
- •Section III. The acidity and basicity of organic compounds. Nucleophilic substitution at a saturated carbon atom.
- •Section IV. The reactivity of carbonyl compounds in nucleophilic reactions.
- •Section V. Heterofunctional connections involved in the processes of life.
- •Section VI. Monosaccharides. Disaccharides. Polysaccharides.
- •Section VII. Saponifiable and unsaponifiable lipids.
- •Section VIII. Biologically important heterocyclic compounds.
- •Safety instructions
С.Ж. АСФЕНДИЯРОВ АТЫНДАҒЫ ҚАЗАҚ ҰЛТТЫҚ МЕДИЦИНА УНИВЕРСИТЕТІ
|
|
КАЗАХСКИЙ НАЦИОНАЛЬНЫЙ МЕДИЦИНСКИЙ УНИВЕРСИТЕТ ИМЕНИ С.Д.АСФЕНДИЯРОВА
|
КАФЕДРА БИОЛОГИЧЕСКАЯ ХИМИЯ ЭКЗАМЕНАЦИОННЫЕ ТЕСТЫ |
||
Examination tests of organic chemistry
Section I. Classification of organic compounds. Nomenclature. Isomerism
1. What is the name of the compound of the international (substitution) nomenclature?
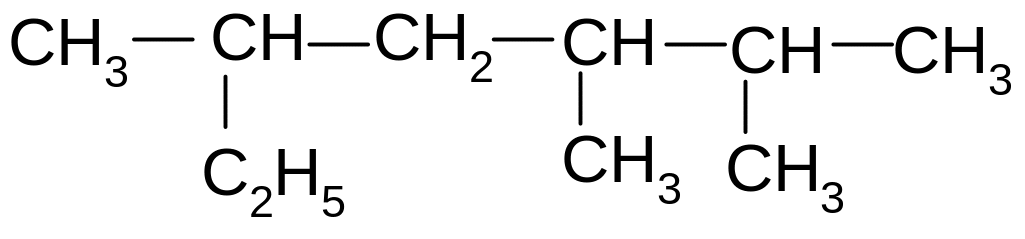
2. What name is a compound of the substitution IUPAC nomenclature?

3. According to International (substitution) nomenclature what the name of this compounds (CH3) 2CH - C(CH 3)2 - CH2 - CH3?
4. According to International (substitution) nomenclature what the name of this compound?

5. What name is a compound of a rational nomenclature?

6. What name is a compound of a rational nomenclature?

7. What name is corresponds to a hydrocarbon radical?

8. What name is corresponds to a hydrocarbon radical?

9. What name is corresponds to a hydrocarbon radical?

10. How many secondary carbon atoms in the compound?

11. What is the number of primary carbon atoms in the molecule 2,2-dimethylbutane?
12. Which class of organic compounds belong this compounds?

13. Which class of organic compounds belong this compounds?

14. Which class of organic compounds belong this compounds?
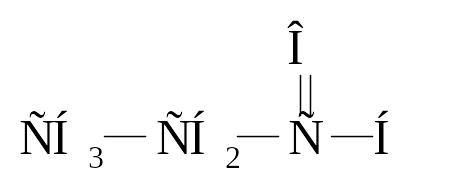
15. Which class of organic compounds belong this compounds СН3–СН2–О–СН2–СН3?
16. What the name of this compounds corresponds to this formula?

17. What the name of this compounds corresponds to this formula?

18. According to the substitution nomenclature which name corresponds to p-aminosalicylic acid (PASA), that it used as anti-TB drugs?

19. We have the next compounds С7Н14, С8Н18, С2Н2, С6Н6, С10Н22. What is the number of connections which are saturated hydrocarbons?
20. We have hydrocarbon radical сн2 сн – сн2 –. Which it hydrocarbon corresponds to this radical?
21. We have hydrocarbon radical С6Н5 –. Which it hydrocarbon corresponds to this radical?
22. Amino acid serine HO-CH2-CH(NH2)-COOH part of proteins. This of the available functional groups in the molecule serine reflected in the title according to the rules substitution IUPAC nomenclature as a prefix:
23. Propanol and methoxyethane are compounds that have the same composition. How are called this compounds?
Section II. The mutual influence of atoms and ways of transfer in biologically important molecules. Classification by type of organic reactions and mechanisms. Reactivity of hydrocarbons. Radical substitution reaction. Electrophilic substitution reactions and addition.
1. Which of formula for the Hückel rule in aromatic compounds is possible to calculate the number of electrons in the π - system?
2. Which product is formed by reduction of toluene?
3.
We have reaction CH3–СН2–СН3
+ Br2
![]() ?
Which of type , mechanism and final product of bromination reaction?
?
Which of type , mechanism and final product of bromination reaction?
4. Which electron effect shows a carboxyl group in benzoic acid?
5. What are the effects of electronic shows nitro group in the molecule СН2 = СН – NО2?
6. What type of sign and electronic effects in the molecule influences the aniline NH2 group on the benzene ring?
7. What type of sign and electronic effects in the molecule CH2 = CH - NH2 influences by amino group?
8. The hydroxyl group in phenol shows electron-donating properties. Which electronic effects are shown hydroxyl group in phenol?
9. Aldehyde group in benzaldehyde shows electron-acceptor properties. Which of electronic effects are shown the aldehyde group in benzaldehyde?
10. What is the type and mechanism of the reaction of butane with chlorine by irradiation with UV light?
11. A the result of this reaction formed the next product?
12. Which product is is formed by the reaction of ethylene with hydrogen chloride. ?
13. Which alcohol is formed by hydration of isobutylene in an acidic midium?
14. What are the type, mechanism and final product nitration of aniline?
15. What electronic effects in the molecule of acrylic acid are marked correctly?

