
- •Dealing with statistics вивчаючи статистику
- •Fundamentals of Statistics
- •Read and translate the text: What is statistics?
- •Complete the following sentences:
- •Present tenses Present Simple. Present Continuous. State Verbs
- •2. Fill in the gaps with the correct form of the verbs in brackets.
- •3. Fill in the gaps with the verbs in the box in the correct present tense.
- •Look at the following extracts. There are six incorrect verbs. Find and correct them.
- •Unit 2. A very brief history of statistics.
- •Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •Read and memorize the following words and word combinations. Use them in the sentences. Pay attention to the prepositions.
- •Read and translate the following sentences:
- •Read and translate the text:
- •Why you need to use statistics
- •Past tenses 1 Past Simple. Past Continuous. Used to/ Would.
- •1. Fill in the gaps in this model answer with verbs from the box in the past simple.
- •3 A teacher and student are talking about local customs. Fill in the gaps with the verbs in brackets in the correct form. Use would or used to where possible.
- •Unit 3. Variable and constant. Discrete and continuous.
- •Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •Read and memorize the following words. Use them in the sentences.
- •Read and translate the following sentences:
- •Read and translate the texts:
- •Variable and constant
- •Discrete and continuous
- •5. Write out the definitions from the texts:
- •6. Complete the following sentences:
- •7. Ask 10 general questions to the text.
- •8. Give examples of:
- •Present perfect Present Perfect. Present Perfect Continuous
- •1 Tick (/) the correct underlined verbs, and correct the verbs that are wrong.
- •3. Underline the correct form of the verbs.
- •4 Fill in the gaps with a verb from the box in the present perfect simple or present perfect continuous. You will need to use some verbs more than once.
- •Unit 4. Cardinal and ordinal. Population and sample.
- •1. Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •Read and memorize the following words. Use them in the sentences.
- •Read and translate the following sentences:
- •Read and translate the texts:
- •5. Write out the definitions out of the texts:
- •6. Complete the following sentences:
- •7. Ask 10 general questions to the text.
- •8. Give examples of:
- •9. Summarize the contents of the text in 10 – 15 sentences. Use the expressions:
- •Past tenses іі Past Perfect. Past Perfect Continuous.
- •1 Fill in the gaps with the past perfect simple of the verbs in brackets in the positive or negative.
- •2 Complete the report with the past simple or past perfect simple of the verbs in brackets
- •Unit 5. Misuses of statistics.
- •Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •Read and memorize the following words. Use them in the sentences.
- •Read and translate the following sentences:
- •Read and translate the texts:
- •Complete the following sentences:
- •6. Ask 10 general questions to the text.
- •7. Answer the following questions:
- •Sum up all the information about statistics and discuss this topic with your group-mates according to the plan:
- •Future 1 Plans, Intentions and Predictions: Present Continuous; Going to; Will
- •Fill in the gaps in the second half of this model answer with phrases from the box.
- •2 Fill in the gaps with the present continuous or will-future form of the verbs in brackets.
- •Unit 6. Basic statistical vocabulary.
- •1. Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •2. Read, translate and memorize the following words. Use them in the sentences.
- •Read and translate the following sentences:
- •Read and translate the texts:
- •Variables and data
- •Complete the following sentences:
- •6. Ask 10 general questions to the text.
- •7. Answer the following questions:
- •8. Write out the definitions of variables from the texts:
- •Give examples of these variables.
- •Summarize the contents of the text in 10 – 15 sentences. Use the expressions:
- •Don’t put all your data into one basket!
- •Future 2 Present Simple; be about to; future continuous; future perfect
- •The following chart shows the results of a class survey about planned activities for Saturday afternoon. Complete the sentences using the future continuous tense.
- •Read the following projections about the future population of Australia
- •3 In six of these sentences there is a verb in the wrong tense. Underline each mistake and write the correction.
- •4 Fill in the gaps with a future form from this unit and the verbs in brackets.
- •Test Practice. Academic Writing Task 1
- •Test Yourself (Unit 1–6)
- •Unit 7. Sources of Data.
- •Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •Read and memorize the following words. Use them in the sentences.
- •Read and translate the following sentences:
- •Read and translate the text:
- •Complete the following sentences:
- •Ask 10 general questions to the text.
