
- •Write down the rsa alg. Step by step in right order without an example. Also show encryption & decryption formulas.
- •Explain the Hash function by using the general formula. Give an example of hash algorithm.
- •Describe the Direct Digital Signature.
- •Kerberos: Give description, short dialogue between user and server.
- •What is the algorithm of message sending in pgp? Number below operations in the right order.
- •What are the types of ‘headers’ that involve in ipSec? Describe these headers in few words.
- •Describe Alert Protocol involving in ssl.
- •Describe the Intrusion Detection System. What is a Statistical Anomaly Detection?
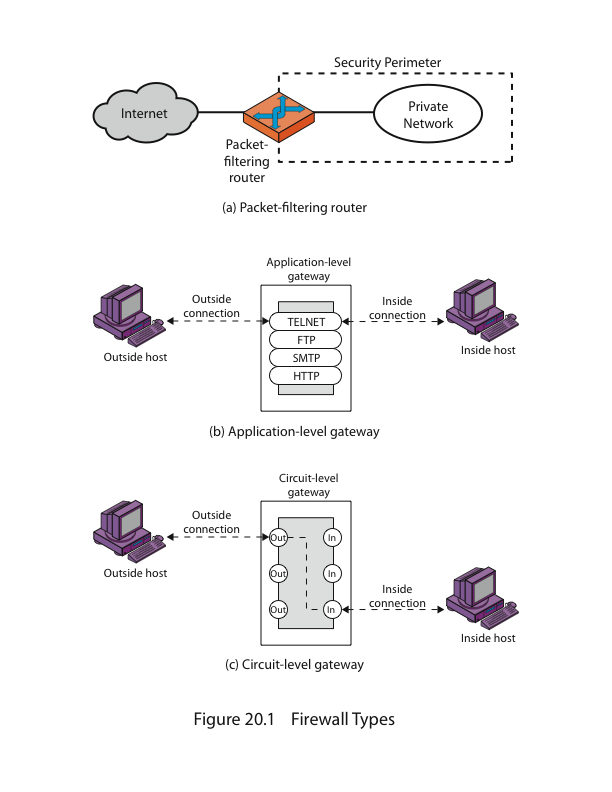
- •What is a Firewall? Name the types of Firewall and describe any one of them.
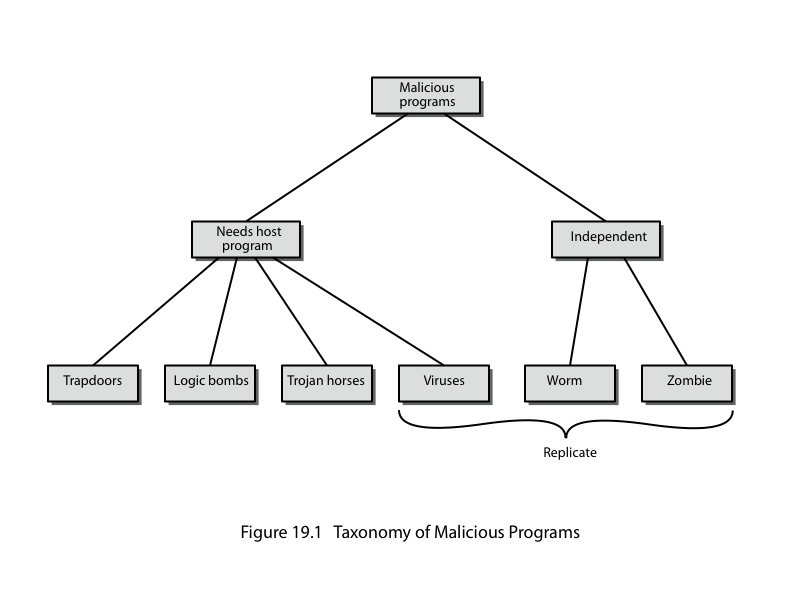
- •What is Malicious Software? Describe ddos and countermeasures.
- •Information Security
- •Write down aes operations in right order for one round:
- •Write down the Diffie-Hellman Key exchange alg. Step by step in right order without an example and for two sides.
- •Describe the Intrusion Detection System. What is a Rule-based detection?
