
- •Multiple choice questions (mcq) – preparing for the first midterm Opportunity Costs & the Production Possibility Frontier
- •Figure No. 1
- •Normal Profits and returns on investments
- •Lecture No. 3; Managing Business Costs
- •Figure No. 2
- •Figure No.3
- •Lecture No. 4 The Firm’s Revenue: Demand & Price Elasticity of Demand
- •Figure No.4
- •Figure No.5
- •The Firm: Output, Prices and Profits
- •Figure No.6
- •Figure No.7
- •Figure No.8
- •Firm a Firm b
- •4 And 5 only Supply and Demand, the Market mechanism
- •Externalities
- •2 And 4 only
- •Slaughter house and processing plant
- •Feed lots
- •Consumer’s optimization
Firm a Firm b
For both firms, at what output will the firms break even and what type of profit will the firms be making?
Firm A: output = 100 units, earning normal profits, Firm B: output = 200 units earning normal profits
Q50 The diagrams below show the weekly total cost and revenue structures for two privately owned firms, producing two very different products. In this example neither firm is experiencing diminishing marginal returns. The firms are run by managers and normal profits of £50 are included in total fixed costs (TFC).

 Firm
A Firm B
Firm
A Firm B
Which of the following statements is false?
1. Firm A has a Low Operational Gearing
2. Compared to Firm A, Firm B will make greater profits when sales are above the break-even point but bigger loses below that point.
3. Over a year both firms will break-even earning a normal profit if weekly sales are 500 units per week on average.
4. If both firm’s return similar annual profits and where put up for sale by their owners, Firm B would always fetch a higher valuation than firm A.
5. Both firms sell their product for £10 and operate with the same mark up.
4 And 5 only Supply and Demand, the Market mechanism
Q51 Which of the following are explanations for the positive relationship between price and the quantity supplied? 1. Costs tend to rise over time.
2. As prices rise, producers find it is worth incurring the higher costs of producing more
3. At higher prices it is worth using additional less productive factors of production.
4. Technological improvements mean that more can be produced and this in turn will affect prices.
5. As consumers offer higher price for a good or service the more profitable it becomes to supply.
All the above
Q52. A right shift in supply good can occur when:
1. The costs of production decrease
2. Incumbent firms increase their capacity by investing in new capital equipment
3. New firms enter the market
4. The price of a substitute goods fall
5. Suppliers of the good expect the price of the good to fall
1, 2, and 3
Q53 Which of the following will NOT cause a shift in the demand curve for DVDs?
The invention of better ways to record and store music
Q54. Which of the following could account for a rise in the price a good and a drop in the quantity of the good bought and sold over a period of time?
A prolonged strike by workers who make the product.
Q55 Good B is a by-product of producing Good A (i.e. they are in joint supply). All other things being equal, what will happen in the market for Good B if the demand for Good A fell?
There would be a glut of Good B; therefore to clear this surplus the suppliers of Good A would reduce production of Good A.
Q56 In the diagram below, the demand for a given good has shifted left (from D’ to D), the original market price was £1.50 for this product. Given this change in demand which of the following is likely to occur?
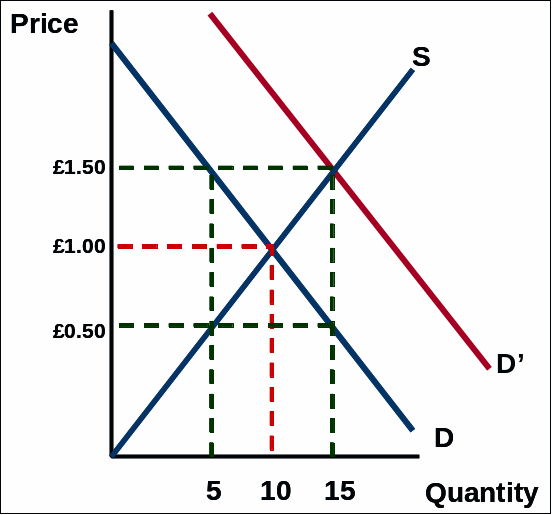
There will be a surplus of 10 units; equilibrium will only be restored at a market price of £1.00, where the quantity demanded and supplied equals 10 units per time period.
Q57 A category 5 hurricane hits Louisiana, USA and causes widespread destruction to the state’s sugar cane crop. The devastation causes the
supply curve for sugar to shift to the left, causing the price of sugar to rise
Q58 Markets A & B are related in that the products are substitutes (e.g. tea and coffee), there is freedom of entry into both markets. Assume that producers of product B find that their costs of production raise and therefore increase their selling price. Under these circumstances which of the following is correct?
1. The supply curve for product B will shift left up along the demand curve for product B
2. The supply curve for product B will shift left up along the demand curve for product A
3. The rise in the price of product B will see the demand curve for product A shift left
4. The rise in the price of product B will see the demand curve for product A shift right, the price of product A will rise.
5. Over the long-term (all other things being equal), the price of product A will remain high.
1, 4, and 5 are correct
Q59 In 2007, India switched from being an exporter of wheat to the world markets to becoming an importer of wheat. This change would cause which of the following occur?
The supply curve for wheat on the world markets would have shifted left, with no change in demand, resulting in a rise in the world price of wheat.
Q60 If the supply and demand curves for a particular product both shift left (i.e. there is a decrease in both the quantity demanded and supplied) we can comnclude which of the following:
The quantity demanded and supplied must fall, but the equilibrium price may rise, fall or remain constant.
