
- •Exercises
- •Translate into Russian.
- •Develop the following ideas. Make use of the active vocabulary given in brackets.
- •Information technology or it
- •3M: an American star in Europe.
- •Exercises
- •Match the words from the-text with their corresponding definitions.
- •Paraphrase the sentences using the active vocabulary.
- •Complete the following passage using the active vocabulary.
- •Read the following description of how 3m developed its famous Post-it notes and answer the questions.
- •II. Dialogue.
- •Listen to the dialogue and reproduce it
- •Company world
- •Choose the best word from the brackets ( ) to fill the gap.
- •Choose the best word from the brackets to fill the gap.
- •Business news The end for Sycamore?
- •Letter writing:
UNIT 5 “COMPANY”
I. Text-1
Business is the activity of producing, buying and selling goods and services. A business, company, firm or more formally, a concern, sells goods or services. Large companies considered together are referred to as big (large) business.
Large businesses differ from small ones in a wide variety of ways. In many countries there are nationalised companies belonging to the state, as well as private companies.
Often one person does not have enough money to start a business. Combining the resources of a number of people and forming a corporation is a way to raise the large amount of money needed. A corporation is a business that, although owned by one or more investors, legally has the rights and duties of an individual. Corporations have the right to buy, sell, and own property. Corporations may make legal contracts, hire and fire workers, set prices, and be sued, fined and taxed. A business must obtain a charter of incorporation from a state legislature to be legally recognized as a corporation.
A corporation issues shares of stock which are certificates representing ownership in the corporation. Investors buy and sell these shares of stock. Often hundreds and even thousands of small investors own stock in a single corporation. Because a corporation may have many owners, the stockholders elect a board of directors. Stockholders have one vote for each share of stock they own. The board of directors hires individuals to manage the day-to-day operation of the corporation. These individuals include the President and other chief administrators of the company. Most important, the board of directors manages the resources of the corporation in order to produce a profit. If the corporation makes a profit, shareholders may receive a dividend — a share of the profit paid on the stock. The board of directors decides how much of the profit should be divided among stockholders. The board may decide to reinvest some of the profit in the corporation for expansion, modernization, or research and development.
Corporations have some advantages over sole proprietorships and partnerships. First, a corporation has limited liability. Thus if the corporation goes bankrupt or is sued, the stockholders lose only the value of their stock. The stockholders, who are the corporation owners, cannot be held personally responsible for any money the corporation owes. Second, corporations have the ability to raise very large amounts of money. They use this money to change models, replace obsolete equipment, and build new factories. Corporations can raise money by selling bonds, as well as stocks. A bond is a certificate that promises to pay the holder of a bond, the investor, a certain amount of money on a certain date. Stocks and bonds differ in two important ways. Bonds, unlike stocks, do not represent ownership in the corporation. Also the rate of return on stocks changes; the rate of return on a bond is set when the bond is sold. Third, a corporation has an unlimited life. That is the corporation continues to function despite death, transfer, or changes in ownership, management, or labour. The work of sole proprietor or partners can end abruptly in such circumstances. This stability attracts small investors. The fourth advantage of corporation is the ease of ownership transfer. Selling a small business may be difficult; selling shares of stock is relatively easy. The investor also has an advantage. The ability to get out of one business, by selling stock, and into another quickly, by buying stock, is quite useful to small investors.
Corporations have disadvantages as well as advantages. First, complex forms must be filed with the state or federal government. A charter must then be issued, investors found, shares sold, and manufacturing or sales begun. The procedure for setting up a corporation is more difficult than that for setting up a sole proprietorship or a partnership. Also, to succeed a corporation must pay stockholders regular dividends and must keep detailed records to satisfy appropriate government agencies.
Second, a corporation's profits are subject to double taxation. A corporation must pay taxes on its profits before the profits are distributed to stockholders as dividends. The stockholders include this dividend money as personal income on their income tax forms. Stockholders pay taxes on this income. The government, then, has taxed the corporation's profits twice.
