perform the factor analysis of the absolute increases of the tax revenues.
• Draw an economic conclusion.
