
- •Boeing 787-8 Dreamliner: Fact Sheet
- •Text 2.
- •The dynamics of airplane flight
- •How Wings Lift the Plane
- •Laws of Motion
- •Controlling the Flight of a Plane
- •How does a Pilot Control the Plane?
- •Regimes of Flight
- •Text 3.
- •Types of Aircraft
- •Text 4. Aircraft Performance
- •Unit 1.5. Aircraft Ground Handling and Maintenance Text 1.
- •Text 2.
Aviation Basics
Exercise 2. Use the fact sheet provided below to compare Boeing 787-8 Dreamliner to any other airplane of your choice belonging to another airplane manufacturer.
Boeing 787-8 Dreamliner: Fact Sheet
Brief Description: The Boeing 787-8 Dreamliner is a superefficient airplane with new passenger-pleasing features. It will bring the economics of large jet transports to the middle of the market, using 20 percent less fuel than any other airplane of its size.
Seating: 210 to 250 passengers
Range: 7,650 to 8,200 nautical miles
(14,200 to 15,200 kilometers)
Configuration: Twin aisle
Cross Section: 226 inches (574 cm)
Wing Span: 197 feet (60 meters)
Length: 186 feet (57 meters)
Height: 56 feet (17 meters)
Cruise Speed: Mach 0.85
Total Cargo Volume: 4,400 cubic feet
Maximum Takeoff Weight: 502,500 pounds (227,930 kg)
Exercise 3. Translate into English:
Boeing 787 Dreamliner ("Лайнер мрії") — широкофюзеляжний двомоторний реактивний пасажирський літак, що розробляється американською компанією Boeing, перший повністю новий літак Boeing після випуску Boeing 777 в 1995 році. Місткість салону лайнера складає 210-330 чоловік залежно від модифікації. Максимальна дальність польоту літака складає 14,2 тисячі кілометрів. Відмітними особливостями нового лайнера повинні стати економічність і екологічність. "Лайнер мрії" повинен витрачати на 20 відсотків менше пального при дальніх перельотах. Boeing 787, вартість якого залежно від комплектації доходить до 205,5 мільйонів доларів, ще до випуску замовили понад півсотні авіакомпаній. Першим "Лайнер мрії" повинна отримати японська авіакомпанія All Nippon Airways. Передбачається, що парк японського авіаперевізника поповниться новим літаком в кінці 2010 року. На даний момент, Боїнг пропонує три варіанти авіалайнера. 787-3 - 296-місцевий варіант з дальністю 6500 км, розрахований для завантажених маршрутів малої протяжності. Цей варіант замінить Боїнги 767 і Аеробуси А300 на внутрішніх рейсах Японії. Початок постачання – 2010 рік. Вартість - $146-151,5 млн. 787-8 - базовий варіант, розрахований як заміна Боїнгу 767-300ER. Вміщає до 250 пасажирів (залежно від конфігурації), дальність – 15 700 км. Вартість - $157-167 млн. 787-9 - Подовжений варіант, що вміщає до 290 з трохи більшою дальністю в порівнянні 787-8. Вартість - $189-200 млн.
Exercise 4. Write a report about aviation companies of the world, main aircraft manufacturers. Be ready to present it in class. Your report should be brief and contain two sections (see below). Take care to get some pictures!
Section one - "Aviation companies of the world":
-
General information on the company
-
Its main activities
-
Its aircraft fleet
Section two - "Main aircraft manufacturers":
-
General information on the manufacturer
-
Its main activities
Unit 1.4. Aircraft Structural Units
Text 1
R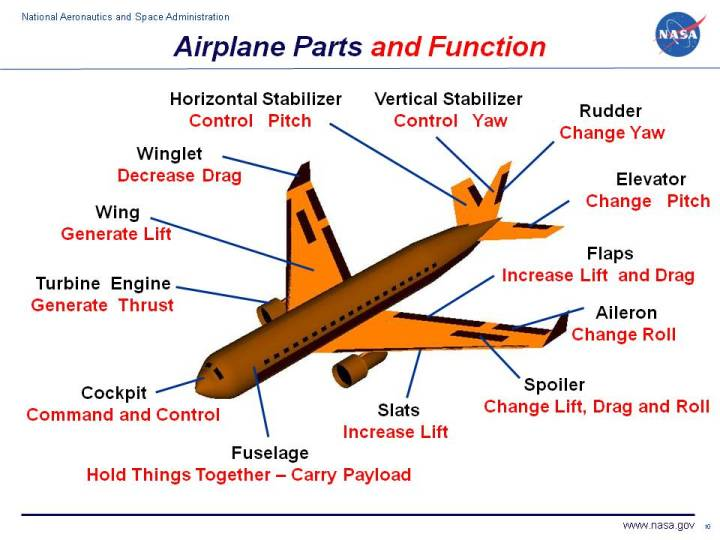 ead
and translate the following text into Ukrainian.
ead
and translate the following text into Ukrainian.
