
- •Англійська мова
- •§2, П.15 (Єдиних правил…)
- •Англійська мова
- •Unit 1 text a Electronics in the home
- •Read and remember the following words and words combinations:
- •2. Read and translate the following text:
- •3. Translate the following phrases:
- •4. Match the words and word combinations with their translation:
- •5. Answer the questions to the text:
- •6. Fill in the gaps in this table with the help of the text:
- •7. Use the space below to make a list of ways you think electronics may be used in the home in the future.
- •1. Read and translate the text in a written form: microelectronics
- •Unit 2 text a Telecommunications: a brief historical review
- •2.Match the words that go together and translate them:
- •3. Read and translate the text.
- •4. Choose the correct variant:
- •5. Complete the sentences with the proper word or phrase:
- •6. Translate into Ukrainian:
- •7. In this description of the changes which have taken place in telephone design, put each verb into correct tense and form.
- •1. Read and translate the text in a written form: History of Electronics
- •4. True or false. If the statement is false correct it.
- •5. Match the words with their definitions:
- •6. Make up sentences using the words and phrases below. Translate them into Ukrainian:
- •7. Answer the questions to the text:
- •1. Read and translate the text in a written form: Evolution of Microelectronics
- •Unit 4 text a Understanding electronic diagrams
- •3. Match the words and their translations:
- •4. Name basic units of the block diagram of a simple radio.
- •5. Translate into English:
- •1. Read and translate the text in a written form: Block Diagrams
- •Resistor values
- •3. Fill in the missing colours in this table with the help of the text.
- •4. Find the values and tolerance of resistors banded as follows:
- •5. Answer the questions below:
- •Capacitors and Capacitor Values
- •1. Read and translate the text in a written form: The Questions that Stump Scientists
- •3. Read and translate the text:
- •4. Complete the sentences with the proper words:
- •5. Ask questions to the underlined words:
- •6. Read the text below and translate it with the help of the given words:
- •1. Read and translate the text in a written form: Transistors
- •3. Match the words and their definitions:
- •1. Read and translate the text in a written form: Bell Telephone Laboratories
- •2. Make up a plan of the text in the form of questions. Text c
- •1.Mind the following words:
- •Unit 9 text a Radio Waves
- •3. Translate the following word-combinations and memorize them.
- •Fill in the table.
- •Choose the correct variant.
- •Answer the following questions.
- •Translate into English.
- •Read and translate the following text making sure you know the following words and phrases.
- •Supersonic – надзвуковий;
- •True (t) or false (f) sentences. Correct the false ones.
- •Answer the following questions about the text.
- •Translate into English.
- •1.Read and translate the text in a written form: What Makes Radio Waves?
- •Transmitter – (радіо)передавач;
- •2. Read and translate the following text.
- •3. Translate and memorize the following word-combinations.
- •Match English words and word-combinations with their Ukrainian equivalents.
- •5. Choose the correct variant.
- •6. Answer the following questions.
- •7. Represent the scheme of a radio transmitter or a microphone transmitter. Describe the principles of their work.
- •8. Translate into English.
- •1. Read and translate the text in a written form: Electromagnetic Waves
- •3. Translate the following word-combinations and memorize them.
- •5. Choose the correct variant.
- •6. Answer the following questions.
- •7. Describe the work of a radio receiver or describe the principle of the resonance.
- •8. Translate into English.
- •1. Read and translate the text in a written form: Receivers
- •Flicker – мерегтіння;
- •6. Complete these sentences using the text.
- •7. Choose the correct variant.
- •8. Answer the following questions about the text.
- •9. Translate into English.
- •10. Speak about: a) Television; b) Colour television. Text b
- •1. Read and translate the text in a written form:
- •Television
- •Unit13 text a Cellphones
- •3. Translate the following word-combinations and memorize them.
- •5. Choose the correct variant.
- •1. All communications take place through a central contral base with …
- •Answer the following questions about the text. Decide which paragraphs are most likely to contain answers to these questions.
- •7. Study these statements about making a cellphone call. Link them into longer sentences. You may omit words and make whatever changes you think are necessary in the word order.
- •8. Translate into English.
- •1. Read and translate the text in a written form: Cellphones
- •Unit14 text a Computers and Computer Systems
- •1. Answer the following questions:
- •2. Match each component with its function:
- •3. Complete the table:
- •4. Label the diagram of a computer system using these terms:
- •1. Read and translate the text in a written form: Unit 14 Computers
- •3. Translate the following word-combinations into Ukrainian and memorize them.
- •4. Match each part of the music centre and its peculiarity.
- •5. Choose the correct variant.
- •6. Answer the following questions about the text.
- •7. Translate into Ukrainian.
- •8. Translate into English.
- •1. Read and translate the text in a written form: Music Centre
- •Unit16 text a Detection Devices
- •3. Translate the following word-combinations and memorize them.
- •4.Match each action with its consequence. Then identify the device or feature described:
- •5. Complete these sentences with suitable action or consequence.
- •6. Choose the correct variant.
- •7. Answer the following questions about the text.
- •8. Complete the table
- •9. Use words from the text to complete the following table:
- •10. Translate into Ukrainian.
- •11. Translate into English.
- •1. Read and translate the text in a written form: Detection Devices
- •Unit 17 text a What is the Morse Code?
- •Find the English equivalents to the following words and phrases:
- •Translate the sentences into Ukrainian:
- •Complete the sentences:
- •Match the words with their definitions:
- •1. Read and translate the text in a written form:
- •Unit18 text a Areas of Employment
- •2. Read and translate.
- •1 Avionics
- •2 Computing
- •3 Defence
- •4Industrial electronics
- •5 Leisure products
- •6Telecommunications and broadcasting
- •7Medical equipment
- •3. Translate and memorize the following words and word-combinations:
- •4.Complete the table.
