ВІРУСКА ЛАБА 11
.docxDNA - vaccines. Immunomodulators
Task:
1. Name and describe the means of specific prophylaxis of viral diseases, including DNA vaccines.
2. Name and describe the modern facilities for immunomodulation.
Sources (guidelines):
1. Калініна О.С., Панікар І.І., Скибіцький В.Г. Ветеринарна вірусологія . м.Львів 2004р., 521 с.
2. Сюрин В.Н., Белоусова Р.В., Фомина Н.В. Диагностика вирусных болезней животных: Справочник. — М.: Агропромиздат, 1991. — 528 с.
1. DNA vaccination is a technique for protecting against disease by injection with genetically engineered DNA so cells directly produce an antigen, producing a protective immunological response. DNA vaccines have potential advantages over conventional vaccines, including the ability to induce a wider range of immune response types.
Several DNA vaccines are available for veterinary use. Currently no DNA vaccines have been approved for human use. Research is investigating the approach for viral, bacterial and parasitic diseases in humans, as well as for several cancers.
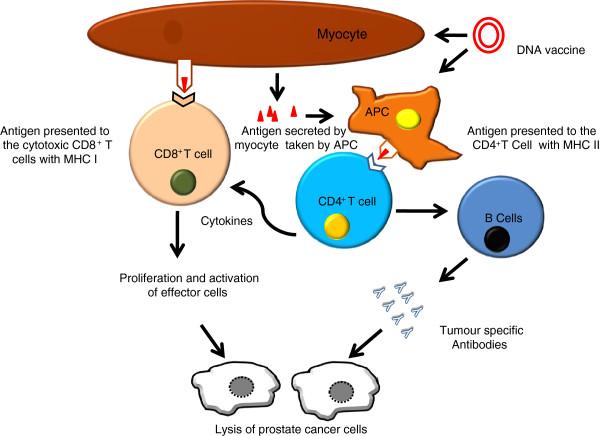
The most common method of introducing a DNA vaccine is intramuscular, so it is believed that the DNA vaccine penetrates into the muscle cell. At the same time, the muscle cell weakly expresses the products of the MHC genes of classes I and II, which are necessary for representing the antigen to T cells. Coming out of the muscle cell, the antigen must find auxiliary cells (macrophages, dendritic cells, etc.) that have a strong antigen-presenting ability.
It is likely that the DNA vaccine can penetrate directly into the macrophage or dendritic cell, in which there are good conditions for the formation of antigen complexes with the products of the MHC genes and the presentation of these complexes to T helper and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. This process can occur at the injection site of the DNA vaccine and in regional lymph nodes and other lymphoid organs, where the antigen comes in rapidly after its intramuscular injection
A DNA mixture can be used to prepare the DNA vaccine, which provides the formation of different antigens against one or (in theory) against several infections.
DNA vaccines can be obtained in large quantities, they are stable and devoid of infectious agents. A promising area is the development of multicomponent vaccines containing two or more plasmid forms that encode different antigens, cytokines or other biologically active molecules. Vaccines from DNA of influenza viruses, rabies, lymphocytic choriomeningitis, hepatitis B and C, herpes simplex, papillomatosis, as well as pathogens of malaria, leishmaniasis, tuberculosis have been studied on animals. At the stage of clinical trials is a DNA vaccine against malaria, HIV infection, influenza, hepatitis B.
In pre-clinical trials, when introducing a DNA vaccine, animals need to study the distribution of plasmid DNA, the duration of its presence in the body, and the degree of risk of DNA integration into the genome of the cell. In studies on animals and humans, the possibility of forming anti-DNA antibodies and antibodies to vaccine impurities should be elucidated.
Control of DNA vaccine in production should be carried out at 3 levels: input control of raw materials, product control at different stages of production and control of the final product. Not all methods used to control DNA vaccine samples in their development should be used to monitor vaccine series. Mandatory control is the identity, degree of purification, activity, sterility, pyrogenicity. When the results of vaccine control are correlated in vivo and in vitro, in vitro methods can be used, and appropriate reference preparations should be used.
