ИТиУвТС / ИТиПСУ_Контрольная
.docxУЧРЕЖДЕНИЕ ОБРАЗОВАНИЯ
Белорусский Государственный Университет Информатики и Радиоэлектроники
Кафедра систем управления
Контрольная работа
по дисциплине «ИТиПСУ»
Вариант №6
Выполнил:
Студент ФЗВиДО, БГУИР
Специальности ИТиУвТС
Группы 602421c
Попов Л. А.
Минск 2009
Лабораторная работа №1. Класс «Двухмерный динамический массив».
#include <iostream.h>
void main(void)
{
int row, col, n;
int i=0, j;
cout << "Vvedite kol ctolbcov i strok: ";
cin >> row >> col;
int **a = new int *[row];
for (i; i<row; i++)
a[i] = new int [col];
for (i=0; i<row; i++)
for (j=0; j<col; j++)
cin >> a[i][j];
cout << "Ishodnii massiv: \n";
for (i=0; i<row; i++)
{
for (j=0; j<col; j++)
cout << a[i][j] << " ";
cout << "\n";
}
for (i=0; i<row; i++) {
for (j=0; j<col; j++) {
if (a[i][j]<0)
continue;
if (a[i][j]>0)
n = i+1;
}
if (n>0) {
cout << n;
break; }
}
cout << "\n\n";
for (i=0; i<row; i++)
delete a[i];
delete a;
}

Лабораторная работа №2. Класс «Динамическая строка» и перегрузка операций.
#include <iostream.h>
#define SIZE 255
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <istream.h>
class X{
char *str;
char *str_return;
public:
X();
X(char*);
~X();
char* Run();
void Set(char*);
friend void print(X&);
friend ostream& operator<<(ostream&,X&);
friend istream& operator>>(istream&,X&);
friend char* Run(X&);
};
X::X(){
str=new char[SIZE];
str[0]='\0';
str_return=new char[SIZE];
str_return[0]='\0';
};
X::X(char *s){
str=new char[SIZE];
strcpy(str,s);
str_return=new char[SIZE];
str_return[0]='\0';
};
X::~X(){
delete[] str;
cout<<"...destructor has been called"<<endl;
};
void X::Set(char* s){
for (unsigned int i=0;i<strlen(s);i++)
str[i]=s[i];
str[i]='\0';
};
char* X::Run(){
int j=0;
if (strlen(str)>15) {
for (unsigned int i=0;i<strlen(str);i++)
if ( ((int)str[i]!=40) && ((int)str[i]!=41) && ((int)str[i]!=91) && ((int)str[i]!=93) && ((int)str[i]!=123) && ((int)str[i]!=125)) {
str_return[j]=str[i]; j++;
};
str_return[j]='\0';
}
else strcpy(str_return,str);
return str_return;
};
char* Run(X &obj){return obj.Run();};
void print(X &obj){cout<<obj.str<<" "<<obj.str_return<<endl;};
ostream& operator<<(ostream &stream,X &ob) {
stream << ob.str ;
return stream;
};
istream &operator>>(istream &stream,X &ob){
stream >> ob.str;
return stream;
};
void main (void){
char s[265];
cout<<"Type anything and press \"Enter\":"<<endl;
cin.getline(s,256);
X str(s);
cout<<"You have type:"<<endl;
print(str);
cout<<"Output string:"<<endl;
cout<<Run(str)<<endl;
cout<<"Type anything and press \"Enter\":"<<endl;
cin.getline(s,256);
X *pstr;
pstr=new X();
pstr->Set(s);
cout<<"You have type:"<<endl;
print(*pstr);
cout<<"Output string:"<<endl;
cout<<Run(*pstr)<<endl;
delete pstr;
};

Лабораторная работа №3. Иерархия классов. Механизм виртуальных функций.
#include <iostream.h>
class X{
protected:
int *x1,*x2;
public:
X(int a, int b)
{x1=new int;
x2=new int;
*x1=a;
*x2=b;};
~X()
{ delete x1;
delete x2;};
virtual void show(void)
{ cout<<"x1="<<*x1<<", x2="<<*x2<<"."<<endl<<endl;};
virtual void set(int a, int b)
{ *x1=a;
*x2=b;};
};
class Y: public X{
protected:
int *y;
public:
Y(int a, int b, int c): X(a,b)
{ y=new int;
*y=c;};
~Y(){ delete y;};
void show(void)
{ cout<<"x1="<<*x1<<", x2="<<*x2<<", y="<<*y<<"."<<endl<<endl;};
virtual void set(int a, int b, int c)
{ *x1=a;
*x2=b;
*y=c;};
void Run(void)
{double x=*x1; cout<<"(x1+x2)*y="<<((x)+(*x2))*(*y)<<endl<<endl;};
};
void main(void)
{
Y *com= new Y(1,2,3);
com->show();
com->Run();
com->set(4,5,6);
com->show();
com->Run();
cout<<"===================="<<endl;
Y p(7,8,9);
p.show();
p.Run();
p.set(9,8,7);
p.show();
p.Run();
cout<<"===================="<<endl;
Y *p2;
p2=&p;
p2->set(6,5,4);
p2->show();
p2->Run();
p2->set(3,2,1);
p2->show();
p2->Run();
delete com;
}

