
- •Dealing with statistics вивчаючи статистику
- •Fundamentals of Statistics
- •Read and translate the text: What is statistics?
- •Complete the following sentences:
- •Present tenses Present Simple. Present Continuous. State Verbs
- •2. Fill in the gaps with the correct form of the verbs in brackets.
- •3. Fill in the gaps with the verbs in the box in the correct present tense.
- •Look at the following extracts. There are six incorrect verbs. Find and correct them.
- •Unit 2. A very brief history of statistics.
- •Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •Read and memorize the following words and word combinations. Use them in the sentences. Pay attention to the prepositions.
- •Read and translate the following sentences:
- •Read and translate the text:
- •Why you need to use statistics
- •Past tenses 1 Past Simple. Past Continuous. Used to/ Would.
- •1. Fill in the gaps in this model answer with verbs from the box in the past simple.
- •3 A teacher and student are talking about local customs. Fill in the gaps with the verbs in brackets in the correct form. Use would or used to where possible.
- •Unit 3. Variable and constant. Discrete and continuous.
- •Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •Read and memorize the following words. Use them in the sentences.
- •Read and translate the following sentences:
- •Read and translate the texts:
- •Variable and constant
- •Discrete and continuous
- •5. Write out the definitions from the texts:
- •6. Complete the following sentences:
- •7. Ask 10 general questions to the text.
- •8. Give examples of:
- •Present perfect Present Perfect. Present Perfect Continuous
- •1 Tick (/) the correct underlined verbs, and correct the verbs that are wrong.
- •3. Underline the correct form of the verbs.
- •4 Fill in the gaps with a verb from the box in the present perfect simple or present perfect continuous. You will need to use some verbs more than once.
- •Unit 4. Cardinal and ordinal. Population and sample.
- •1. Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •Read and memorize the following words. Use them in the sentences.
- •Read and translate the following sentences:
- •Read and translate the texts:
- •5. Write out the definitions out of the texts:
- •6. Complete the following sentences:
- •7. Ask 10 general questions to the text.
- •8. Give examples of:
- •9. Summarize the contents of the text in 10 – 15 sentences. Use the expressions:
- •Past tenses іі Past Perfect. Past Perfect Continuous.
- •1 Fill in the gaps with the past perfect simple of the verbs in brackets in the positive or negative.
- •2 Complete the report with the past simple or past perfect simple of the verbs in brackets
- •Unit 5. Misuses of statistics.
- •Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •Read and memorize the following words. Use them in the sentences.
- •Read and translate the following sentences:
- •Read and translate the texts:
- •Complete the following sentences:
- •6. Ask 10 general questions to the text.
- •7. Answer the following questions:
- •Sum up all the information about statistics and discuss this topic with your group-mates according to the plan:
- •Future 1 Plans, Intentions and Predictions: Present Continuous; Going to; Will
- •Fill in the gaps in the second half of this model answer with phrases from the box.
- •2 Fill in the gaps with the present continuous or will-future form of the verbs in brackets.
- •Unit 6. Basic statistical vocabulary.
- •1. Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •2. Read, translate and memorize the following words. Use them in the sentences.
- •Read and translate the following sentences:
- •Read and translate the texts:
- •Variables and data
- •Complete the following sentences:
- •6. Ask 10 general questions to the text.
- •7. Answer the following questions:
- •8. Write out the definitions of variables from the texts:
- •Give examples of these variables.
- •Summarize the contents of the text in 10 – 15 sentences. Use the expressions:
- •Don’t put all your data into one basket!
- •Future 2 Present Simple; be about to; future continuous; future perfect
- •The following chart shows the results of a class survey about planned activities for Saturday afternoon. Complete the sentences using the future continuous tense.
- •Read the following projections about the future population of Australia
- •3 In six of these sentences there is a verb in the wrong tense. Underline each mistake and write the correction.
- •4 Fill in the gaps with a future form from this unit and the verbs in brackets.
