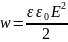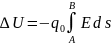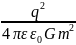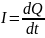- •A gas is taken through the cyclic process described in Figure. Find the net energy transferred to the system by heat during one complete cycle.
- •Calculate the resistance per unit length of a 22-gauge Nichrome wire, which has a radius of 0.321 mm (The resistivity of Nichrome is 1.5·10-6 ω·m).
- •Calculate the power delivered to the load resistor, if the current in the circuit is 3.93 a, the load resistance is 3.00 ω.
- •Calculate the power delivered to the internal resistance of the battery, if the current in the circuit is 3.93 a, the internal resistance of 0.05 ω.
- •Three identical objects, each of mass m, are fastened to a massless rod of length l as shown. The rotational inertia about one end of the rod of this array is:
Three identical objects, each of mass m, are fastened to a massless rod of length l as shown. The rotational inertia about one end of the rod of this array is:
5ML2/4
Two point-like charges in air (ε=1) at the distance r1=20 sm from each other interact with some force. At what distance r2 one needs to place this charges in oil (ε2=5) to get the same force of interaction?
r2=8.94 sm
The electron and proton of a hydrogen atom are separated (on the average) by a distance of approximately 5.3·10-11 m. Find the magnitudes of the electric force between the two particles. (ke=8.99·109 N·m2/C2)
8.2·10-8 N
Three resistors are connected in parallel as shown in Figure. A potential difference of 18.0 V is maintained between points a and b. Find the current I1.
I1=6.00 A
Three resistors are connected in parallel as shown in Figure. A potential difference of 18.0 V is maintained between points a and b. Find the current I2.
I1=3.00 A
Three resistors are connected in parallel as shown in Figure. A potential difference of 18.0 V is maintained between points a and b. Find the current I3.
I1=2.00 A
Three resistors are connected in parallel as shown in Figure. A potential difference of 18.0 V is maintained between points a and b. Calculate the power delivered to resistor R1.
P1=108 W
Three resistors are connected in parallel as shown in Figure. A potential difference of 18.0 V is maintained between points a and b. Calculate the equivalent resistance of the circuit.
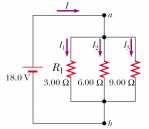
Req=1.64 Ω
The concrete sections of a certain superhighway are designed to have a length of 25.0 m. The sections are poured and cured at 10.0°C. What minimum spacing should the engineer leave between the sections to eliminate buckling if the concrete is to reach a temperature of 50.0°C? (Average linear expansion coefficient for concrete is α=12* 10-6 °C-1).
1.20 cm
The unit for permeability is
Wb/At × m
The direction of a magnetic field within a magnet is
from south to north
The ability of a material to remain magnetized after removal of the magnetizing force is known as
retentivity
The voltage induced across a certain coil is 200 mV. A 120
 resistor
is connected to the coil terminals. The induced current is
resistor
is connected to the coil terminals. The induced current is
1.7 mA
The induced voltage across a stationary conductor in a stationary magnetic field is
zero
Three identical capacitors connected in series. What single capacitance C is “equivalent” to this combination?
(1/3)C
The resonant angular frequency of series RLC circuit is
1/(LC)1/2
The total number of electron states with n=3 and l=1 for an atom is:
six
The thermal conductivity is the analog to:
Diffusivity
The emf inducted in an isolated circuit when the current in the circuit is changing by 10 A/s is 0.3 V. What is the self-inductance?
30 mH
The magnetic field for a given electromagnetic wave has Bmax = 10-6T. Emax equals
3*102 V/m
The magnitude of emf induced in an isolated circuit when the current in the circuit is changing by -10A/s is 0.2 V. What is the self-inductance?
20mH
The rapid exponential decay in just a few cycles of the charge on the plates of capacitor in an RLC circuit might be due to:
a large resistance
The pressure at the surface of the ocean is 1 atm (1 x 105 Pa). At what approximate depth in the ocean water (ρ = 1025 kg/m3) would the absolute pressure be 2 atm?
10 m
The temperature of a silver bar rises by 10.0°C when it absorbs 1.23 J of energy by heat. The mass of the bar is 525 g. Determine the specific heat of silver.
234 J/kg . °C
For an object undergoing simple harmonic motion,
the acceleration is greatest when the displacement is greatest
Find the currents I1, I2, and I3 in the circuit shown in Figure.

I1=2 A, I2=-3 A, I3=-1 A
For a uniform block of material of cross sectional area A and length l, the resistance over the length l is:
For a given wirewound core, an increase in current through the coil
increases the flux density
For a uniform block of material of cross sectional area A and length l, the resistance over the length l is:
Find the equivalent capacitance between a and b for the combination of capacitors shown in Figure. All capacitances are in microfarads.

