
- •1. Complete the sentences with the correct form of the verbs from the box.
- •1. Our company’s mission is to __________ customized, engineered, high quality solutions and services to secure electrical power supply in critical industrial applications.
- •2. The Comprehensive Development Area __________ a total of 5670 acres of which 424 available for industrial development.
- •2. Read this text quickly and identify the paragraphs which contain information on each of the following topics. (The first one has been done for you.)
- •4. Match each of these motor components to its function.
- •Translate these sentences from English into Russian, paying attention to the use of the Absolute Participial Construction.
- •6. Read the text which follows to find the answers to these questions, then complete the table.
- •7. Make pairs of words by matching a word in a to a word in b. Then complete the
- •8. Paraphrase the sentences using the Absolute Participial Construction instead of italicized clauses.
- •10. Watch the video again and explain how we can make an electric motor produce
- •11. Find equivalents of the following phrases in the texts “Electric Motors” and “Stepper
- •12. Translate from Russian into English.
- •13. Translate the text from English into Russian.
- •14. List as many items in the home as you can which use electric motors. Choose one item and describe how it works. Use the text in exercise 13 as an example.
UNIT 4
Electric Motor
Active Vocabulary |
to transform – превращать, преобразовывать to convert - превращать to reverse – поворачивать в противоположном направлении, разворачивать reverse – противоположный, обратный to rotate – вращать unidirectional - однонаправленный to supply - снабжать similar - подобный winding - обмотка armature - якорь commutator – коммутатор sufficient - достаточный powerful - мощный torque – вращающий момент range – ассортимент, ряд to perform – выполнять, совершать innumerable - бесчисленный equally - одинаково valuable - ценный capable – способный capability – способность, возможность, мощность, производительность rate – скорость, темп bearing – подшипник, опора, несущая поверхность |
shaft – вал, ось stepper motor - шаговый (электро)двигатель accurate – точный, правильный accuracy – точность, правильность robotics – робототехника plotter – графопостроитель, самописец precise – точный, определённый to trigger – запускать, включать, приводить в действие pulse – импульс, толчок rotor- ротор stator – статор arrangement- расположение, размещение reluctance motor - реактивный синхронный (электро)двигатель detent - упор, стопор acceleration – ускорение, увеличение скорости (хода), разгон to comprise – включать в себя, содержать angle – угол inertia – инерция peripherals - периферийное оборудование, внешние устройства |
1. Complete the sentences with the correct form of the verbs from the box.
trigger perform supply rotate convert comprise reverse transform |
1. Our company’s mission is to __________ customized, engineered, high quality solutions and services to secure electrical power supply in critical industrial applications.
2. The Comprehensive Development Area __________ a total of 5670 acres of which 424 available for industrial development.
3. In most cases, a tsunami _________ by a distant earthquake.
4. The Moon __________ so slowly that synchronous orbit is not achievable.
5. His discovery completely __________ the way we think about space and time.
6. Students __________ increasingly difficult tasks as the course continues.
7. More changes are required to __________ the trend towards centralized power.
8. The computer system __________ typed words into speech.
Reading 1 |
2. Read this text quickly and identify the paragraphs which contain information on each of the following topics. (The first one has been done for you.)
a the definition of an electric motor - 1
b what the shunt field winding provides
c application of motors
d why the motors have both shunt and series winding
e the components of a motor
f range of sizes of motors
g difference between a generator and a motor
h types of motors
Electric Motors
1) The electric motor is a device employed for transforming electrical energy into mechanical energy. We know it to rotate machinery and various appliances. The two main types of electric motors are direct current (DC) motors and alternating current (AC) motors. Direct current motors, as the name implies, use direct-unidirectional current. Alternating current (AC) motors use an electrical current, which reverses its direction at regular intervals. The main advantage of DC motors over AC motors is that speed is more difficult to control for AC motors.
2) You know from the course of physics that the generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Now, the process is reversed. It is electricity that is supplied to the machine and it is motion that we obtain. From what has been said about our getting magnetism from electricity and about the generation of electric current by using magnetism, it is obvious that generators and motors are similar in certain respect. There is certainly some difference in detail but in both of them we find an armature with windings, a commutator and brushes combined with an electromagnet for producing the magnetic field.