The Parts of an Airplane
Introduction to the Airplane
Airplanes come in many different shapes and sizes depending on the mission of the aircraft, but all modern airplanes have certain components in common. These are the fuselage, wing, tail assembly and control surfaces, landing gear, and powerplant(s).
For any airplane to fly, it must be able to lift the weight of the airplane, its fuel, the passengers, and the cargo. The wings generate most of the lift to hold the plane in the air. To generate lift, the airplane must be pushed through the air. The engines, which are usually located beneath the wings, provide the thrust to push the airplane forward through the air.
The fuselage is the body of the airplane that holds all the pieces of the aircraft together and many of the other large components are attached to it. The fuselage is generally streamlined as much as possible to reduce drag. Designs for fuselages vary widely. The fuselage houses the cockpit where the pilot and flight crew sit and it provides areas for passengers and cargo. It may also carry armaments of various sorts. Some aircraft carry fuel in the fuselage; others carry the fuel in the wings. In addition, an engine may be housed in the fuselage.
The wing provides the principal lifting force of an airplane. Lift is obtained from the dynamic action of the wing with respect to the air. The cross-sectional shape of the wing as viewed from the side is known as the airfoil section. The planform shape of the wing (the shape of the wing as viewed from above) and placement of the wing on the fuselage (including the angle of incidence), as well as the airfoil section shape, depend upon the airplane mission and the best compromise necessary in the overall airplane design.
The control surfaces include all those moving surfaces of an airplane used for attitude, lift, and drag control. They include the tail assembly, the structures at the rear of the airplane that serve to control and maneuver the aircraft and structures forming part of and attached to the wing.
The tail usually has a fixed horizontal piece (called the horizontal stabilizer) and a fixed vertical piece (called the vertical stabilizer). The stabilizers provide stability for the aircraft—they keep it flying straight. The vertical stabilizer keeps the nose of the plane from swinging from side to side (called yaw), while the horizontal stabilizer prevents an up-and-down motion of the nose (called pitch). (On the Wright brothers' first successful aircraft, the horizontal stabilizer was placed in front of the wings. Such a configuration is called a canard after the French word for "duck").
The hinged part found on the trailing edge of the wing is called the aileron. It is used to roll the wings from side to side. Flaps are hinged or pivoted parts of the leading and/or trailing edges of the wing used to increase lift at reduced airspeeds, primarily at landing and takeoff. Spoilers are devices used to disrupt the airflow over the wing so as to reduce the lift on an airplane wing quickly. By operating independently on each wing, they may provide an alternate form of roll control. Slats at the front part of the wing are used at takeoff and landing to produce additional lift.
At the rear of both the aileron surfaces and elevators and rudders are small moving sections called trim tabs that are attached by hinges. Their function is to (1) balance the airplane if it is too nose heavy, tail heavy, or wing heavy to fly in a stable cruise condition; (2) maintain the elevator, rudder, and ailerons at whatever setting the pilot wishes without the pilot maintaining pressure on the controls; and (3) help move the elevators, rudder, and ailerons and thus relieve the pilot of the effort necessary to move the surfaces.
The landing gear, or undercarriage, supports the airplane when it is resting on the ground or in water and during the takeoff and landing. The gear may be fixed or retractable. The wheels of most airplanes are attached to shock-absorbing struts that use oil or air to cushion the blow of landing. Special types of landing gear include skis for snow and floats for water. For carrier landings, arrester hooks are used.
Forward motion, or thrust, is generated by a thrust-producing device or powerplant to sustain flight. The powerplant consists of the engine (and propeller, if present) and the related accessories. The main engine types are the reciprocating (or piston type), and the reaction, or jet, engine such as the ram jet, pulse jet, turbojet, turboprop, and rocket engine. The propeller converts the energy of a reciprocating engine's rotating crankshaft into a thrust force. Usually the engines are located in cowled pods hung beneath the wings, but some aircraft, like fighter aircraft, will have the engines buried in the fuselage.