Лабораторная работа №4. Шаблоны классов.
#include <iostream.h>
#include <math.h>
template <class Type> class Tarr {
Type* ad;
int size;
public:
Tarr(int);
~Tarr();
Type* Run();
void Set(Type a,int in);
Type Get(int in);};
template<class Type> Tarr<Type>::Tarr(int n){
size=n;
ad=new Type[n];};
template<class Type> Tarr<Type>::~Tarr(){delete[] ad;};
template<class Type> Type* Tarr<Type>::Run(){
//size-=2;
Type *result=new Type[size];
for (int i=0;i<size;i++)result[i]=ad[i]+(i+1);
return result;};
template<class Type> void Tarr<Type>::Set(Type a,int in){ad[in]=a;};
template<class Type> Type Tarr<Type>::Get(int in){return ad[in];};
void main(){
int n;
cout<<"Vvedite koli4estvo elementov massiva"<<endl;cin>>n;
Tarr<int> aray(n);
Tarr<double> arayD(n);
Tarr<char> arayC(n);
cout<<endl<<"Vvedite massiv celyh elementov"<<endl;
for (int i=0;i<n;i++){
int t;
cin>>t;
aray.Set(t,i);}
cout<<endl<<" Massiv:"<<endl;
for (i=0;i<n;i++)cout<<" "<<aray.Get(i);
cout<<endl;
int *tt=aray.Run();
cout<<endl<<" Rezul'tat:"<<endl;
for (i=0;i<n;i++)cout<<" "<<tt[i];
cout<<endl;
cout<<endl<<"Vvedite massiv drobnyh elementov"<<endl;
for (i=0;i<n;i++){
double t;
cin>>t;
arayD.Set(t,i);}
cout<<endl<<" Massiv:"<<endl;
for (i=0;i<n;i++)cout<<" "<<arayD.Get(i);
cout<<endl;
double *tD=arayD.Run();
cout<<endl<<" Rezul'tat:"<<endl;
for (i=0;i<n;i++)cout<<" "<<tD[i];
cout<<endl;
cout<<endl<<"Vvedite massiv simvolov elementov"<<endl;
for (i=0;i<n;i++){
char t;
cin>>t;
arayC.Set(t,i);}
cout<<endl<<" Massiv:"<<endl;
for (i=0;i<n;i++)cout<<" "<<arayC.Get(i);
cout<<endl;
char *tC=arayC.Run();
cout<<endl<<" Rezul'tat:"<<endl;
for (i=0;i<n;i++)cout<<" "<<tC[i];
cout<<endl;
}

Лабораторная работа №5. Обработка исключительных ситуаций.
#include <iostream.h>
#include <conio.h>
#include <math.h>
float Z1(float&, float&);
float Z2(float&, float&);
void main(void)
{
float m, n, z1, z2;
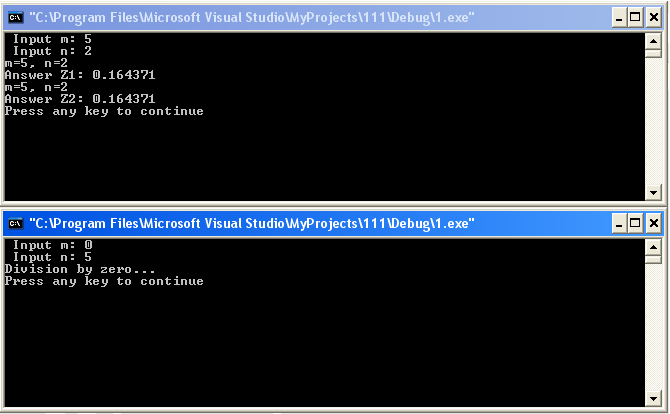
cout << " Input m: "; cin >> m;
cout << " Input n: "; cin >> n;
try
{
z1=Z1(m,n);
cout << "m=" << m << ", n=" << n << "\n";
cout << "Answer Z1: " << z1 << "\n";
z2=Z2(m,n);
cout << "m=" << m << ", n=" << n << "\n";
cout << "Answer Z2: " << z2 << "\n";
}
catch (float x)
{
cout << "Division by zero..." << "\n";
}
}
float Z1(float& m1, float& n1)
{
if (m1==0) throw m1;
return ((m1-1)*sqrt(m1)-(n1-1)*sqrt(n1))/(sqrt(pow(m1,3)*n1)+n1*m1+m1*m1-m1);
}
float Z2(float& m2, float& n2)
{
if (m2==0) throw m2;
return (sqrt(m2)-sqrt(n2))/m2;
}