6.0 μF
Find the electric flux Φe though the spherical surface, covers the point-like charges q1=5 nC and q2=-2 nC. (ε0=8.85·10-12 C2/N·m2)
Φe=339 N·m2/C
Find the attractive force F between nuclei of hydrogen atom and electron. Radius of hydrogen atom is r=0.5·10-10 m; modules charge of nuclei are equal and opposite to charge sign of electron (ε0=8.85·10-12 C2/N·m2).
F=92.3·10-9 N
Four resistors are connected as shown in Figure. Find the equivalent resistance between points a and b.

12 Ω
Four resistors are connected as shown in Figure. Find the equivalent resistance between points b and c.
2 Ω
Four resistors are connected as shown in Figure. Find the equivalent resistance between points a and c.
14 Ω
Find the currents I1, I2, and I3 in the circuit shown in Figure.
I1=2 A, I2=-3 A, I3=-1 A
Force is that agent which produces or tends to produce the __________.
Acceleration in the body
Four identical particles, each with mass m, are arranged in the x, y plane as shown. They are connected by light sticks to form a rigid body. If m = 2.0 kg and a = 1.0 m, the rotational inertia of this array about the y-axis is:

12 kg m2
Find a sample of the physical pendulum:
Find the equivalent capacitance between a and b for the combination of capacitors shown in Figure. All capacitances are in microfarads.
6.0 μF
Find the electric flux Φe though the spherical surface, covers the point-like charges q1=5 nC and q2=-2 nC. (ε0=8.85·10-12 C2/N·m2)
Φe=339 N·m2/C
Find the attractive force F between nuclei of hydrogen atom and electron. Radius of hydrogen atom is r=0.5·10-10 m; modules charge of nuclei are equal and opposite to charge sign of electron (ε0=8.85·10-12 C2/N·m2).
F=92.3·10-9 N
Four resistors are connected as shown in Figure. Find the equivalent resistance between points a and b.
12 Ω
Four resistors are connected as shown in Figure. Find the equivalent resistance between points b and c.
2 Ω
Four resistors are connected as shown in Figure. Find the equivalent resistance between points a and c.
14 Ω
For the serial circuit work out the readings on the voltmeters V1 and V2 given the following values for R1=2Ohm and R2=10 Ohm, I1=1A, I2=1A
V1=2V; V2=10V;
Formula for energy density of electric field is
When a thin uniform stick of mass M and length L is pivoted about its midpoint, its rotational inertia is ML2/12. When pivoted about a parallel axis through one end, its rotational inertia is:
ML2/3
Which of the following statements is not true regarding a mass- spring system that moves with simple harmonic motion in absence of friction?
The potential energy stored in the system is greatest when the mass passes through the equilibrium position.
When the force and displacement are perpendicular to each other, then work is __________.
Zero
Whenever a constant force is applied on a body then it will move with __________.
Constant Acceleration
Which statements are correct?
Charges of opposite sign attract one another and charges of the same sign repel one another. Total charge in an isolated system is conserved. Charge is quantized.
Which statements are correct?
Conductors are materials in which electrons move freely. Insulators are materials in which electrons do not move freely.
What are the opposite ends of a magnet called?
Its north and south poles
Which of the following is not a state function?
Mole
When a positive test charge q0 is moved between points A and B in an electric field E, the change in the potential energy of the charge–field system is:
Which statements are correct?
An equipotential surface is one on which all points are at the same electric potential. Equipotential surfaces are perpendicular to electric field lines.
Which of the following is not generally observed in a geomagnetic storm?
Disruption of microwave propagation
When the speed at which a conductor is moved through a magnetic field is increased, the induced voltage
Increases
What happens when you turn off the current in an electromagnet?
The magnetism is turned off
When the current through the coil of an electromagnet reverses,
direction of the magnetic field reverses
What is the reluctance of a material that has a length of 0.07 m, a cross-sectional area of 0.014 m2, and a permeability of 4,500
 Wb/At
× m?
Wb/At
× m?
1111 At/Wb
What is the flux density when the flux is 5.5 Wb and the cross-sectional area is 6 × 10–3 m2?
917 µT
What is the flux density in a magnetic field in which the flux in 0.1 m2 is 600 Wb?
6,000 µT
Which statements are correct?
Charges of opposite sign attract one another and charges of the same sign repel one another. Total charge in an isolated system is conserved. Charge is quantized.
Which statements are correct?
Conductors are materials in which electrons move freely. Insulators are materials in which electrons do not move freely.
When a positive test charge q0 is moved between points A and B in an electric field E, the change in the potential energy of the charge–field system is:
Which statements are correct?
