
- •Language work: Articles
- •Listening
- •What can computers do?
- •Language work: The Present Simple Passive
- •Living with computers
- •Other applications
- •In pairs, discuss the elements of a simple computer system.
- •Read the text, translate it and get ready to do the exercises after the text.
- •Unit 3 Types of computer system reading material
- •Study in the table the details of different types of computer.
- •Find the answers to these questions. Which type of computer is:
- •From mainframes to wearable computers
- •Language work: Comparison
- •Aids to communication
- •Problem-solving
- •Writing
- •Language work: Compound Adjectives
- •Wearable computers, aren’t they chic?
- •Inside the system reading material
- •What's inside a pc system?
- •Language work: Relative Clauses
- •Vocabulary quiz
- •Processors and memory.
- •Your ideal computer system
- •Unit 5 units of memory reading material
- •Bits - basic units of memory
- •Bytes and characters
- •The ascii code
- •Kilobytes, megabytes and gigabytes
- •Word building
- •Bits for pictures
- •Buying a computer.
- •Input devices-1 reading material
- •Work in pairs.
- •About the keyboard
- •The mouse
- •Voice input
- •Input devices-2 reading material
- •Word building
- •Language work: Instructions and Advice
- •Unit 10 magnetic drives
- •Technical details
- •World building
- •What are the advantages and disadvantages of optical disks?
- •Read the text to check your answer.
- •Connectors and modifiers
- •Products available
- •Iomega's removable drives
- •Unit 12 operatung systems and database sytems reading material
- •What is the function of os?
- •How many parts does it consist of?
- •Operating Systems
- •Language work: Countable and Uncountable Nouns
- •Systems Programs and Databases
- •Writing
- •Unit 13 The Graphical User Interface reading material
- •Language work: The Passive Voice (Present, Past)
- •Writing
- •Graphics and design
- •Writing
- •Unit 14 Word-processing facilities reading material
- •Word-processing facilities
- •Language Work: -ing forms
- •Unit 15 Databases reading material
- •Basic features of database programs
- •Unit 16 faces of the internet
- •Internet software
- •Irc, audio and video chatting
- •Unit 17 Programming languages reading material
- •Algorithm
- •Flowchat
- •Programming languages
- •Language work: Infinitive constructions.
- •Make a list of as many computer languages as you can think of.
- •Language work: The passive
- •A short description of Visual Basic
- •What is Java?
- •Language work: The Past Simple
- •Read the text and do the following exercises.
- •Support
- •Charles Graham
- •Language work: Past Activities.
- •Animator
- •Video game creator
- •Network security administrator
- •Webmaster
- •Unit 20 Electronic communications reading material
- •How can a pc be connected to another computer?
- •What data communication systems can you think of? Make a list.
- •Channels of communication
- •Word building: Prefixes
- •If you are not sure, look them up in a dictionary.
- •Unit 21
- •Internet issues reading material
- •Security and privacy on the Internet
- •Security on the Web
- •Network security
- •Virus protection
- •Preventative tips
- •Internet security
- •Internet crime
- •Hackers!
- •Language work: The Past Simple (revision)
- •Unit 22 laNs and waNs reading material
- •Network configurations
- •Language work: Predicting Consequences
- •WaNs and worldwide communications
- •Read the following text.
- •Mobile phones: definition and technology
- •A brief history
- •Features and functions
Other applications
Ex. 1. In small groups, choose one of the areas in the diagram below and discuss what computers can do in this area.
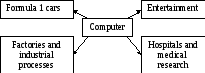
Useful words
Formula 1: racing car, car body, design, mechanical parts, electronic components, engine speed
Entertainment: game, music, animated image, multimedia, encyclopedia
Factories: machinery, robot, production line, computer-aided manufacturing software
Hospitals: patients, medical personnel, database program, records, scanner, diagnose, disease, robot, surgery
Useful constructions
Computers are used to ...
A PC can also be used for...
