
- •Lesson 2: Operators, Types, and Variables
- •Variants
- •Example
- •Theoretical introduction
- •Variables and Types
- •The Boolean Type
- •Listing 2-1. Displaying Boolean Values: Boolean.Cs
- •Integral Types
- •Floating Point and Decimal Types
- •Table 2-2. The Floating Point and Decimal Types with Size, precision, and Range
- •The string Type
- •Table 2-3. C# Character Escape Sequences
- •C# Operators
Lesson 2: Operators, Types, and Variables
Objectives:
Understand what a variable is.
Familiarization with C# built-in types.
Get an introduction to C# operators.
Learn how to use Arrays.
Problem statement:
Calculate y, as a result of a given arithmetic equation.
Calculate z, as a result of a given logical equation.
Calculate s, as a result of a given string expression (text message).
Variants
Вариант № 1
1)
Y= ;
;

2)
Z=

Variant № 2
1)
Y=

2)
Z=
Variant № 3
1)
Y=

2)
Z=
Variant № 4
1)
Y=
2)
Z=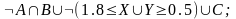
Variant № 5
1)
Y=

2)
Z=
Variant № 6
1)
Y= ;
; 
2)
Z=
Variant № 7
1)
Y=

2)
Z=
Variant № 8
1)
Y=

2)
Z= ;
;
Variant № 9
1)
Y=
2)
Z=
Variant № 10
1)
Y= ;
; 
2)
Z= ;
;
Variant № 11
1)
Y= ;
; 
2)
Z=
Variant № 12
1)
Y= ;
; 
2)
Z=
Variant № 13
1)
Y= ;
;
2)
Z=
Variant № 14
1)
Y= ;
; 
2)
Z=
Variant № 15
1)
Y= ;
;
2)
Z=
Variant № 16
1)
Y= ;
; 
2)
Z=
Variant № 17
1)
Y= ;
; 
2) Z=
Variant № 18
1)
Y=

2) Z=
Variant № 19
1)
Y= ;
;
2)
Z=
Variant № 20
1)
Y=
2)
Z=
Variant № 21
1)
Y= ;
; 
2)
Z=
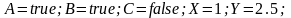
Variant № 22
1)
Y=

2)
Z=
Variant № 23
1)
Y=

2)
Z= ;
;
Variant № 24
1)
Y=
2)
Z=
Variant № 25
1)
Y= ;
; 
2)
Z= ;
;
Variant № 26
1)
Y= ;
; 
2)
Z=
Variant № 27
1)
Y= ;
;
2)
Z=
Variant № 28
1)
Y= ;
; 
2)
Z=
Variant № 29
1)
Y= ;
; 
2)
Z=
Variant № 30
1)
Y= ;
; 
2)
Z= ;
;
Example
Calculate value of the next expression:

if

Calculate
 if
if
 ,
where
,
where
 logic operator NOT,
logic operator NOT,
 -
logic multiplication AND,
- logic addition OR.
-
logic multiplication AND,
- logic addition OR.Print out author’s full name, if first name –Ivan, and surname - Petrov.
STEP1
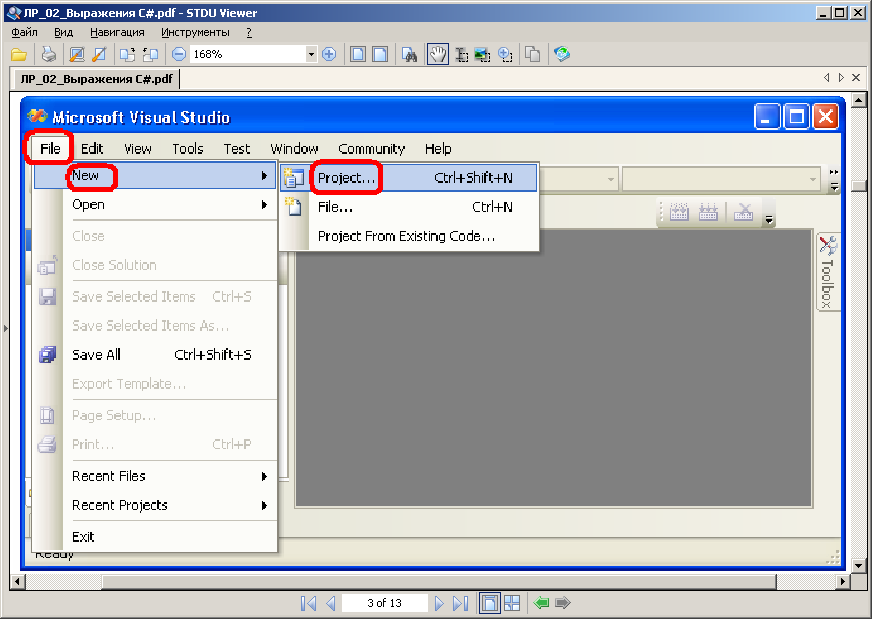
STEP2
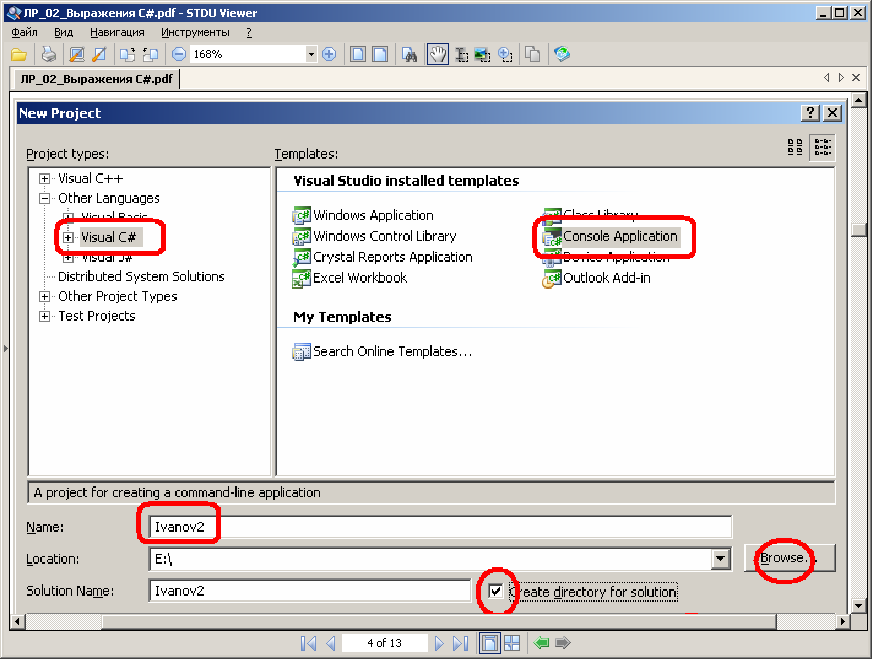
STEP3
STEP4
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Text;
namespace Ivanov2
{
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
double
y,
x=3.5,
z=1e-5,
Denominator, Numerator,
X = 6.3, Y=5.1;
int
b=-4;
string FullName = "";
string FirstName = "Petr";
string Surname = "Ivanov";
bool
Z,
A = true,
B = false;
int
iFirstName
iSurname, iFullName;
Console.WriteLine(" ***** Initial data*****:\n");
Console.WriteLine(" x={0} z={1} b={2}", x, z, b);
Console.WriteLine(" X={0} Y={1}", X, Y);
Console.WriteLine(" A={0} B={1}", A, B);
Console.WriteLine(" Name={0}", FirstName);
Console.WriteLine(" Surname={0}", Surname);
Numerator=Math.Atan(z)*Math.Pow(z,1/3.0)*Math.PI/Math.Exp(x)+
Math.Pow(z,2)-4.5*Math.Pow(10.0,2.5)*Math.Sqrt(x)*Math.Asin(z);
Denominator = Math.Tan(2.7e-3) - Math.Acos(z) * Math.Log(x) +
Math.Pow(z, x) + Math.Abs(Math.Sin((double)b)) - Math.Log10(z);
y = Numerator / Denominator;
Z=!A && (X<=Y) || (X>0) && B;
iFirstName = FirstName.Length;
iSurname=Surname.Length;
FullName = FirstName + " " + Surname;
iFullName = FullName.Length;
Console.WriteLine("\n ***** Results *****:\n");
Console.WriteLine(" Arithmetic equation: y={0}", y);
Console.WriteLine(" Logical equation: Z={0}", Z); Console.WriteLine(" String type: FullName={0}", FullName);
Console.WriteLine(" Number of letters in the full name={0}", iFullName);
Console.WriteLine("Number of letters in the name ={0}", iFirstName);
Console.WriteLine("Number of letters in the surname={0}", iSurname);
}
}
}
STEP5