An equipotential surface is one on which all points are at the same electric potential. Equipotential surfaces are perpendicular to electric field lines.
What is the cross product of two vectors A and B, if the angle between them is 30 degree, and magnitudes are |A|=4, |B|=2
4
When a box rests on the floor, it is acted upon by the gravitational and the _________________ force.
Normal
When the force and displacement are parallel to each other, then work is __________.
Maximum
What is the direction of angular momentum for the bowling ball that rotates about z-axis?

+z
What times the gravitational force between two protons less the electrostatic force of their repulsion? The charge of proton is equal on module and opposite on sign of charge of electron.
What is the magnetomotive force in a 75-turn coil of wire when there are 4 A of current through it?
300 At
When the north poles of two bar magnets are brought close together, there will be
a force of repulsion
When a solenoid is activated, the force that moves the plunger is
an electromagnetic field
What is the magnetomotive force (mmf) of a wire with 8 turns carrying three amperes of current?
24 At
What is the maximal number of electrons at shell with n=3
18
What is a good insulator of electricity?
Rubber
Which relation defines equipotential surface:
What is an insulator of electricity?
A material that doesn’t allow the free electrons to easily travel through it.
What times the gravitational force between two protons less the electrostatic force of their repulsion? The charge of proton is equal on module and opposite on sign of charge of electron.
Work done by a grass cutter is maximum when he pulls it __________.
Making an angle 900 with the floor
If we define V = 0 at rA = ∞ the electric potential due to a point charge at any distance r from the charge is:
If two or more capacitors are connected in series, the equivalent capacitance of the series combination is given by:
1/Ceq=1/C1+1/C2+1/C3+...
Inside the wall of a house, an L-shaped section of hot-water pipe consists of a straight horizontal piece 28.0 cm long, an elbow, and a straight vertical piece 134 cm long (Figure). A stud and a second-story floorboard hold stationary the ends of this section of copper pipe. Find the magnitude of the displacement of the pipe elbow when the water flow is turned on, raising the temperature of the pipe from 18.0°C to 46.5°C.
0.663 mm
If the electric field is uniform and makes an angle θ with the normal to a surface of area A, the electric flux through the surface is:
ΦE=EAcosθ
If a wire coil has 10 turns and carries 500 mA of current, what is the magnetomotive force in ampere-turns?
5.0
If the cross-sectional area of a magnetic field increases, but the flux remains the same, the flux density
Decreases
If the steel disk in a crankshaft position sensor has stopped with the tab in the magnet's air gap, the induced voltage
is zero
If the electric field is uniform and makes an angle θ with the normal to a surface of area A, the electric flux through the surface is:
ΦE=EAcosθ
If we define V = 0 at rA = ∞ the electric potential due to a point charge at any distance r from the charge is:
If two or more capacitors are connected in series, the equivalent capacitance of the series combination is given by:
1/Ceq=1/C1+1/C2+1/C3+...
If a potential difference of 10 V is maintained across a 1.0-m length of the Nichrome wire with resistance 4.6 Ω, what is the current in the wire?
2.2 A
If vector B is added to vector A, which two of the following choices must be true in order for the resultant vector to be equal to zero?
A nd B are parallel in the same direction and have same magnitude
In inelastic collision between the two bodies __________.
Only momentum of the system is conserved
In elastic collision between the two bodies __________.
Both the kinetic Energy and Momentum of the system remain the same
In rotational motion, the quantity, which plays the same role as the inertial mass in linear motion, is called ___________.
Moment of inertia
If a loop in a basic dc generator suddenly begins rotating at a faster speed, the induced voltage
increases
If an electron moves perpendicular to the uniform magnetic field of magnitude 0.35 T with the speed equal to 4.69×106, what is the radius of its circular orbit? (me = 9.11×10-31kg)
7.63×10-5
If a potential difference of 10 V is maintained across a 1.0-m length of the Nichrome wire with resistance 4.6 Ω, what is the current in the wire?
2.2 A
In a photoelectric experiment at a frequency above cut off, the stopping potential is proportional to:
The energy of the most energetic electrons after it is ejected
Induction current opposes the reason causing it. It is the shortest formulation of
Lentz law
In an electromagnetic wave E0=3*106V/m. B0 equals
10-2T
Intrinsic semiconductors are
Pure elemental materials without impurities
In a charge-free region of space, closed container is placed in an electric field. A requirement for the total electric flux through the surface of the container to be zero is that
The requirement does not exist – the total electric flux is zero no matter what
In RLC circuit angular frequency of AC source rises. Inductive reactance
Increases
H
 ow
does the internal energy of an ideal gas change as it follows path
ow
does the internal energy of an ideal gas change as it follows path
 in figure?
in figure?
 increases
increases
H ow does the internal energy of an ideal gas as it follows path
 along the isotherm labeled
along the isotherm labeled
 in figure ?
in figure ?
stays the same
he electric current I in a conductor is defined as:
How are electrical charges and magnetic poles similar?