3) However, in an electric motor one shunt winding is not sufficient and a second one called a series winding should be added. “Why is it necessary?’ one might ask. The fact is that the motor should have a powerful effect at the very moment when the current is switched on, as for instance, in an electric tram or a train. A very strong magnetic field is needed to obtain a so-called powerful starting torque. This is achieved by adding a series winding to the magnetic coils. It is connected with the armature not in shunt but in series. Thus, heavy starting current, passing through the armature winding, now passes through the series field coil and provides a strong field necessary for starting, the shunt field winding providing the running conditions.
4) No appliance ever created by man has probably such a wide range of size and such a variety of application as a motor. In fact, on the one hand, there are all kinds of mighty giants in the motor world. These giants are known to perform innumerable operations wherever required. On the other hand, there exist all kinds of small-sized and even minute motors, which are able to power various complex machines and operate equally well under any conditions.
5) So far nothing was said of what a motor does in our homes. In a modern home there are many different electric motors in machines and devices utilized to meet our daily needs: to tell the time, to wash clothes, to cool the refrigerator, to clean things, to shave, to circulate air on a hot summer day and so on. In effect, vacuum cleaners, washing machines and modern refrigerators do work thanks to electric motors. It follows that in the electric motor we have the valuable and powerful appliance capable of fulfilling the required operations exactly and with just the desirable power and rate of motion. It is readily switched on, at will, and it continues running until we switch it off. There are often cases when it is simply impossible to replace it by any other means. In short, the motor finds application in industry and engineering, in agriculture and transport, in medicine and our homes.
3. Match each of these diagrams with the correct description A, B, C or D. One of the descriptions does not match any of the diagrams. The diagrams are in the correct sequence, but the descriptions are not.
DC motor
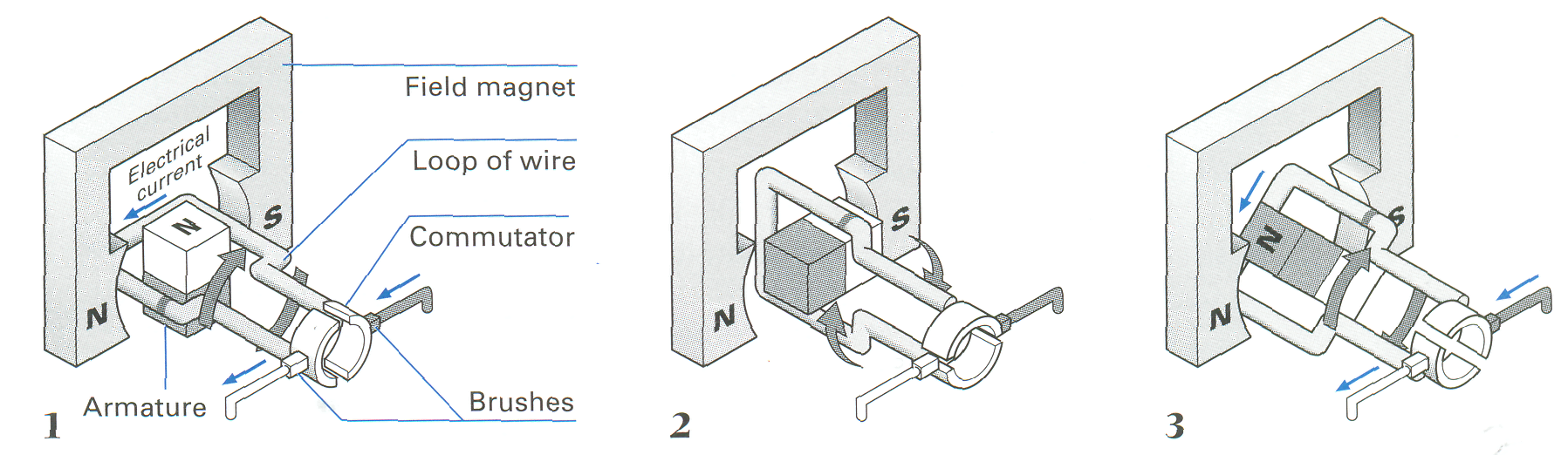
А
The armature turns a quarter of a turn. Then electric contact is broken because of the gap in the commutator, but the armature keeps turning because there is nothing to stop it.
В
When current flows, the armature becomes an electromagnet. Its north pole is attracted by the south pole and repelled by the north pole of the field magnet.
С
When a universal motor is run on direct current, the magnetic poles in the armature change while those of the field magnet remain constant.
D
When the commutator comes back into contact with the brushes, current flows through the armature in the opposite direction. Its poles are reversed and the turn continues.
Use of English 1: vocabulary |
