
- •Topic 5. Chemical Reactions
- •R ates of reactions
- •4. Stoichiometry
- •5. Thermodynamics heat and cold
- •Thermochemistry
- •Energy in chemical bonds
- •6. Equilibrium 1 equilibrium basics
- •It happens on its own
- •7. Equilibrium 2 more about equilibrium
- •T he position of equilibrium
- •L e chatelier, what did he say?
- •8. Catalyst and inhibitors c atalysts speed it up
- •I nhibitors slow it down
- •9. Acids and Bases acids and bases are everywhere
- •Names to know
- •What really happens
T he position of equilibrium
When a bunch of molecules is left alone, they reach a state of equilibrium. But that position of equilibrium can change if something happens to the molecules. Here's a list of things that can change the equilibrium point. 1. New molecules or substances are added. 2. The temperature of the system is changed. 3. The pressure of the system is changed. 4. The concentrations are changed, like adding more water to a solution or adding more of one substance.
L e chatelier, what did he say?
There was a French guy named Henri Le Chatelier and he came up with a principle for systems in equilibrium. The principle says that if you have a system in equilibrium and you do anything to it that messes up the equilibrium, the system will try to move back to the original state of equilibrium. Or, if you have a happy system and you make it unhappy, it will try to make itself happy again. His exact words were, "A system in equilibrium, when subjected to a stress resulting from a change in temperature, pressure, or concentration, and causing the equilibrium to be upset, will adjust its position of equilibrium to relieve the stress and reestablish equilibrium."
8. Catalyst and inhibitors c atalysts speed it up
A catalyst is like adding a bit of magic to a
reaction. Reactions need a certain amount of energy to happen. If
they don't have it, oh well, the reaction probably can't happen. A
catalyst lowers the amount of energy needed so that a reaction can
happen easier. A catalyst is about energy; it doesn't have to be
another molecule. If you fill a room with hydrogen gas and oxygen
gas, very little will happen. If you light a match in that room (or
just a spark), all of the hydrogen and oxygen will combine to create
water molecules. It is an explosive reaction.
The energy needed
to make a reaction happen is called the activation
energy. As everything moves
around, energy is needed. The energy a reaction needs is usually in
the form of heat. When a catalyst is added, something special
happens. Maybe a molecule shifts it's structure. Maybe that catalyst
makes two molecules combine and they release a ton of energy. That
extra energy might help another reaction to occur. In our earlier
example, the spark added the activation
energy.
C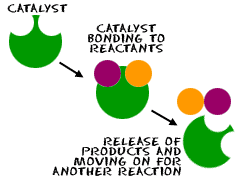 atalysts
are also used in the human body, not to cause explosions but to make
very difficult reactions happen. They help very large molecules
combine. There is another interesting fact about catalysts. Catalysts
lower the activation energy required for a reaction to occur. With
the activation energy lower, the products can also combine more
easily. Therefore, the forward and reverse reactions are both
accelerated. It helps both reactions.
atalysts
are also used in the human body, not to cause explosions but to make
very difficult reactions happen. They help very large molecules
combine. There is another interesting fact about catalysts. Catalysts
lower the activation energy required for a reaction to occur. With
the activation energy lower, the products can also combine more
easily. Therefore, the forward and reverse reactions are both
accelerated. It helps both reactions.
I nhibitors slow it down
There is also something called an inhibitor that works exactly the opposite of catalysts. Inhibitors slow the rate of reaction. Sometimes they even stop the reaction completely. You might be asking, "Why would anyone need those?" You could use an inhibitor to make the reaction slower and more controllable. Without them, some reactions could keep going and going and going. If they did, all of the molecules would be used up. That would be bad, especially in your body.