Third, in corporations with many owners or stockholders the individual share of profits in the form of dividends is comparatively small. In a single proprietorship or partnership, profits are divided among fewer individuals. Therefore, individual incomes are often greater.
Fourth, a corporation's owners do not directly control the business. Most individual stockholders take little interest in management decisions. In contrast, sole proprietors or partners manage their own business. The main concern of the owner-managers is the success of the business. Managers of large corporations, though, may not have invested their own money in the business. Career decisions may be different from, and more important than, decisions to improve the business. For this reason many corporations arrange for management to own shares of stock.
In very large firms the shareholders have very little to do with the day-to-day running of the firm. This is left to the management. Large companies may be organized into several large departments, sometimes even divisions. The organisational structure of some companies is very hierarchical with a board of directors at the top and the various departmental heads reporting to them. Often the only time shareholders can influence the board is at the yearly shareholders' meeting.
Exercises
Translate into Russian.
to raise the large amount of money needed to sue to fine to tax a charter of incorporation shares of stock a stockholder a board of directors limited liability equipment
|
a bond ownership the rate of return on stocks ownership transfer to be filed with to keep detailed records to be subject to double taxation income tax forms hierarchical report to smb
|
Explain
to be dominated
to make legal contracts
to receive a dividend
to keep detailed records
to owe
to set prices
Answer the questions.
What is the role of business?
How do different businesses differ?
What are the rights and duties of a corporation?
What should be done in order to be legally recognized as a corporation?
What is a share of stock? What role do the stockholders play in the activities of a corporation?
Who runs the day-to-day operation of the corporation?
What is a dividend? Who decides in what way the profit of the company should be distributed?
What are the advantages of corporations over the other forms of businesses?
What disadvantages do the corporations face?
Why do many corporations arrange for management to own shares of stock?
Say whether these statements are true or false, explain why?
Corporations are easy to organize, decisions can be made quickly, profits are shared with only a few people, and the owners are responsible for success or failure of the business.
If the corporation makes a loss the board may decide to reinvest some of the profit in the corporation for expansion, modernization, or research and development.
If the corporation goes bankrupt or is sued, the stockholders lose the value of their stock. They are personally responsible for any money the corporation owes.
Bonds represent ownership in the corporation.
In corporations with many owners or stockholders the individual share of profits in the form of dividends is comparatively small.
In very large firms the shareholders have very little to do with the day-to-day running of the firm.
Develop the following ideas. Make use of the active vocabulary given in brackets.
1. The basic economic institution in different economic systems is the business.
(to produce goods and services; to come in every shape and size; to be dominated by large firms; to differ in a wide variety of ways; to require natural resources, labour, and capital; to organize these resources; to be an entrepreneur)
2. The stockholders elect a board of directors.
(to have a vote; to manage the day-to-day operation; the president and other chief administrators; to manage the resources of the corporation; to produce a profit; to receive a dividend; to reinvest the profit)
