
- •Part II
- •Unit III
- •Section 1. Basic course
- •Word usage and common errors.
- •Pronunciation practice.
- •Read the text.
- •Answer the questions.
- •True or false?
- •Translate into English.
- •Complete the sentences.
- •II. Pronunciation practice. 2
- •III. Read the text. 2
- •Correct the mistakes in the computer translation.
- •If you can translate these word-combinations your total score is 192. Congratulations!
- •Task 2. Pipelines. History and Development
- •I. Word usage and common errors.
- •P ronunciation practice.
- •Read the text and answer the questions at the beginning of the passages. Pipelines
- •IV. Make up and translate word — combinations choosing from the words given under the table.
- •V.Complete the sentences.
- •II. Pronunciation practice. 2
- •III. Read the text. 2
- •VII.Complete the sentences.
- •Read the passage and correct the computer translation of it.
- •Learn the definition by heart.
- •What is a Pipeline?
- •If you can translate these word-combinations your total score is 204. Congratulations!
- •Task 3. What is the Difference between Oil and Gas Pipeline?
- •I. Word usage and common errors.
- •Pronunciation practice.
- •Read the text and underline the international words.
- •Make up word combinations.
- •Make up questions to the answers.
- •True or false?
- •Fill in the gaps and read the extract.
- •Did you know that...
- •Complete the sentences using information in the right — hand column.
- •If you can translate these word-combinations your total score is 216. Congratulations!
- •Task 4. Pipeline Components
- •Word usage and common errors.
- •Pronunciation practice.
- •Read the text and underline the international words. Pipeline components
- •Find the meaning of the words in the right-hand column.
- •What element of the pipeline network is this? Guess, please.
- •Translate into Ukrainian and make the report on the topic.
- •If you can translate these word-combinations your total score is 228. Congratulations!
- •Task 5. Pipelines Classification
- •Word usage and common errors.
- •Pronunciation practice.
- •Translate the international words and find more of them in the text.
- •In general, pipelines can be classified in three categories depending on purpose:
- •Look through these descriptions and give the words they describe. Try to improve the incomplete descriptions.
- •Fill in prepositions and translate the sentences. Of, at, with, from, to, in, of, for, between
- •Translate into English.
- •Choose the correct word. In these sentences there are some words which you do not know. Guess what they mean and explain them to each other.
- •Read and translate the text; draw the table of oil pipelines classification.
- •Reproduce this piece of information filling in the right letter. Gas pipelines
- •Fill in the blanks with the necessary tense form. Don’t forget about Passive Voice. Offshore (submarine) pipelines
- •II. Pronunciation practice. 2
- •III. Read the text. 2
- •Fill in the gaps with: to transport, be transported, transported.
- •If you can translate these word-combinations your total score is 240.Congratulations!
- •Word usage and common errors.
- •Pronunciation practice.
- •Translate the international words and find more of them in the text.
- •Read and translate the text. Underline adjectives and adverbs in the text.
- •Find the meaning of the word and the antonym (if any) in the right — hand columns.
- •Fill in the gaps with the verbs in the necessary tense form.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Study the picture and read the sentences in the right order.
- •Study the material and prepare the report. Business of Pipelines
- •How Are Pipelines Operated?
- •How Are Pipelines Monitored?
- •If you can translate these word-combinations your total score is 252. Congratulations!
- •Task 7. Leak Detection Systems
- •Word usage and common errors.
- •Pronunciation practice.
- •True or false?
- •Make up the titles of the scientific articles.,
- •Single or double? Fill in the missing letter if necessary.
- •Task 8. Safety. Ecological and Environmental Impact
- •Word usage and common errors
- •Pronunciation practice. Read and translate the words.
- •Read and translate the text. Find in the text and discuss the leading causes of pipeline failures. Safety
- •Fill in the table using the list.
- •Find the word in the list of letters and complete the word combination.
- •Answer the questions.
- •Complete the sentences.
- •II. Pronunciation practice. 2
- •III. Read the text. 2
- •VIII. Translate into English.
- •If you can translate these word-combinations your total score is 276. Congratulations! You have finished the basic course.
Learn the definition by heart.
Remember!
Pipelines can be categorized in different ways. In what follows, pipelines will be categorized according to the commodity transported and the type of fluid flow.