- •5. True (t) or false (f) sentences. Correct the false ones.
- •6. Answer the following questions about the text.
- •7. Translate into English.
- •1. Read and translate the text in a written form:
- •2. Make up a plan of the text in the form of questions. Unit19 text a
- •1.Read and memorize the following words and word-combinations and their translations.
- •2. Read and translate the job advertisement. Wanted
- •3. Answer the following questions.
- •4. Read the cv of Charles Dunkin and his letter of application. Curriculum vitae
- •5. Imagine that you are Mr. Clark of Communicate (uk) Limited. List Charles’ strong points and his weak points.
- •6. Study the cv and the letter of application one more time. Make up a scheme of a cv and a plan of a letter of application.
- •7. Create your own cv and a letter of application using your scheme and plan.
- •8. Study the job advertisements and try to find a suitable job for these candidates:
- •Texts for listening
- •Electronics in the Home
- •History of Electronics
- •Electronic Diagram
- •The Nature of Electricity
- •The History of Transistors
- •Semiconductor
- •Radio Waves
- •Receiver
- •Television
- •Cell phone
- •Computers
- •Music Centre
- •Time to Dust Indicator
- •Using the Morse code
Unit 4 text a Understanding electronic diagrams
1. Translate the words and phrases. Make up your own sentences with them.
Basic unit, block diagram, component, tuner, detector, amplifier, aerial.
2. Read and translate the following text:
Although electronic devices may look complicated, they are made up of common basic units (building blocks) connected together. The function of each of these units and the path of the signals between them can be shown in a block diagram. For example, the block diagram of a simple radio is shown below
a
tuner
detector




AF amp
volume control
power amp
speaker
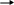

To understand how the radio works, it is more important to understand the function of each unit than to know what components are used. This is known as a system approach to electronics. For example, in the picture the tuner selects the required signal, the detector then separates off the audio part of the signal, and the AF amplifier (amp) amplifies it.
The connection and values of the components inside these basic units can be shown in a circuit diagram using standard electronic symbols.
3. Match the words and their translations:
1. complicated a) посилювати
2. select b) підхід
3. approach c) складний
4. separate d) обирати
5. amplify e)розподіляти
6. value f) значення, величина
4. Name basic units of the block diagram of a simple radio.
5. Translate into English:
1. Всі електронні пристрої складаються з основних одиниць, які з’єднані в одну систему.
2. Щоб зрозуміти роботу цілого пристрою, потрібно знати функції кожного компонента.
3. Знання роботи кожної складової одиниці – є системний підхід в електроніці.
4. Антена приймає сигнали, тюнер обирає потрібний сигнал, детектор виділяє аудіо частину сигналу.
5. На мікросхемі показується з’єднання та значення компонентів використовуючи стандартні електронні символи.
TEXT B
1. Read and translate the text in a written form: Block Diagrams
Block diagrams are a method of explaining complex systems (not necessarily electronic) in a simple manner.
They are made up from labeled blocks which are joined by arrows. The arrows indicate the direction of flow, and inputs to and outputs from the blocks.
At this stage it is not necessary to know how the block does its job. That will come later with a greater understanding of electronics.
In the example the low level signals from the three microphones are mixed together by the MIXER which gives a mixed low level signal out. The mixed signal is applied to the POWER AMPLIFIER which provides a high level signal to drive the loudspeaker.
The POWER SUPPLY UNIT converts the ac mains supply voltage to a dc voltage suitable for the system.
Even with this limited knowledge we can apply a little logical fault finding.
A circuit diagram (also known as an electrical diagram, elementary diagram, or electronic schematic) is a simplified conventional pictorial representation of an electrical circuit. It shows the different components of the circuit as simplified standard symbols, and the power and signal connections between the devices. Arrangement of the components interconnections on the diagram does not correspond to their physical locations in the finished device.
Unlike a block diagram or layout diagram, a circuit diagram shows the actual wire connections being used. The diagram does not show the physical arrangement of components. A drawing meant to depict what the circuit actually looks like is called "artwork" or "layout".
Circuit diagrams are used for the design (circuit design), construction and maintenance of electrical and electronic equipment.
On a circuit diagram, the symbols for components are labelled with a descriptor (or reference designation) matching that on the list of parts.
2. Make up a plan of the text in the form of questions.
TEXT C
1. Mind the following words:
circuitry – схема, ланцюг
layout – схема розташування
audio amplifier system – система посилення звукового сигналу
2. Listen to the text “Electronic Diagram “and try to understand it.
3. Answer the following questions:
1. What are circuit diagrams?
2. Are they made of standard symbols?
3. What does “READING a circuit diagram” mean?
4. What components does audio amplifier system include?
5. What components are there in a receiver system?
UNIT 5
TEXT A
Component Values
1. Read and remember the words and word combinations:
Band-стрічка
digit-цифра
tolerance-похибка
value-значення
capacitor-конденсатор
semiconductor-напівпровідник
application-застосування
significance-важливість
voltage-напруга
2.Read and translate the texts:
If you've ever looked down on a city from a skyscraper window, you'll have marvelled at all the tiny little buildings beneath you and the streets linking them together in all sorts of intricate ways. Every building has a function and the streets, which allow people to travel from one part of a city to another or visit different buildings in turn, make all the buildings work together.
The circuits inside pieces of electronic equipment are a bit like cities too: they're packed with components (similar to buildings) that do different jobs and the components are linked together by cables or printed metal connections (similar to streets). Unlike in a city, electronic circuits are built up from a small number of standard components.
These are some of the most important components you'll encounter: resistors, diodes, capacitors