Other configurations have sometime been used. For instance, the Wright brothers' 1903 Flyer had pusher propellers (propellers at the rear of the plane) and the elevators at the front of the aircraft. Many fighter aircraft also combine the horizontal stabilizer and elevator into a single stabilator surface. There are many possible aircraft configurations, but any configuration must provide for the four forces needed for flight.
Exercise 1. Transcribe the following words and word combinations:
Landing gear, airfoil section, control surfaces, vertical stabilizer, aileron, flaps, spoilers, turboprop, propellers, trim tabs.
Exercise 2. Answer the following questions:
1. What are the main components of the airplane?
2. What are the functions of the airplane?
3. Where do aircrafts carry fuel?
4. What includes all those moving surfaces of an airplane?
5. How does stabilizer keep the nose of the plane from swinging from side to side?
6. Why do spoilers use to disrupt the airflow over the wing?
7. What is a function of trim tabs?
8. When does the landing gear support the airplane?
9. What are the main engine types?
10. What must provide configuration for?
Exercise 3. Finish the sentences:
1. … generate most of the lift to hold the plane in the air.
2. The engines, which are usually located beneath the wings, provide …
3. They include the tail assembly, the structures at the rear of the airplane that...
4. The vertical stabilizer keeps the nose of...
5. … or pivoted parts of the leading and/or trailing edges of the wing used to increase lift at reduced airspeeds, primarily at landing and takeoff.
6. Spoilers are devices used to disrupt the airflow over the wing so as …
7. … called trim tabs that are attached by hinges.
8. The wheels of most airplanes are …
9. The main engine types are …
10. … combine the horizontal stabilizer and elevator into a single stabilator surface
Exercise 4. Match the word to the appropriate definition.
|
1. spoilers |
A) a part along the back edge of an aircraft's wing which can be moved to help the aircraft turn or to keep it level |
|
2. engine |
B) a device which helps an aircraft, ship or vehicle to balance |
|
3. landing gear |
C) a flat piece of wood or metal at the back of a boat or aircraft, which is moved from side to side in order to control the direction of travel |
|
4. fuselage |
D) If an aircraft or ship yaws, it moves slightly to the side of its intended direction |
|
5. stabilizer |
E) a device on a car or aircraft which is positioned so that it stops the air from flowing around the vehicle in a smooth way and so helps to control it |
|
6. yaw |
F) the main body of an aircraft |
|
7. aileron |
G) the set of wheels and other parts which support a plane when it is on the ground and make it possible to take off and land |
|
8. flap |
H) part of the back of an aircraft wing which can be moved up or down to help the aircraft go up or down |
|
9. wing |
I) a machine that uses the energy from liquid fuel or steam to produce movement |
|
10. rudder |
J) the flat part of the body which a bird, insect or bat uses for flying, or one of the flat horizontal structures that stick out from the side of an aircraft and support it when it is flying |
Exercise 5. Offer all possible ways of translation the following sentences:
-
The hinged part found on the trailing edge of the wing is called the aileron.
-
The human activity which surrounds aircraft is called aviation.
-
Aircraft may be classified by different criteria, such as lift type, propulsion, usage and others.
-
The airframe of an aircraft is its mechanical structure, which is typically considered to exclude the propulsion system
-
Typically wheels are used, but skids, floats or a combination of these and other elements can be deployed, depending on the surface.
-
The fuselage also serves to position control and stabilization surfaces in specific relationships to lifting surfaces, required for aircraft stability and maneuverability.
-
The common wing configuration types have included monoplanes which has one wing each side, biplane which have 4 wings.
-
Aircraft engines are almost always either lightweight piston engines or gas turbines.
-
An aircraft cabin is the section of an aircraft in which any passengers travel, often just called the cabin.
-
The empennage is also known as the tail or tail assembly; all three terms may be used interchangeably.
Exercise 6. Translate into Ukrainian.
-
The cross-sectional shape of the wing as viewed from the side is known as the airfoil section.
-
Flaps are hinged or pivoted parts of the leading and trailing edges of the wing used to increase lift at reduced airspeeds, primarily at landing and takeoff.
-
The power plant consists of the engine and the related accessories.