Computers can help ... make ... control... store ... keep ... provide ... manage ... give ... perform ... measure ... test... provide access to ...
Ex. 2. Now write a short paragraph summarizing your discussion. Then ask one person from your group to give a summary of the group's ideas to the rest of the class.
Examples In business, computers are used for financial planning, accounting and specific calculations.
In the office, computers are used to write letters and e-mails, and keep records of clients, suppliers and employees.
Unit 2
Computer essentials
READING MATERIAL
T E X T A
Task
-
In pairs, discuss the elements of a simple computer system.
-
Read the text, translate it and get ready to do the exercises after the text.
What is a computer?
Computers are electronic machines which can accept data in a certain form, process the data and give the results of the processing in a specified format as information.
Three basic steps are involved in the process. First, data is fed into the computer's memory. Then, when the program is run, the computer performs a set of instructions and processes the data. Finally, we can see the results (the output) on the screen or in printed form.
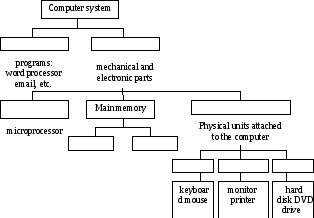
Information in the form of data and programs is known as software, and the electronic and mechanical parts that make up a computer system are called hardware. A standard computer system consists of three main sections: the central processing Unit (CPU), the main memory and the peripherals.
Perhaps the most influential component is the central processing unit. Its function is to execute program instructions and coordinate the activities of all the other units. In a way, it is the 'brain' of the computer. The main memory holds the instructions and data which are currently being processed by the CPU. It has two main sections: RAM (random access memory) and ROM (read only memory). The peripherals are the physical units attached to the computer. They include storage devices and input/output devices.
Storage devices (floppy, hard or optical disks) provide a permanent storage of both data and programs. Disk drives are used to handle one or more floppy disks. Input devices enable data to go into the computer's memory. The most common input devices are the mouse and the keyboard. Output devices enable us to extract the finished product from the system. For example, the computer shows the output on the monitor or prints the results onto paper by means of a printer.
On the rear panel of the computer there are several ports into which we can plug a wide range of peripherals – modems, fax machines, optical drives and scanners.
These are the main physical units of a computer system, generally known as the configuration
Ex. 1. Use the information in the text to help you match the terms in the box with the appropriate explanation or definition below.
|
a. software b. peripheral devices с. monitor d. floppy disk e. hardware f. input g. port h. output i. central processing unit j. speaker k. CD/DVD drive |
11.Mechanism that reads and/or writes to optical discs. |
Ex. 2. Read these slogans or quotations, and say what computer element they refer to.
1. a) “Point and click here for power.”
b) “Right click to display a context-sensitive menu.”
2. a) “Displays your ideas with perfect brilliance.”
b) “See the difference – sharp images and a fantastic range of colours.”
3. a) “I love this drive. It's quiet and fast.”
b) “With this it's easy to back up your data before it's too late.”
4. a) “Power and speed on the inside.”
b) “Let your computer's brain do the work.”
5. a) … a big impact on the production of text and graphics.”
b) “This will produce high-quality output, with sharp text and impressive graphics.”
6. a) “Press any key to continue.”
b) They consist of flexible plastic material.
Ex. 3. Answer these questions.
-
Have you got a computer at home, school or work? What kind is it?
-
How often do you use it? What do you use it for?
-
What are the main components and features (the configuration) of your computer system?
Ex. 4. Label this diagram with the correct terms.
Ex. 5. Complete the sentences below with the following words: storage, output, input, processing.
-
Computer … is the visible or audible result of data processing – information that can be read, printed or heard by the user.
-
The CPU will process data as instructed by the programs you're running. … includes functions like calculating, sorting, editing, drawing and searching.
-
DVDs are expected to replace CDs as … devices.
-
As a scanner, the Sigma-100 can be used to … photographs as well as documents into the computer.