What is a Pipeline?
Definition. A pipeline comprises all parts of the physical facility through which liquids (crude oil, petroleum products) or gases (natural gas, carbon dioxide) are transported, including pipe, valves and other equipment attached to the pipe, compressor units, pump stations, metering stations, regulator stations, delivery stations, holders and fabricated assemblies.
Pipelines are the safest and most efficient means of transporting crude oil and natural gas from producing fields to refineries and processing plants and of distributing petroleum products and natural gas to the consumer.
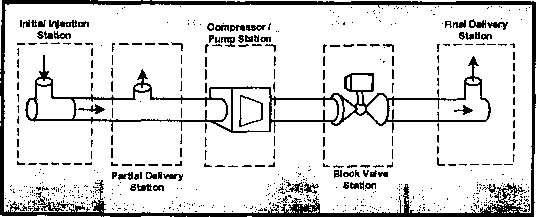
Check yourself!
If you can translate these word-combinations your total score is 204. Congratulations!
Pipeline manufacture |
|
Large - diameter concrete pressure water pipes |
|
Pipeline leak detection |
|
Computer control initialization |
|
Pipeline construction facilitation |
|
Regulator delivery station |
|
Fluid flow type |
|
Treatment plant |
|
Smaller-diameter branch lines |
|
Stoneware pipe system |
|
Capital city development |
|
Chain pumps |
|
Task 3. What is the Difference between Oil and Gas Pipeline?
I. Word usage and common errors.
We say that people or things differ when we are talking about differences with a group. Compare: “I asked the class and opinions differed”. (There were many different opinions). “I asked the class again and opinions were different” (different from the first time).
Make a distinction between A and B = not regard or treat A and B in the same way.
To avoid confusion, only should be placed as near as possible to the word or phrase that it modifies.
۷ The level of pollution can be reduced only by the introduction of new laws.
X The level of pollution can only be reduced by the introduction of new laws.
Pronunciation practice.
Volumetric, expansion, megapascal, environment, associated, unique, wildlife, challenge, eventually, source, avoid, construction, encounter, occur, sequence, refrigeration, multiproduct, permafrost, ploughing, physical.
Read the text and underline the international words.
Gas and oil pipelines are very different in their design and
modes of operation. Gas has a low volumetric heat capacity, warms quickly when compressed, and cools quickly when expanded. The quantity of gas transported is greater when the gas is compressed to a high density. However, the gas will get hot when passing through the compressor system. Between compressor stations some expansion and cooling will occur.
Deliberate cooling of the gas is necessary when it is transported through a pipeline buried in the permafrost. The gas in some pipelines is at a pressure as great as 12 megapascals. After compression, the hot gas must be cooled by refrigeration. A detailed discussion of gas pipeline construction and the environmental problems associated with its traversal of permafrost or of active soil layers is found in the city of Williams (1979).
An application was made to the Canadian government in 1974 to build a gas pipeline up the Mackenzie River valley. The Canadian government decided not to allow the Mackenzie valley route, but agreed inistead to build the Alcan gas pipeline parallel to the oil pipeline from Prudhoe Bay to Fairbanks, Alaska; this pipeline was to cross the southern Yukon and follow the Alcan highway to southern Canada, where the pipeline would branch out to California or to the upper Midwest. (This route avoids the northern Yukon coastal plain, where there is unique wildlife habitat and where the native rights of Eskimos are an important consideration). However, because of a changing oil and gas market, this Alcan gas pipeline has not been built.
Other gas pipeline proposals are under consideration. Among these is a proposal for a pipeline to carry gas from sources in the Canadian Arctic Islands down the west side of Hudson Bay and into eastern Canada. This particular pipeline would need to be installed under the Arctic Ocean between the Boothia Peninsula, Bathurst Island, and Milville Island. The technical challenge of doing this will be enormous. Grooves in the seabed caused by the ploughing of icebergs can occur. Pressure ridges of winter sea ice may scrape the seabed, and floating ice islands may rake the bottom. The pipeline going from the seabed to shore encounters severe problems with waves and floating ice-problems more severe than those encountered with river crossings. However, these technical problems eventually will be solved, and we will have gas pipelines in the Arctic Ocean and in the Antarctic Ocean.