- •Test Practice. Academic Writing Task 1
- •Test Yourself (Unit 1–6)
- •Unit 7. Sources of Data.
- •Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •Read and memorize the following words. Use them in the sentences.
- •Read and translate the following sentences:
- •Read and translate the text:
- •Complete the following sentences:
- •Ask 10 general questions to the text.
- •Answer the following questions:
- •Agree or disagree with the following statements. Use the expressions:
- •Get ready to speak about sources of data. Use the following phrases:
- •Adjectives and Adverbs Describing things; adding information about manner, place, time, frequency and intensity.
- •1 Read the test task and the students' responses. Some of the adjectives they used are underlined. If they are used correctly, put a tick (/). If they are wrong, write the correct answer.
- •2 Write the missing adjectives and adverbs.
- •3 Match the beginnings (1-8) and the endings (a-h) of the sentences. Join them by adding a suitable -ed or -ing adjective formed from one of the verbs in the box. Use each verb once.
- •4 Underline the correct words.
- •Unit 8. Presenting Categorical Data.
- •1. Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •2. Read and memorize the following words. Use them in the sentences.
- •3. Read and translate the following sentences:
- •4. Read and translate the text:
- •Column Variable
- •5. Complete the following sentences:
- •6. Ask 10 general questions to the text.
- •7 Answer the following questions:
- •8. Agree or disagree with the following statements. Use the expressions:
- •9. Get ready to speak about “Presenting Numerical Data”. Use the following phrases:
- •Comparing things Comparative and superlative adjectives and adverbs; other ways of comparing
- •1 Fill in the gaps with the adjectives in the box in a comparative or superlative form.
- •2 Fill in the gaps with the words in brackets in a comparative or superlative form.
- •3 Fill in the gaps in the model answer below. Use one word in each gap.
- •Academic Writing Task 2
- •Unit 9. Analysing and Presenting Data.
- •1. Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •Read and memorize the following words. Use them in the sentences.
- •3. Read and translate the following sentences:
- •4. Read and translate the texts:
- •5. Complete the following sentences:
- •6. Ask 10 general questions to the text.
- •7. Answer the following questions:
- •Give examples of graphs you know. Modals I
- •I Obligation and necessity; suggestion and advice; adverbs
- •2 Fill in the gaps below with the correct form of (not) have to, must, (not) need or should.
- •3 Read the extract. Decide if the underlined phrases are correct or not. Tick (✓) them if they are right and correct them if they are wrong.
- •4 Fill in the gaps with the correct form of (not) have to, ought to or must(n't) and the verbs in brackets.
- •Modals II Ability; possibility; alternatives to modals
- •5 Underline the most suitable words. Sometimes both options are possible
- •6 Tick (✓) the sentence, a or b, which best matches the sentence on the right.
- •7 Replace the underlined phrases with a suitable past modal phrase.
- •Unit 10. Describing data.
- •Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •Read and memorize the following words. Use them in the sentences.
- •3. Read and translate the following sentences:
- •4. Read and translate the texts:
- •Inferring differences and relationships
- •5. Complete the following sentences:
- •6. Ask 10 general questions to the text.
- •7. Answer the following questions:
- •11. Changes can also be described in more detail by modifying a verb with an adverb. Using a verb from box a and an adverb from box b make sentences describing the changes represented on the graph.
- •12. Read the following summary of the Magic Music Downloads. The expressions in bold refer to time and amount. Underline the expression that you think is correct according to the graph.
- •Write a brief summary of your own graph using the language you have covered in this lesson.
- •14. Extension. (If you have time in this lesson or for the beginning of the next lesson)
- •Up close and personal: Survey results
- •If your data are categorical:
- •If your data are numerical:
- •Reported speech Tense changes; time references; reporting questions; reporting verbs
- •1 Here is a conversation between Tanya and her teacher.
- •2 Underline the correct verb in each sentence.
- •3 Correct the mistakes in these sentences.
- •4 Report each of the sentences below using a verb from the box. Remember that you do not need to report the original words exactly.