Vaccines can be obtained not only from DNA, but also from RNA. Such vaccines are safer against the blastogenic effect, but they are unstable and cause short-term immunity.
2. Immunomodulators are natural or synthetic substances that can have a regulating effect on the immune system. By the nature of their influence on the immune system, they are divided into immunostimulating and immunosuppressive.
In Russia and in Western countries, various groups of drugs can be understood as immunomodulators. In the Russian market there are about a hundred immunomodulators developed internally and practically not used outside the CIS. In Russia, this group of substances has significant sales volumes (more than 30 million packs in 2010), second only to antibiotics and oncopies .
In Western countries, immunomodulators with a rare secondary immunodeficiency are mainly used .
Immunomodulators, depending on their origin, are divided into six main groups: microbial, thymic, bone marrow, cytokines, nucleic acids and chemically pure immunomodulators.
Microbial immunomodulators. The main target for microbial immunomodulators are phagocyte cells. Under the influence of such drugs, the functional properties of phagocytes increase, phagocytosis and intracellular killing of absorbed bacteria improve, the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines necessary for activation of humoral and cellular immunity increases. The use of immunomodulators of this kind as a result, increases the production of antibodies, activates the formation of T-helpers and T-killers. The first immunomodulator of microbial origin that was approved for use was the well-known BCG vaccine, which has a pronounced ability to strengthen factors, both innate immunity and acquired.
Thymic immunomodulators. As the name suggests, the use of immunomodulators of this group sees T-lymphocytes as its main target. With initially lowered values, thymic immunomodulators increase the number of T cells and their functional activity. Timic immunomodulators Timalin, Taktivin, Timoptin, Vilozen contain hormones of the thymus gland and are largely close in their action.
Bone marrow immunomodulators. From the other organ of the immune system - the bone marrow was obtained the medullary immunomodulator Myelopid. It consists of six bone marrow-specific mediators of the immune response, called myelopeptides, and have the ability to stimulate various parts of the immune response and especially humoral immunity. When immunodeficiencies the drug restores the indices of B- and T-systems of immunity, as well as stimulates the production of antibodies and the functional activity of immunocompetent cells, facilitates the restoration of a number of other parameters of the humoral immunity.
Immunomodulators cytokines are low molecular weight hormone-like biomolecules that produce activated immunocompetent cells. Cytokines are regulators of interactions between cells. Their several groups - interleukins, growth factors (epidermal, nerve growth factor), colony-stimulating factors, chemotactic factors, tumor necrosis factor. Interleukins are the main participants in the development of an immune response to microorganisms, the formation of an inflammatory reaction, the implementation of antitumor immunity, etc. Cytokines are a complex complex of endogenous immunoregulatory molecules that are the basis for the creation of a large group of natural and recombinant immunomodulators.
Nucleic acids. A wide range of positive effects on the human body is also characteristic of immunomodulators from the group of nucleic acids, which are divided into synthetic (Poludan) and natural (Derinat, sodium nucleate). Derinat activates antiviral, antifungal and antimicrobial local immunity due to immunomodulatory action at the cellular and humoral levels and increases phagocytosis, it also implements radioprotective, reparative, anti-inflammatory, analgesic and antitumor and light anticoagulant effects. This causes the use of immunomodulators of this group with a very large range of diseases, especially infectious, of different nature and localization.
Chemically pure immunomodulators. The group of these immunomodulators is divided into two subgroups - low-molecular and high-molecular. The first subgroup includes drugs that have immunotropic activity. Their ancestor was levamisole (Decaris) - a remedy against helminths, in which pronounced immunostimulating properties were found. Another immunomodulator from this subgroup is Galavit, a derivative of phthalhydrazide. The use of immunomodulators Galavit differs not only immunomodulating, but also expressed anti-inflammatory properties. Immunomodulators list of a subgroup of low-molecular immunomodulators includes three synthetic oligopeptides: Gepon, Glutoxim and Alloferon. High-molecular chemically pure immunomodulators, obtained by directional chemical synthesis. As an example, - Polyoxidonium. This drug is allocated a wide range of pharmacological effects on the body, including immunomodulating, detoxifying, antioxidant and membrane-protective effects.