- •Answer the following questions:
- •Agree or disagree with the following statements. Use the expressions:
- •Get ready to speak about sources of data. Use the following phrases:
- •Adjectives and Adverbs Describing things; adding information about manner, place, time, frequency and intensity.
- •1 Read the test task and the students' responses. Some of the adjectives they used are underlined. If they are used correctly, put a tick (/). If they are wrong, write the correct answer.
- •2 Write the missing adjectives and adverbs.
- •3 Match the beginnings (1-8) and the endings (a-h) of the sentences. Join them by adding a suitable -ed or -ing adjective formed from one of the verbs in the box. Use each verb once.
- •4 Underline the correct words.
- •Unit 8. Presenting Categorical Data.
- •1. Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •2. Read and memorize the following words. Use them in the sentences.
- •3. Read and translate the following sentences:
- •4. Read and translate the text:
- •Column Variable
- •5. Complete the following sentences:
- •6. Ask 10 general questions to the text.
- •7 Answer the following questions:
- •8. Agree or disagree with the following statements. Use the expressions:
- •9. Get ready to speak about “Presenting Numerical Data”. Use the following phrases:
- •Comparing things Comparative and superlative adjectives and adverbs; other ways of comparing
- •1 Fill in the gaps with the adjectives in the box in a comparative or superlative form.
- •2 Fill in the gaps with the words in brackets in a comparative or superlative form.
- •3 Fill in the gaps in the model answer below. Use one word in each gap.
- •Academic Writing Task 2
- •Unit 9. Analysing and Presenting Data.
- •1. Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •Read and memorize the following words. Use them in the sentences.
- •3. Read and translate the following sentences:
- •4. Read and translate the texts:
- •5. Complete the following sentences:
- •6. Ask 10 general questions to the text.
- •7. Answer the following questions:
- •Give examples of graphs you know. Modals I
- •I Obligation and necessity; suggestion and advice; adverbs
- •2 Fill in the gaps below with the correct form of (not) have to, must, (not) need or should.
- •3 Read the extract. Decide if the underlined phrases are correct or not. Tick (✓) them if they are right and correct them if they are wrong.
- •4 Fill in the gaps with the correct form of (not) have to, ought to or must(n't) and the verbs in brackets.
- •Modals II Ability; possibility; alternatives to modals
- •5 Underline the most suitable words. Sometimes both options are possible
- •6 Tick (✓) the sentence, a or b, which best matches the sentence on the right.
- •7 Replace the underlined phrases with a suitable past modal phrase.
- •Unit 10. Describing data.
- •Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •Read and memorize the following words. Use them in the sentences.
- •3. Read and translate the following sentences:
- •4. Read and translate the texts:
- •Inferring differences and relationships
- •5. Complete the following sentences:
- •6. Ask 10 general questions to the text.
- •7. Answer the following questions:
- •11. Changes can also be described in more detail by modifying a verb with an adverb. Using a verb from box a and an adverb from box b make sentences describing the changes represented on the graph.
- •12. Read the following summary of the Magic Music Downloads. The expressions in bold refer to time and amount. Underline the expression that you think is correct according to the graph.
- •Write a brief summary of your own graph using the language you have covered in this lesson.
- •14. Extension. (If you have time in this lesson or for the beginning of the next lesson)
- •Up close and personal: Survey results
- •If your data are categorical:
- •If your data are numerical:
- •Reported speech Tense changes; time references; reporting questions; reporting verbs
- •1 Here is a conversation between Tanya and her teacher.
- •2 Underline the correct verb in each sentence.
- •3 Correct the mistakes in these sentences.
- •4 Report each of the sentences below using a verb from the box. Remember that you do not need to report the original words exactly.
- •Uniit 11 categorical data in tables and graphs
- •Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •Memorize the following words and word combinations. Use them in the sentences. Pay attention to the prepositions.
- •Read and translate the following sentences:
- •Read and translate the text:
- •Complete the following sentences:
- •Ask 10 general questions to the text.
- •Answer the following questions:
- •Get ready to speak about presenting categorical data using tables. Draw the examples of a frequency, a cross-classification table and graphs to support your talk.