-
On powered aircraft, one or more aircraft engines are propulsion units that provide thrust to push the aircraft forward through the air.
-
A wing with an airfoil cross-section shape, used to generate aerodynamic lifting force to support the aircraft in flight by deflecting air downward as the aircraft moves forward.
-
The horizontal stabiliser (also known as tailplane) is usually mounted near the rear of the fuselage, or at the top of the vertical stabiliser, or sometimes a canard is mounted near the front of the fuselage for the same purpose.
-
A fixed-wing aircraft, typically called an aeroplane, airplane or simply plane, is an aircraft capable of flight using forward motion that generates lift as the wing moves through the air.
-
Most fixed-wing aircraft are flown by a pilot on board the aircraft, but some are designed to be remotely or computer controlled.
-
Planes include jet engine and propeller driven vehicles propelled forward by thrust, as well as unpowered aircraft (such as gliders), which use thermals, or warm-air pockets to inherit lift.
-
The fuselage carries the human flight crew if the aircraft is piloted, the passengers if the aircraft is a passenger aircraft, other cargo or payload, and engines and/or fuel if the aircraft is so equipped.
Exercise 7. Fill in the correct word / word combination (from the box below).
|
range takeoff equipment distance aircraft maximal powered landing extra fuel tanks maximal |
The _______total range is the _________an aircraft can fly between _______and________, as limited by fuel capacity in __________aircraft, or cross-country speed and environmental conditions in unpowered aircraft.
______ range means the maximum ______the aircraft can fly. This usually means maximum fuel load, optionally with ______________ and minimum__________. It refers to transport of _______for use on remote location.
Exercise 8. Write the correct form of the word in brackets and complete the sentences.
International commercial air travel (reach) levels of safety and convenience which (be unimaginable) just a generation ago. Although almost always extremely tragic events, the lessons from accidents (play) an important role in the process (continue) (improve) this safety.
This Lessons Learned from Aviation Accidents library (represent) some of the most major accidents and their (relate) lessons. The U. S. Federal Aviation Administration, with support from many others, (plan) to continue adding to this material on an annual basis. The (object) is (populate) the material with many more of the most historically significant, policy shaping accidents, in order that the lessons that can be learned from their review may be available to all users of the library.
Exercise 9. Say whether the following statements are true or false. Correct false statements.
-
Airplanes come in many different shapes and sizes depending on the mission of the aircraft.
-
The wings generate most of the lift to hold the plane in the ground.
-
The fuselage is generally streamlined as much as possible to increase drag.
-
The wing provides the principal lifting force of an airplane.
-
They include the tail assembly, the structures at the rear of the airplane that serve to control and maneuver the engine.
-
Spoilers are devices used to disrupt the airflow over the wing so as to reduce the lift on an airplane wing quickly.
-
At the rear of both the aileron surfaces and elevators and rudders are small moving sections called spoilers that are attached by hinges.
-
The hinged part found on the trailing edge of the wing is called the fuselage.
-
The gear may be fixed or retractable.
-
There is one aircraft configuration.
Exercise 10. Have a look at the following text. It contains a number of mistakes and inaccuracies. Act as a proofreader and rewrite the sentences in accord with the rules of style, grammar and word combinability.
|
Covert tests reveal airport screening failure Undercover tests of aviation screening operations revealed widespread problems, raising concerns that explosives and weapons could get into airport sterile areas and checked baggage systems, the Homeland Security Department's inspector general said Wednesday. Covert tests of the Transportation Security Administration's screeners and equipment were conducted at hundreds of airports across the country from July to November 2003. The bulk of the report remains classified, but an eight-page summary was released Wednesday. The report is based on interviews with employees and officials at relevant agencies, direct observations and document reviews. "Improvements are needed in the screening process to ensure that dangerous prohibited items are not being carried into the sterile areas of heavily used airports or do not enter the checked baggage system," the report states. "There were four areas that caused most of the test failures and were in need of improvement: training; equipment and technology; policy and procedures; and management and supervision." |
Таємні тести показують відмову передполітного контролю Таємні тести операцій по показу авіації показали широко поширені проблеми, ставлячи питання, що вибухові речовини і зброя могли увійти до аеропорту безплідні області і перевіряли системи багажу головний інспектор Міністерства національної безпеки сказав в середу. Таємні тести співробітників догляду Забезпечення режиму Транспортування і устаткування проводилися в сотнях аеропортів по всій країні з липня до листопада 2003. Велика частина звіту залишається класифікованою, але резюме на вісім сторінок було випущене в середу. Звіт грунтується на інтерв'ю із службовцями і чиновниками у відповідних агентствах, безпосередніх спостереженнях і оглядах документу. "Удосконалення потрібні в процесі показу, щоб гарантувати, що небезпечні заборонені пункти не несуть у безплідні області великою мірою використовуваних аеропортів або не входять в перевірену систему багажу," в доповіді говориться. "Були чотири області які викликали більшість випробувальних відмов і потребували удосконалення: навчання; устаткування і технологія; політика і процедури; і управління і спостереження". |
Exercise 11. Look at the following picture. Fill in the blanks.
