
- •#3. Role of Econometrics.
- •#4. Main Application of Econometrics.
- •#5. Cross Section Data.
- •#8. Panel or Longitudinal Data.
- •#12. Simple Regression Model (srm)
- •# 13. Simple Linear Model (slm)
- •#18. What is rss, ess, tss?
- •#25. The Random Components of the Regression Coefficients.
- •#26. The Gauss – Markov Theorem.
- •Indeed there have to be satisfied four conditions, known as the Gauss-Markov conditions, if ordinary least squares regression analysis is to give the best possible result.
- •#27. Unbiasedness of the Regression Coefficients.
- •#28. Precision of the Regression Coefficients.
- •#29. Testing Hypotheses Relating to the Regression Coefficients.
- •It has to be estimated by the standard error of b2, given by
- •#30. Confidence Intervals.
- •#35. What Can You Do about Heteroscedasticity?
- •#38. What Can You Do about Autocorrelation?
- •#45. Тhе apt model.
#8. Panel or Longitudinal Data.
We observe a cross-section of m individuals over T periods of time. In statistics and econometrics, the term panel data refers to multi-dimensional data. Panel data contains observations on multiple phenomena observed over multiple time periods for the same firms or individuals.
Time series and cross-sectional data are special cases of panel data that are in one-dimension only.
A panel has the form
![]() where i is
the individual dimension and t is
the time dimension. A general panel data regression model is written
as yit =
α
+ β'Xit + uit. Different
assumptions can be made on the precise structure of this general
model. Two important models are the fixed
effects model and
the random
effects model.
The fixed effects model is denoted as
where i is
the individual dimension and t is
the time dimension. A general panel data regression model is written
as yit =
α
+ β'Xit + uit. Different
assumptions can be made on the precise structure of this general
model. Two important models are the fixed
effects model and
the random
effects model.
The fixed effects model is denoted as
yit = α + β'Xit + uit,
uit = μi + νit.
μi are individual-specific, time-invariant effects (for example in a panel of countries this could include geography, climate etc.) and because we assume they are fixed over time, this is called the fixed-effects model. The random effects model assumes in addition that
![]() and
and
![]() that is, the two error components are independent from each other.
that is, the two error components are independent from each other.
#9. Principles of specification econometrics models.
1. Rule of specification of econometric model is transformation of economic law to mathematical equation.
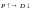
2. Rule of specification quantative of equations must be equal to number of independent variables
3. The variable must be date(d)
y=7,85+0,99x
#10. What is regression analysis?
Regression is the most important tool at the econometrician disposal
Regression analyses is concerned with describing & evaluating the relationship between given variables.
Denote dependent variables as y
Independent
variables as
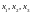
y x
regressand regressor
effect variable causul var.
explained var explanatory var
The coefficient of correlation may indicate 2 var. are associated with one another, but it doesn’t.
#11. Difference between Regression and Correlation.
Regression attempts to model one variable as a function of one or more explanatory variables, such as trying to predict annual income based on years of education. Correlation, on the other hand, attempts to measure the strength of the relationship between two variables. Given two variables, correlation "grades" the strength of the relationship between them. There are several measures of correlation, but the most common returns larger absolute values for stronger relationships, and lower absolute values for weaker ones.
In linear correlation analysis, we identify the strength and direction of a linear relation between two random variables. Correlation does not imply causation. Regression analysis takes the analysis one step further, to fit an equation to the data. One or more variables are considered independent variables (x1, x2, ... xn). responsible for the dependent or "response" variable or y variable.