- •1 Fill in the gaps with the correct form of the verbs in brackets.
- •2 Underline the correct form of the verbs.
- •4 Fill in the gaps in the letter using both of the verbs in brackets.
- •Unit 12 numerical data in tables and graphs
- •1. Practice the pronunciation of the words:
- •2. Memorize the following words and word combinations. Use them in the sentences. Pay attention to the prepositions.
- •3. Read and translate the following sentences:
- •4. Read and translate the text:
- •Complete the following sentences:
- •6. Ask 10 disjunctive questions to the text.
- •7. Answer the following questions:
- •8. Get ready to speak about the graphs. Use the following phrases:
- •Likelihood based on conditions
- •I. Zero, first and second conditionals; other ways to introduce a condition
- •2 Fill in the gaps in the extracts below using the verbs in brackets in the correct form.
- •3 Decide if the underlined verbs are correct or not. Tick (✓) them if they are right and correct them if they are wrong
- •4 Underline the correct words.
- •II Third conditional; mixed conditionals; wishes and regrets; should(n’t) have
- •1 Fill in the gaps with the correct form of the verbs in brackets.
- •2 Read about two scientific discoveries that were made due to chance and complete the sentences.
- •3 Find and correct the mistakes in the sentences below.
- •Test Practice. Academic Reading
- •Academic Writing Task 3
- •Test Yourself (Units 7 – 12)
- •Keys to grammar exercises удалено Grammar references
- •Future continuous
- •Future perfect
- •Future perfect continuous
- •1 Adjectives
- •2 Adverbs
- •Irregular adverbs
- •Reported Statements
- •Reported Questions
- •Reported Orders
- •Reported Commands, Requests, Suggestions, etc
- •Difference in meaning between the to-infinitive and -ing form
- •The infinitive without to (also called bare infinitive) is used:
- •Conditionals:Types 2 and 3
- •Other words to introduce a condition
- •In case
- •Mixed conditionals
- •Irregular verbs
- •Glossary
- •Key vocabulary index
- •References
- •Content
9. Get ready to speak about “Presenting Numerical Data”. Use the following phrases:
To begin with, I’ll consider …
First I’ll describe …
Now I’ll pass to …
I’d like to draw your attention to …
Finally …
To conclude …
Comparing things Comparative and superlative adjectives and adverbs; other ways of comparing
1 Fill in the gaps with the adjectives in the box in a comparative or superlative form.
Brave effective exciting expensive fast
happy
good heavy small
I travelled through Turkey by train because it was the fastest way to cross the country.
Scientists have discovered a tiny bacteria living in the deep ocean. They say it is ________ living organism known to man.
It is almost impossible to find a parking space in the city centre so it is _______ to travel by public transport if you need to go there.
Pain killers are much _______ now so they reduce pain a lot faster than in the past.
I like all kinds of sports, but I think football is _________ game to watch because it is so fast-moving.
Nick did a bungee-jump, but I was too scared. He's much _______ than me.
I think people from the north of my country are ___________ than people from the south. In the south no one ever seems to smile, but it's the opposite in the north.
The website listed hotels in a wide price range. I was amazed that the _______ ones cost over $500 a night.
Weightlifters these days are lifting _________ weights than ever before.
2 Fill in the gaps with the words in brackets in a comparative or superlative form.
Teacher: What are 1 the most obvious (obvious) differences you have noticed between your own country and this one?
Student: Oh there are so many! In my country people are 2 not as interested (not/interested) in foreigners as people here, who are much 3 ______ (friendly). They are always kind and welcoming. Also, the weather is very different It's much 4 _______ (hot) in my country. It's only autumn but I am feeling cold here already and it's getting 5 ________ (cold) every day. I don't like that. Then there's the food. Your food is 6 ________ (not/good) ours. Our food is 7 _______ (spicy) and 8 _________ (delicious). think it's 9 _________ (good) in the world! It is 10 __________ (not/expensive) either. I've also noticed that people here eat slightly 11 _______ (early) and they eat their meals 12 ________ (quickly). And I am beginning to change my own habits too! 13 _________ (long) I stay here 14 ________ (fast) I seem to be eating.