- •Uniit 11 categorical data in tables and graphs
- •Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •Memorize the following words and word combinations. Use them in the sentences. Pay attention to the prepositions.
- •Read and translate the following sentences:
- •Read and translate the text:
- •Complete the following sentences:
- •Ask 10 general questions to the text.
- •Answer the following questions:
- •Get ready to speak about presenting categorical data using tables. Draw the examples of a frequency, a cross-classification table and graphs to support your talk.
- •1 Fill in the gaps with the correct form of the verbs in brackets.
- •2 Underline the correct form of the verbs.
- •4 Fill in the gaps in the letter using both of the verbs in brackets.
- •Unit 12 numerical data in tables and graphs
- •1. Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •2. Memorize the following words and word combinations. Use them in the sentences. Pay attention to the prepositions.
- •3. Read and translate the following sentences:
- •4. Read and translate the text:
- •Complete the following sentences:
- •6. Ask 10 disjunctive questions to the text.
- •7. Answer the following questions:
- •8. Get ready to speak about the graphs. Use the following phrases:
- •Likelihood based on conditions
- •I. Zero, first and second conditionals; other ways to introduce a condition
- •2 Fill in the gaps in the extracts below using the verbs in brackets in the correct form.
- •3 Decide if the underlined verbs are correct or not. Tick (✓) them if they are right and correct them if they are wrong
- •4 Underline the correct words.
- •II Third conditional; mixed conditionals; wishes and regrets; should(n’t) have
- •1 Fill in the gaps with the correct form of the verbs in brackets.
- •2 Read about two scientific discoveries that were made due to chance and complete the sentences.
- •3 Find and correct the mistakes in the sentences below.
- •Test Practice. Academic Reading
- •Academic Writing Task 3
- •Test Yourself (Units 7 – 12)
- •Keys to grammar exercises удалено Grammar references
- •Future continuous
- •Future perfect
- •Future perfect continuous
- •1 Adjectives
- •2 Adverbs
- •Irregular adverbs
- •Reported Statements
- •Reported Questions
- •Reported Orders
- •Reported Commands, Requests, Suggestions, etc
- •Difference in meaning between the to-infinitive and -ing form
- •The infinitive without to (also called bare infinitive) is used:
- •Conditionals:Types 2 and 3
- •Other words to introduce a condition
- •In case
- •Mixed conditionals
- •Irregular verbs
- •Glossary
- •Key vocabulary index
- •References
- •Content
Discrete and continuous
Quantitative variables are divided into ‘discrete’ and ‘continuous’. A discrete variable is one that can only take certain values, which are clearly separated from one another – for instance, a sales department can have 2 or 15 or 30 people within it. It cannot, however, contain 38 or 48.1 people. A continuous variable is one that could take any value in an interval. Examples of continuous variables include body mass, height, age, weight or temperature. Where continuous variables are concerned, whatever two values you mention, it is always possible to have more values (in the interval) between them. An example of this is height – a child may be 1.21 metres tall when measured on 27th September this year, and 1.27 metres on 27 September next year. In the intervening 12 months, however, the child will have been not just 1.22 or 1.23 or 1.24 and so on up to 1.27 metres, but will have been all the measurements possible, however small they might be, between 1.21 and 1.27.
Sometimes the distinction between discrete and continuous is less clear. An example of this is a person’s age, which could be discrete (the stated age at a particular time, 42 in 2007) or continuous, because there are many possible values between the age today (42 years, 7 weeks and 3 days) and the age next week (42 years, 8 weeks and 3 days).
5. Write out the definitions from the texts:
Variable (in everyday language);
Variable (in statistics);
Discrete variable;
Continuous variable;
Constant (in everyday language);
Constant (in statistics);
Attributes.
6. Complete the following sentences:
In every day language variable….
In statistical language variable is…..
In every day language constant ….
In statistical language constant is …..
