7 семестр (Бормотов А) / 1man_bw_l23_30_chn_23_30_instruktsiya_po_ekspluatatsii / MAN-BW L23-30 (ЧН 225_300)+ / MAN-BW L23-30 H Vol-1 (Instruction)+
.pdf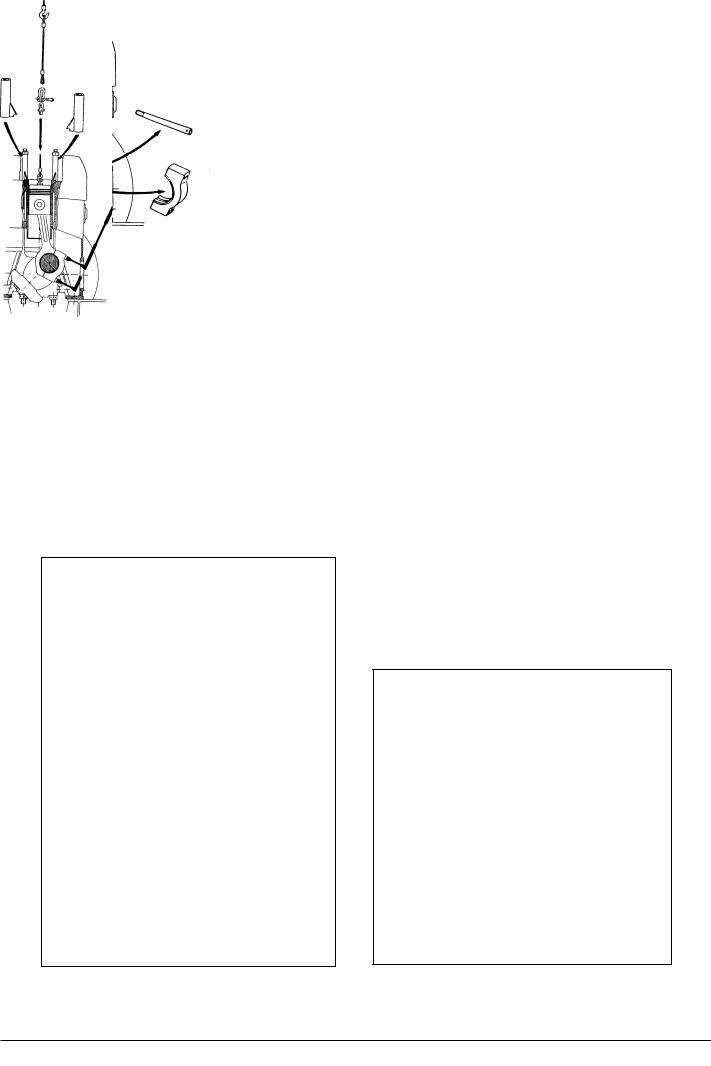
506-01.00 |
Dismounting of Piston and Connecting Rod |
Working Card |
Edition 01H |
Page 2 (3) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
L23/30H
Preparations before Dismounting
1) Clean the upper part of the cylinder. If not, the piston may get stuck during removal in the carbon deposited in this area.
a)Turn the piston to the buttom.
b)Place a used piston ring on top of the piston.
c)Mount the tube (for holding down the cylinder liner during the piston withdrawal) on one of the cylinder head studs, screw on the nut and tighten it slightly.
d)Turn the piston in top, in order to push the flame ring out of the cylinder by means of the piston ring.
Info: It is the used piston ring which pushes the flame ring out of the cylinder.
2)Remove the gangway, if any installed, in order to improve the access conditions.
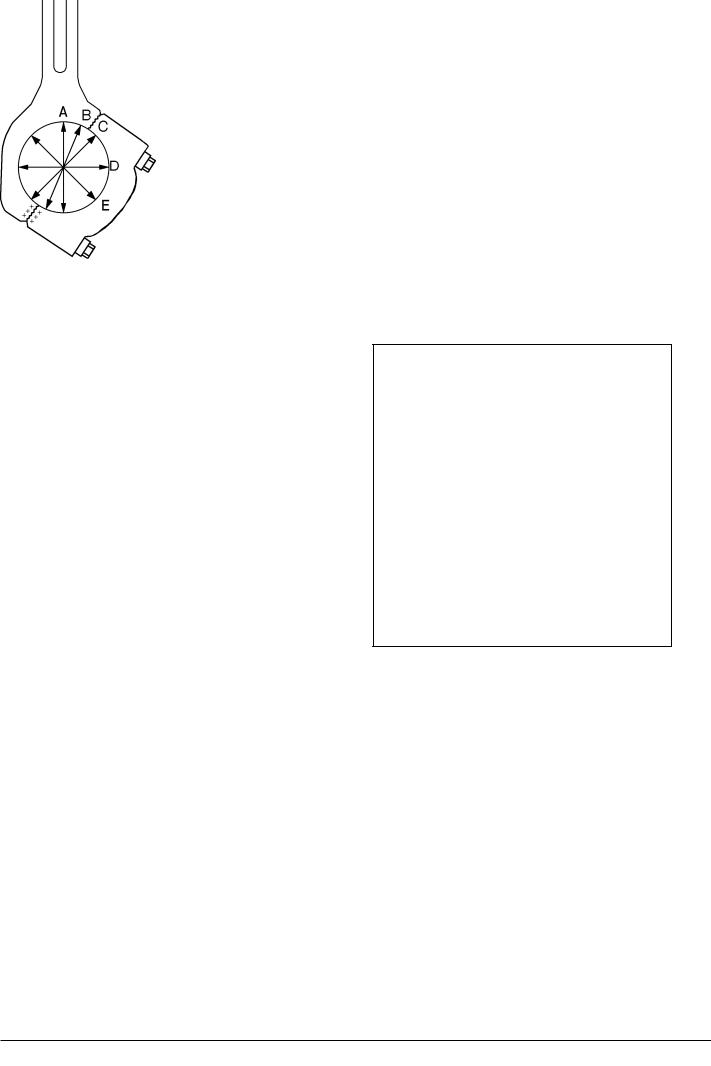
3)Turn the crankshaft to bring the crank throw concerned into a position of approx. 50 degrees before TDC.
This position is identifiable by the connecting rod shaft being very close to the cylinder liner shirt, see fig. 1.
4)Clean the threaded hole in the piston top, and mount the eye screw.
5)Mount the tube (for holding down the cylinder liner during the piston withdrawal) on one of the cylinder head studs, screw on the nut and tighten it slightly.
6)Attach a wire rope to the eye bolt by means of a shackle, hook the wire on to a tackle and pull the wire rope tight.
Note! If minor adjustments of the crank throw position appear necessary for access to the connecting rod screws, the wire rope must be slackened before turning of the crankshaft and tightened up again in the new crank throw position.
08028-0D/H5250/94.08.12
Fig 1. Mounting of tools (placing). |
Fig 2. Removal of bearing cap. |
96.20 - ES0S