3 Fill in the gaps in the model answer below. Use one word in each gap.
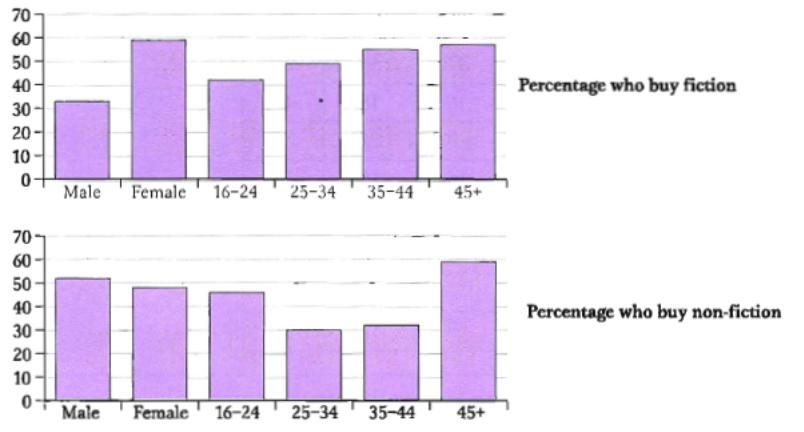
The charts below show the number and types of books bought by men and women and four different age groups in the UK.
Summarise the information by selecting and reporting the main features, and make comparisons where relevant
The charts give information about the types of books that British men and women and different age groups boy. The initial impression from the charts is that women tend to buy 1 _____ books than men overall, although they buy slightly 2 _______ non-fiction books. The people that buy the 3 _____ books are in the 45+ age group.
Nearly 60% of women buy fiction, which is almost 4 _______ as many as the number of men who choose this type of book Nevertheless, most age groups buy 5 _______ fiction books than non-fiction ones showing that non-fiction is generally 6 _________ popular than fiction.
The number of people buying fiction increases steadily from ages 16 to 45 with the 7 ______ number of books, at just over 40% of the age group bought by 16 -- to 24-year-olds and the 8 ______ number, at just over 50%. bought by the over 45s.
However the pattern is different for non-fiction. The number of books bought by 25- to 44-year-olds is 9 ______ lower than the number bought by 16- to 24-year-olds and those over 45. Just over 40% of 16- to 24-year-olds buy non-fiction but this number is not 10 ________ high as the number of people aged HS and over buying non-fiction, at nearly 60%. Only 31% of 35 - to 44 --year-olds buy non-fiction, and the number of 24 - to 34-year-olds is 11 ________ lower at 28%
4 Read the description of the table below. Decide if the underlined comparisons are correct or not. Tick (/) them if they are right and correct them if they are wrong.
2004 Olympic Games Medal Table |
|||||
Rank |
Country |
Gold |
Silver |
Bronze |
Total |
1 |
United States |
35 |
39 |
29 |
103 |
2 |
China |
32 |
17 |
14 |
63 |
3 |
Russia |
27 |
27 |
38 |
92 |
4 |
Australia |
17 |
16 |
16 |
49 |
5 |
Japan |
16 |
.9 |
12 |
37 |
6 |
Germany |
14 |
16 |
18 |
48 |
7 |
France |
11 |
9 |
13 |
33 |
8 |
Italy |
10 |
11 |
11 |
32 |
9 |
South Korea |
9 |
12 |
9 |
30 |
10 |
Great Britain |
9 |
9 |
12 |
30 |
The table shows the number of medals won by the top ten countries in the 2004 Olympic Games. The USA won 1 greatest number of medals overall with a total of 103. They won 2 more silver medals as gold and 3 more medals than any other country in both categories. China had 4 the second high number of medals at 63, but unlike the USA, China won 5 less silver medals than gold medals. While Russia's silver medal total was 6 more good than China's, they did not do 7 well as China in the gold medals, winning just 27. In fact China had a 8 more lower overall medal total than Russia but, as the table is based on the number of gold medals won, they were placed second. Similarly, Germany was 9 significantly successful at winning medals than Japan, with a total of 48 compared to Japan's 37, but because Japan won 10 two more gold medals that Germany they were ranked 11 higher. Great Britain gave 12 the worse performance in this group, winning only nine gold and nine silver medals |
|