3. Corporations have disadvantages as well as advantages.
(to be filed with the state or federal government; to issue a charter; to set up a corporation; to pay stockholders regular dividends; to keep detailed records; to be subject to double taxation; to include smth. on income tax forms; to control the business; to invest own money in the business; to arrange for management to own shares of stock)
a). Consider the following information:
Most companies are made up of three groups of people: the shareholders (who provide the capital), the management, and the workforce. The management structure of a typical company is shown in the following organisation chart:
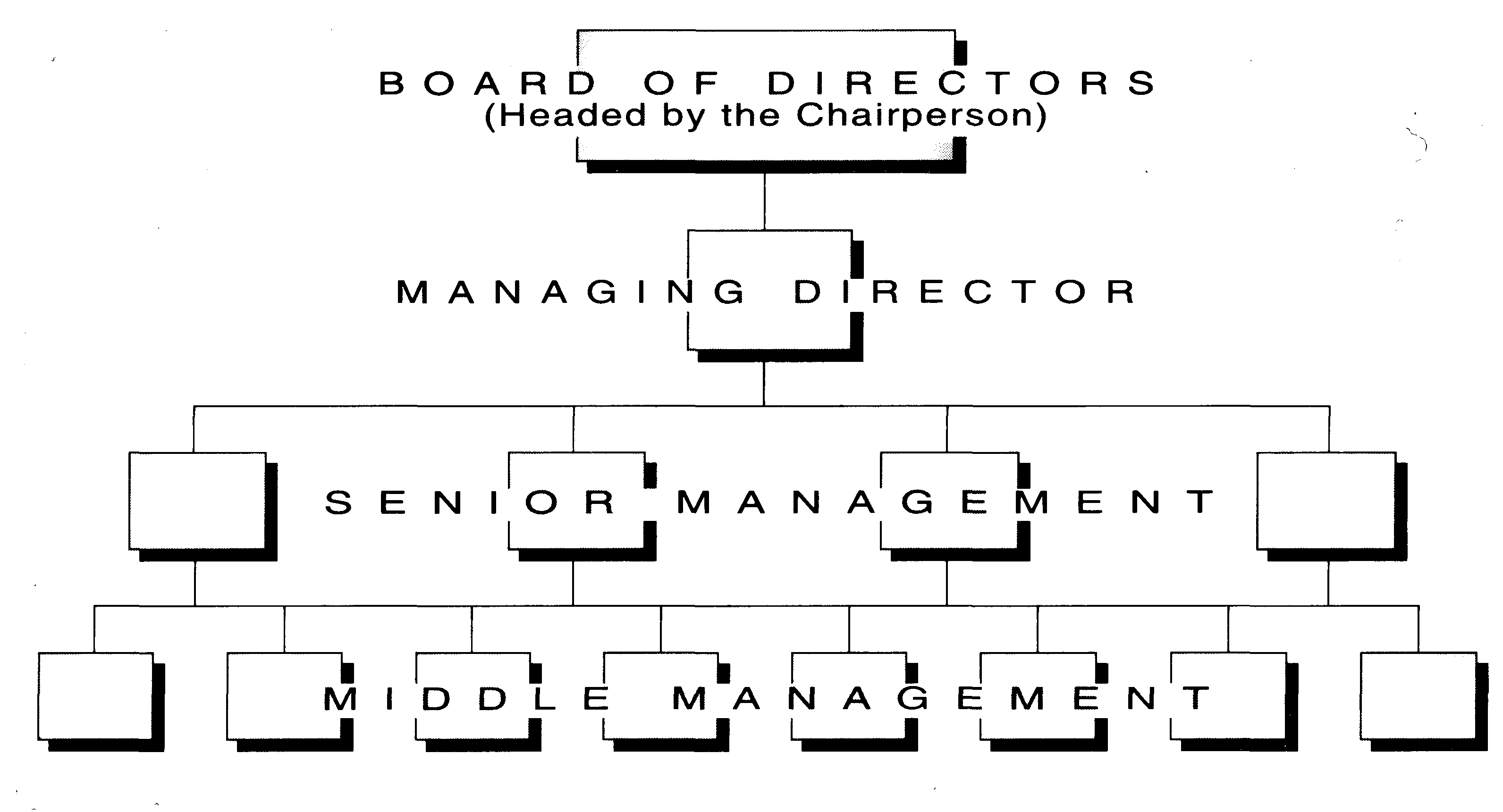
At the top of the company hierarchy is the Board of Directors, headed by the Chairperson (or President). The Board is responsible for making policy decisions and for determining the company's strategy. It will usually appoint a Managing Director (or Chief Executive Officer) who has overall responsibility for the running of the business. Senior managers head the various departments or functions within a company, which may include the following:
Marketing Public Relations Personnel (or Human Resources)
Finance Production Research and Development