In statistical language, when your variables and constants are categorical…
Quantitative variables are divided into…
A discrete variable is…
A continuous variable is ….
Where continuous variables are concerned….
Sometimes the distinction between discrete and….
7. Ask 10 general questions to the text.
8. Give examples of:
Variable (in everyday language);
Variable (in statistics);
Discrete variable;
Continuous variable;
Constant (in everyday language);
Constant (in statistics).
Present perfect Present Perfect. Present Perfect Continuous
1 Tick (/) the correct underlined verbs, and correct the verbs that are wrong.
I would like to be considered for your degree course In Zoology starting in October next year. I feel I am a good candidate for the course as I (1) have always been interested in natural history and even as a child I (2) have enjoyed studying animals and insects in my garden. Your science faculty has a good reputation and I would very much life to be part of it
As you (3) already saw in Section A of this application, I have a good academic record and I (4) just received the results of my recent exams, all of which (5) have been excellent
In addition, your university attracts me because I enjoy sports and I (6) have read in your prospectus about the large number of sports on offer. Last year I (7) have represented my school at badminton and I (8) played in football teams since I was eleven. I (9) have recently joined a basketball team which competes at a national level.
1 (10) did not travel abroad much yet although as a young child I (11) have been to Singapore and Hong Kong with my family. I realize that I (12) have not spent roach time away from home up to now, but am keen to become more independent
Percentage of UK adults to
have used the Internet
Men women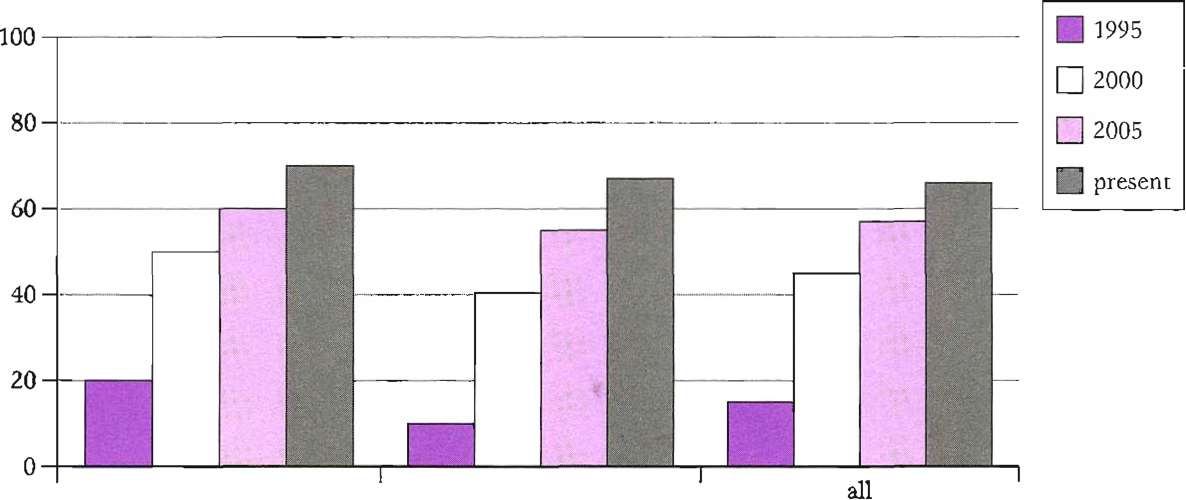
1 The chart shows the percentage of British adults who have used (use) the Internet since 1995.
2 The number of women who have ever used the Internet _________ (increase) by more than 60% since 1995.
3 The percentage of men who have accessed the Internet ________ (rise) to 60% in 2005.
4 The number of women to have accessed the Internet _________ (rise) each year.
5 The percentage of men who used the Internet _________ (be) greater than the percentage of women from 1995 to 2005.
6 However, British women _________ (overtake) British men in Internet usage since 2005.
7 The total number of people accessing the Internet _________ (grow) each year although the most significant rise _________ (occur) between 1995 and 2000.