16. What electronic effects in the molecule of benzaldehyde marked correctly?

17. The four tubes are alkene, alkane, diene, and alkyne. In three of them there was a reaction to the mild oxidation reagent. Which reagent should be added to the test substance, to prove the existence of double bonds?
18. Medicinal product "Linetol"obtained from the flax seed oil contains a mixture of esters of unsaturated fatty acids - oleic, linoleic, linolenic. It is used for prevention and treatment of atherosclerosis and externally for burns and radiation injuries of the skin. Which reaction can be determined whether the drug "Linetol" unsaturated compound?
19. Hydrocarbons with the general formula С8Н8 discolour bromine water and the result of oxidation forms an aromatic acid. What is the name of this compound?
20. The two tubes are tested compounds. One of the tubes after the addition of the reagent [Ag (NH3) 2] OH formed of silver plaque. Which pair of compounds can be distinguished from each other by means of this reagent?
Section III. The acidity and basicity of organic compounds. Nucleophilic substitution at a saturated carbon atom.
1. Which type of acid belongs to phenols?
2. Which type of acids belongs to acetylene?
3. According to the theory of Bronsted-Lowry how called the base, which joins proton by the electron pair of the nitrogen atom?
4. Which of these formulas corresponds to the name methylisopropylamen?
5. Which of these formulas corresponds to the name the secondary propyl alcohol?
6. Which product is formed by the reaction of intermolecular dehydration of ethanol?
7. What do you call the reaction of alcohol with a carboxylic acid?
8. Which compounds are formed with interaction alcohol with a carbon acid?
9. Which of the formula corresponds to the product of oxidation of isopropyl alcohol?
10. Which of the formula corresponds to the product of oxidation of ethyl alcohol?
11. What compound is formed by oxidation of (СН3)2СНСН(ОН)СН3?
12. What the type and mechanism of this reaction CH3CH2 COOH + CH3CH2OH?
13. Which reagent is used to distinguish between phenol and propanol - 2?
14. Which compound is formed by the reaction of CH3-CH(OH)-CH3 + NAD+ →?
15. Which compound is formed by the reaction of СН3 – СН2 – СН2 – ОН + НАД+ →?
16. Xylitol is a five-atom alcohol, has a sweet taste, very soluble in water, is used as a substitute for sugar in diabetes. Which of the reagents must be added in order to prove the presence of diol fragment in xylitol?
17. The first antidote for poisoning by arsenic was proposed 2.3-dimerkaptopropanol. What acid centers in the molecule mainly involved in the formation of salts of arsenic?
Section IV. The reactivity of carbonyl compounds in nucleophilic reactions.
1. Which compound is formed by heating malonic (propandiovic) acid?
2. Which compound is formed by heating succinic (butandiovic) acid?
3. What formula is oxalic acid?
4. What formula is succinic acid?
5. Which compound is formed by the interaction of acid with ammonia?
6. Which functional group in the structure has aldehydes and ketones?
7. Which acid is formed by hydrolysis C4H9C(O)OC2H5?
8. Which of the compounds interact with the water solution of sodium hydroxide:
1) С6Н5ОН, 2) С6Н5СН2ОН, 3) С2Н5SН, 4) С2Н5ОН, 5) С6Н5SH
9. Which is the structure of the product reduction of propenal?
10. Which reagent is used to distinguish between a pair of agents propanone and propanal?
11. What substance is formed by the reaction of hydrobromination propenoic acid?
12. What the type, the mechanism and the final
product of this reaction2R–OH + R–CH=O
![]() ?
?
13. What the type, the mechanism and the final product of this reaction R–CH=O + R–CH=O ?
14. As a result of the aldol addition forms a compound of the following structure СН3СН2СН(ОН)СН(СН3)СН = О.. Which is the aldehyde parent compound?
15. Using the esterification reaction of the parent compounds which can obtain etilpropanoat?
16. Oxalic acid HOOC-COOH is widespread in the plant world. Calcium oxalate crystals appear in the urine in certain pathological conditions. What reagent can detect the presence of oxalic acid?
17. Butanol-1 - a component of fusel oil. Which of carbonyl compounds can be prepared butanol-1, using aluminum hydride reaction?