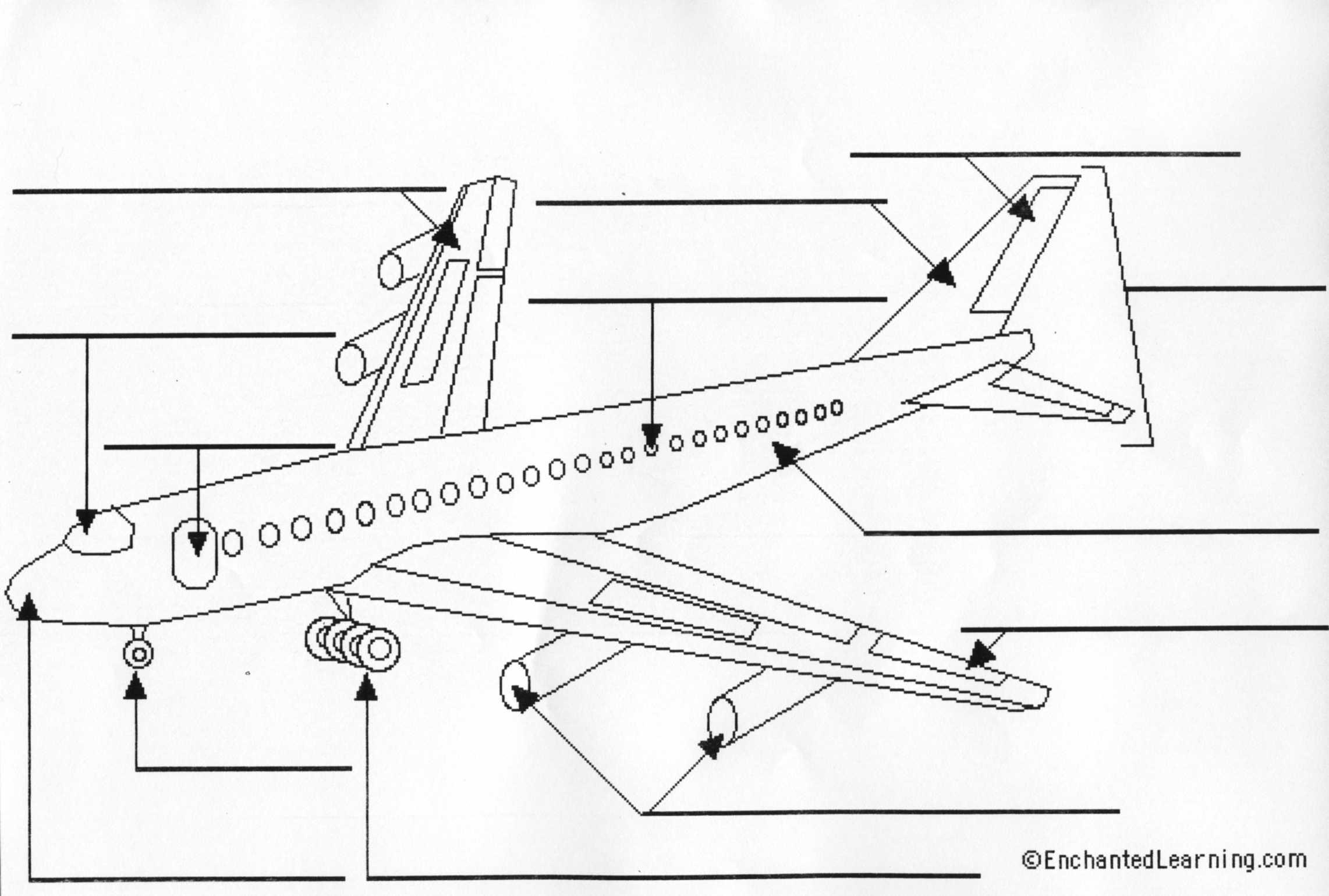
B. cockpit - where the pilots fly the plane, located at the front of the plane.
C. door - allows people to enter and exit the plane.
D. elevator - the movable part of the 2 horizontal parts of the tail section that moves up or down to help the plane remain level during flight (the elevator controls pitch) and helps control altitude.
