
- •Midterm exam in microeconomics (November, 2006)
- •If average quality of Washington wines increases then the demand for these wines goes up which in turn leads to the increase in price of these wines
- •Income growth will result in the decrease in demand for inferior goods.
- •If either demand or supply is perfectly inelastic (corresponding curve is vertical) then imposition of a per-unit tax will have no effect on the equilibrium quantity.
- •15% Price increase results in 30% decrease in the quantity demanded, while the 10% increase in income results in 30% increase in the quantity demanded. Thus these two effects compensate each other.
- •If the share of income spent on a good does not depend on income then 1% increase in income leads to 1% increase in spending on that good, thus the income elasticity is 1.
- •For Brockway’s, computer equipment and supplies are normal goods
- •Negative
- •Complements
- •When consumers receive an increase in their income, they spend less money on inferior goods
- •The ratio of the price of the good listed on the horizontal axis to that of the good on the vertical axis
- •It could be shown using simple formal derivation.
- •As the price of oranges decreased, the consumer consumed more oranges
- •I) This reflects the movement along the demand curve
- •II) An increase in the price of a substitute will lead to the increase in the demand for X and consequently shift the demand curve to the right
- •If the good is not a Giffen good then fall in the price of that good must result in the increase of consumption of that good
- •47. According to the law of diminishing returns, what will happen if all inputs increase k times?
- •The law of diminishing returns says nothing about it.
- •If marginal cost is negative then the increase in production leads to the decrease in the total costs, thus at current output costs are not minimized
- •I) For any level of output costs in the short-run can not be lower than costs in the long run because in the long run firm has more opportunities to lower costs.
- •II) There is no variable-fixed costs classification in the long run
Midterm exam in microeconomics (November, 2006)
Section 1. Multiple Choice Questions
Marking scheme: 1 point for a correct answer, -0.25 for a wrong answer, 0 if the answer has not been given.
1. Which of the following involves a tradeoff?
A) Going to college.
B) Buying a new car.
C) Watching a football game on Friday night.
D) Searching for a new boyfriend or girlfriend.
E) All of the above.
All of the situations explained above undermine making a choice given scarce or limited resources, choosing one of several alternatives
2. The figure below depicts the production possibilities frontier for a country that can produce only clothes and food. What could be said about points A, B and C on this figure?
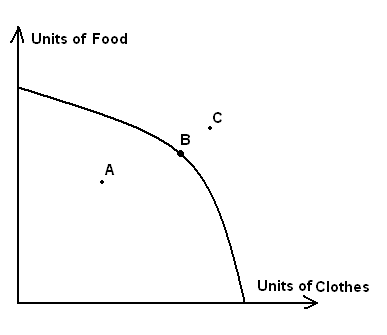
A) Points A and C are unattainable; point B is attainable and efficient
B) Point A and C are efficient, but point C is unattainable
C) Only point B is attainable and efficient
D) Both A and B are attainable and efficient
E) None of the above
Only point B is attainable and efficient, other points either not attainable or not efficient
3. In 2005 there was an excellent weather in the State of Washington. In 2006 it is known that the average quality of Washington State wines is higher than usual. The average quality of California wines does not change. Hence in 2006:
A) California wines should increase in price, and the number of bottles sold should decrease;
B) California wines should decrease in price, and the number of bottles sold should increase;
C) California wines should increase in price, and the number of bottles sold should increase;
D) Washington State wines should increase in price, and the number of bottles sold should increase.
E) None of the above.
If average quality of Washington wines increases then the demand for these wines goes up which in turn leads to the increase in price of these wines
4. Due to a large crop, the price of grapes falls in California:
A) California wines should increase in price, and the number of bottles sold should decrease;
B) California wines should decrease in price, and the number of bottles sold should increase;
C) California wines should decrease in price, and the number of bottles sold should decrease;
D) California wines should increase in price, and the number of bottles sold should increase;
E) None of the above.
The direct outcome of the large crop is the increase in supply of the California wines so the price is expected to fall and quantity sold decrease
5. Coal is used as a fuel at a power station. An increase in coal price will eventually result in:
A) An increase in quantity demanded for electricity.
B) A reduction in quantity demanded for electricity.
C) A reduction in demand for electricity.
D) An increase in supply of electricity.
E) None of the above.
Coal price increase will lead to the decrease of the electricity supply (because coal is the input of electricity production) which will in turn lead to the growth of electricity prices and thus fall in quantity demanded
6. Geometrically, consumer surplus equals the area beneath the:
A) demand curve and above the price;
B) price and above the demand curve;
C) price and above the supply curve;
D) demand curve;
E) more than one answer above is correct.
Each unit consumed contribute to the consumer surplus the difference between the maximum price which consumers are ready to pay for that unit and the market price for which that unit was bought.
7. Suppose that the supply curve for taxi rides slopes up and the demand curve slopes down. If the market equilibrium fare is $1 per mile, a ceiling of 80 cents per mile will surely result in:
A) a gain in consumer surplus;
B) a loss in producer surplus.
C) a loss in consumer surplus.
D) deadweight loss.
E) more than one answer is correct.
Price ceiling for sure results in a decrease in producer surplus (due to price decrease) and in deadweight loss (because output is different from free market equilibrium), so the correct answer is E (B+D)
8. In New York city the demand curve for rental apartments slopes down while the supply is absolutely inelastic. If the current equilibrium rental price is $10000 per apartment, a ceiling of $5000 per apartment will result in:
A) a surplus of apartments;
B) a decrease in the quantity demanded;
C) an increase in the quantity supplied;
D) no change in the quantity demanded or the quantity supplied;
E) none of the above.
Effective price ceiling leads to increase in quantity demanded, decrease in the quantity supplied, which in turn results in shortages ( Qd > Qs ).
9. Suppose that a per unit tax is imposed on the suppliers of a good and its supply curve is upward sloping. If the price elasticity of demand for the good is zero, the tax will:
A) increase the equilibrium price of the good;
B) reduce the equilibrium price of the good;
C) reduce the equilibrium quantity of the good;
D) increase the equilibrium quantity of the good;
E) both (A) and (C).
Zero price elasticity of demand means that the demand curve is vertical (quantity demanded does not depend on price). Thus increase in supply due to the imposition of tax will only result in the price increase.
10. Which of the following can cause a decrease in the demand for a good?
A) Increase in price of that good
B) Decrease in quantity supplied
C) Increase production inputs’ price
D) Increase in the price of its substitutes
E) Income growth