Unlike attract and the same type repel
How can you show that electricity creates a magnetic field?
Use a compass near a wire with current flowing through it
How can you make an electromagnet?
Run current through a wire wrapped around an iron rod
How can you create electricity with a magnet?
By moving a wire through a magnetic field
How defines period of physical pendulum?
he electric current I in a conductor is defined as:
Ohm’s law in the differential form is:
J=σE
Ohm’s law in the integral form is:
I=U/R
On a day when the temperature reaches 50°F, what is the temperature in degrees Celsius and in kelvins?
100 C, 283 K.
Ohm’s law in the differential form is:
J=σE
Ohm’s law in the integral form is:
I=U/R
Ohm’s law in differential form is
j=γE, where j is a current density, γ is a conductivity
Of the three chief kinds of magnetic materials (diamagnetic, paramagnetic and ferromagnetic), which are used to make permanent magnets?
Only ferromagnetic
On what picture you can see non –uniform electric field?
Suppose a heat engine is connected to two energy reservoirs, one a pool of molten aluminum (660°C) and the other a block of solid mercury (-38.9°C). The engine runs by freezing 1.00 g of aluminum and melting 15.0 g of mercury during each cycle. The heat of fusion of aluminum is 3.97 * 105 J/kg; the heat of fusion of mercury is 1.18* 104 J/kg. What is the efficiency of this engine?
55.4 %
Sound travels faster in
steel
Electric theory of dispersion was evaluated by:
Lorentz
Energy may be transferred by
all answers are correct
Every action or force upon an object must have an equal and ____________ reaction.
Opposite
Magnetic flux through closed conducting loop changed from 10Wb to 5Wb in 10ms. The average EMF induced in the loop is
-500V
Motion is produced by
unbalanced forces
Potential energy of current carrying loop with magnetic dipole moment µ=1Am2 in magnetic field B of 0.1T, when B and µ make angle 600 is
-0.05J
Paramagnetism is closely associated with
The tendency of electron dipole moments to align with an applied magnetic field
Pairs of forces of equal magnitude act on identical cylinders as shown in the figures. In which example is the cylinder in translational and rotational equilibrium?
Parallel wires carrying currents I1 and I2 respectively
repel if they are directed opposite
Power is a __________.
Scalar Quantity
Loop is uniformly rotating with angular velocity ω in uniform magnetic field. Loop has N coils and area of the loop is S. Rotating axis lies on loop’s plane and perpendicular to induction. What is the maximal EMF appeared in the loop:
NBSω
Latent heat is
the heat released or absorbed by a thermodynamic system during a process that occurs without a change in temperature
Gauss’s law says that the net electric flux ΦE through any closed gaussian surface is equal to:
ΦE=qin/ε0
Gauss’s law says that the net electric flux ΦE through any closed gaussian surface is equal to:
ΦE=qin/ε0
D
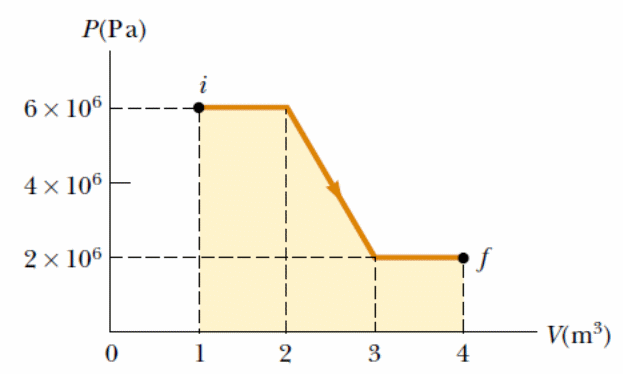 etermine
the work done on a fluid that expands from i
to
f
as
indicated in Figure.
etermine
the work done on a fluid that expands from i
to
f
as
indicated in Figure.
-12 MJ
Velocity of a body depends on time by the following form
 .
What is the unit of the coefficient [B]?
.
What is the unit of the coefficient [B]?
Just 9.00 g of water is placed in a 2.00-L pressure cooker and heated to 500°C. What is the pressure inside the container? (Molar mass of water M(H2O) = 18 g/mol, universal gas constant R= 8.314 J/mol*K ).
1.61 MPa
You charge parallel-plate capacitor. When you pull the plates apart to a larger separation and battery remains connected to the capacitor
Decreases
Resistance of metals in classical theory of electric conductivity is caused by
Collision of free electrons with ions of crystal structure