E. fin - the vertical part of the rear of the tail. The rudder is located on the trailing edge of the fin.
F. flaps - the hinged, rear edge of a wing (located near the body of the plane); the flaps move downwards during takeoff and landing in order to increase the wing surface and therefore increase lift.
G. fuselage - the body of the airplane (excluding the wing and tail). Passengers and cargo are carried towards the rear of the fuselage.
H. jet engines - the part of the aircraft that provides the power for the flight.
I. landing gear - the retractable wheels fastened to the main part of the body (by struts) - it is used for landing and moving the plane around on the ground.
J. nose - the forward part of the plane.
K. nosewheel - the part of the landing gear located under the nose of the plane.
L. rudder - the vertical part of the tail; it can move left/right to stabilize the airplane during takeoffs and landings in strong wind or in crosswinds (it controls yaw).
M. slats - the hinged forward edge of a wing; the slats are used during takeoff and landing in order to increase the wing surface and therefore increase lift.
N. spoiler - small hinged plates located on the top surface of the wings; spoilers are used to slow an aircraft or help it descend by disrupting (spoiling) the flow of air around the wing, increasing the drag.
O. windows - sealed viewing portals, located along the sides of the plane.
P. wing - the airplane's two wings produce lift as the plane moves through the air. The wings have four moveable controls: ailerons, flaps, slats, and spoilers.
Exercise 12. Form nouns from verbs provided below.
Stabilize, combine, configurate, elevate, move, operate, fly, equip, locate, attach.
Exercise 13. Work in pairs. Make up dialogues. Imagine you are visiting aircraft hangar in our university and talk to your instructor. Ask questions about the parts of the aircraft you are looking at. (One person should be a student, another- an instructor). Use words and information from the text.
Exercise 14. In groups of two or three make up PowerPoint presentation about parts of aircraft (choose one from the list): fuselage, wing, tail unit, power plant, landing gear. Your presentations should contain information about functions, about its structure and pictures of it. There should be not more than 10 slides in your presentations.
Exercise 15. Have a look at the following text. Its translation contains a number of mistakes and inaccuracies. Correct it rewriting in accord with the rules of style, grammar and word combinality.
|
Passenger boarding stairs, sometimes referred to as 'air-stairs', 'boarding ramps' or 'aircraft steps', provide a mobile means to traverse between aircraft doors and the ground. Because larger aircraft have door sills 5 to 20 feet high, stairs facilitate safe boarding and deboarding. While smaller units are generally moved by being towed or pushed, larger units are self-powered. Most models have adjustable height to accommodate various aircraft. Optional features may include canopy, heat, supplementary lighting and red carpet. |
Пасажирські сходинки, що піднімаються на борт, іноді посилався на те, оскільки 'авіа-сходинки', 'піднімаючись на борт трапи' або 'кроки авіації', забезпечують автофургон має намір перетнути між дверима авіації і землею. Оскільки більша авіація мають підвіконня дверей 5 до 20 футів високо, сходинки полегшують безпечну посадку і deboarding. Поки більше маленькі одиниці загалом переміщають буксирує або штовхнув, більші одиниці self-powered. Найбільше моделей мають регульовану висоту, щоб пристосувати різну авіацію. Необов'язкові особливості, можливо, включають навіс, тепло, додаткове освітлення і червоний килим. |
Exercise 16. Role play.
Student A: Imagine you are a Ukranian air carrier CEO who wishes to invest into all possible advanced technologies concerning aircraft passenger boarding stairs. Ask questions about details on this matter.
Student B: You are a translator for a Ukranian air carrier CEO. Translate the discussion on the matter.
Student C: You are an aircraft designer of the world’s famous design bureau. Present your ideas on advanced technologies for aircraft passenger boarding stairs.