- •What is a Firewall? Name configurations of Firewall and describe any one of them.
- •What is Malicious Software? Describe Worms and their phases.
Describe Alert Protocol involving in ssl.
conveys SSL-related alerts to peer entity
severity
warning or fatal
specific alert
fatal: unexpected message, bad record mac, decompression failure, handshake failure, illegal parameter
warning: close notify, no certificate, bad certificate, unsupported certificate, certificate revoked, certificate expired, certificate unknown
compressed & encrypted like all SSL data
Describe the Intrusion Detection System. What is a Statistical Anomaly Detection?
inevitably will have security failures
so need also to detect intrusions so can
block if detected quickly
act as deterrent
collect info to improve security
assume intruder will behave differently to a legitimate user
but will have imperfect distinction between
Statistical Anomaly Detection
threshold detection
count occurrences of specific event over time
if exceed reasonable value assume intrusion
alone is a crude & ineffective detector
profile based
characterize past behavior of users
detect significant deviations from this
profile usually multi-parameter
What is a Firewall? Name the types of Firewall and describe any one of them.
threshold detection
count occurrences of specific event over time
if exceed reasonable value assume intrusion
alone is a crude & ineffective detector
profile based
characterize past behavior of users
detect significant deviations from this
profile usually multi-parameter
Firewalls – Packet Filters
simplest, fastest firewall component
foundation of any firewall system
examine each IP packet (no context) and permit or deny according to rules
hence restrict access to services (ports)
possible default policies
that not expressly permitted is prohibited
that not expressly prohibited is permitted
What is Malicious Software? Describe ddos and countermeasures.
DDoS Countermeasures
three broad lines of defense:
attack prevention & preemption (before)
attack detection & filtering (during)
attack source traceback & ident (after)
huge range of attack possibilities
hence evolving countermeasures
Information Security
Final
2-variant
Name, surname: Group:
Good Luck!!!
Questions: (1-10 questions are main and q.11 is bonus)
Write down aes operations in right order for one round:

Write down the Diffie-Hellman Key exchange alg. Step by step in right order without an example and for two sides.
shared session key for users A & B is KAB:
KAB = axA.xB mod q
= yAxB mod q (which B can compute)
= yBxA mod q (which A can compute)
KAB is used as session key in private-key encryption scheme between Alice and Bob
if Alice and Bob subsequently communicate, they will have the same key as before, unless they choose new public-keys
attacker needs an x, must solve discrete log
Explain the MAC by using the general formula. Give an example of MAC algorithm.
a MAC is a cryptographic checksum
MAC = CK(M)
condenses a variable-length message M
using a secret key K
to a fixed-sized authenticator
is a many-to-one function
potentially many messages have same MAC
but finding these needs to be very difficult
Describe the Arbitrated Digital Signature.
involves use of arbiter A
validates any signed message
then dated and sent to recipient
requires suitable level of trust in arbiter
can be implemented with either private or public-key algorithms
arbiter may or may not see message
X.509: Give description and definitions of the following: Certificate, and CA?
What is the algorithm of message receiving in PGP? Number below operations in the right order.
4… PGP retrieves the sender's public key from the public-key ring, using the Key ID field in the signature key component of the message as an index.
5… PGP recovers the transmitted message digest.
3… PGP then recovers the session key and decrypts the message.
6… PGP computes the message digest for the received message and compares it to the transmitted message digest to authenticate.
2… PGP prompts the user for the passphrase to recover the unencrypted private key.
1… PGP retrieves the receiver's private key from the private-key ring, using the Key ID field in the session key component of the message as an index.
What are the types of ‘modes’ that involve in IPSec? Describe these modes in few words.
Describe SSL Record Protocol involving in SSL.
SSL Record Protocol defines two services for SSL connections:
• Message Integrity: The Handshake Protocol also defines a shared secret key that is used to form a message authentication code (MAC), which is similar to HMAC
• Confidentiality: The Handshake Protocol defines a shared secret key that is used for conventional encryption of SSL payloads. The message is compressed before being concatenated with the MAC and encrypted, with a range of ciphers being supported as shown.
