
- •Quick Quiz 4.1 Suppose you are standing directly behind someone who steps back
- •Course of lectures «Contemporary Physics: Part1»
- •We now direct our attention to the study of thermodynamics, which involves situations
- •Temperature and the Zeroth
- •Temperature and the Zeroth
- •Temperature and the Zeroth
- •Thermometers and the Celsius
- •The Constant-Volume Gas
- •The Constant-Volume Gas
- •The Constant-Volume Gas
- •Thermal Expansion of Solids
- •Thermal Expansion of Solids
- •Thermal Expansion of Solids
- •Thermal Expansion of Solids
- •Thermal Expansion of Solids
- •Thermal Expansion of Solids
- •The Unusual Behavior of Water
- •Macroscopic Description of an
- •Macroscopic Description of an
- •Macroscopic Description of an
- •Macroscopic Description of an
- •Heat and Internal Energy
- •Units of Heat
- •The Mechanical Equivalent of
- •Specific Heat and Calorimetry
- •Specific Heat and Calorimetry
- •Specific Heat and Calorimetry
- •Conservation of Energy:
- •Latent Heat
- •Latent Heat
- •Work and Heat in Thermodynamic Processes
- •Work and Heat in Thermodynamic Processes
- •Work and Heat in Thermodynamic Processes
- •Work and Heat in Thermodynamic Processes
- •The First Law of Thermodynamics
- •The First Law of Thermodynamics
- •The First Law of Thermodynamics
- •Quick Quiz 5.1
- •Quick Quiz 5.2

Thermal Expansion of Solids
and Liquids
Thermal expansion is a consequence of the change in the average separation between the atoms in an object.
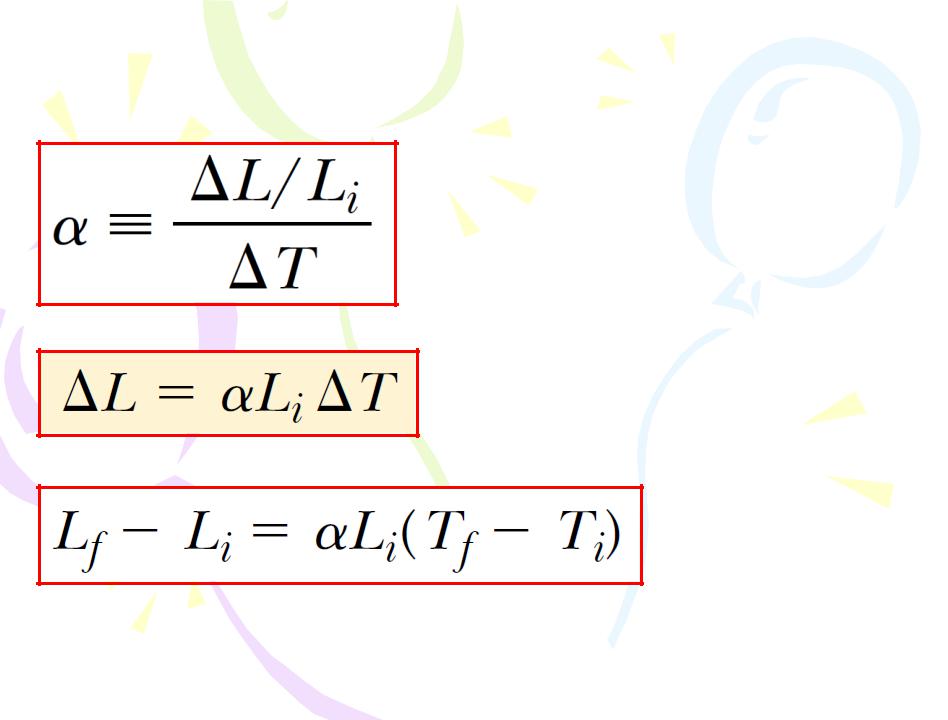
Thermal Expansion of Solids
and Liquids
average coefficient of linear expansion
(9.1)
(9.2) 
A cavity in a piece of material expands in the same way as if the cavity were filled with the material.

Thermal Expansion of Solids
and Liquids
Table 9.1

Thermal Expansion of Solids
and Liquids
(9.3) β is the average coefficient of
volume expansion.

Thermal Expansion of Solids
and Liquids
Thermal Expansion of Solids
and Liquids
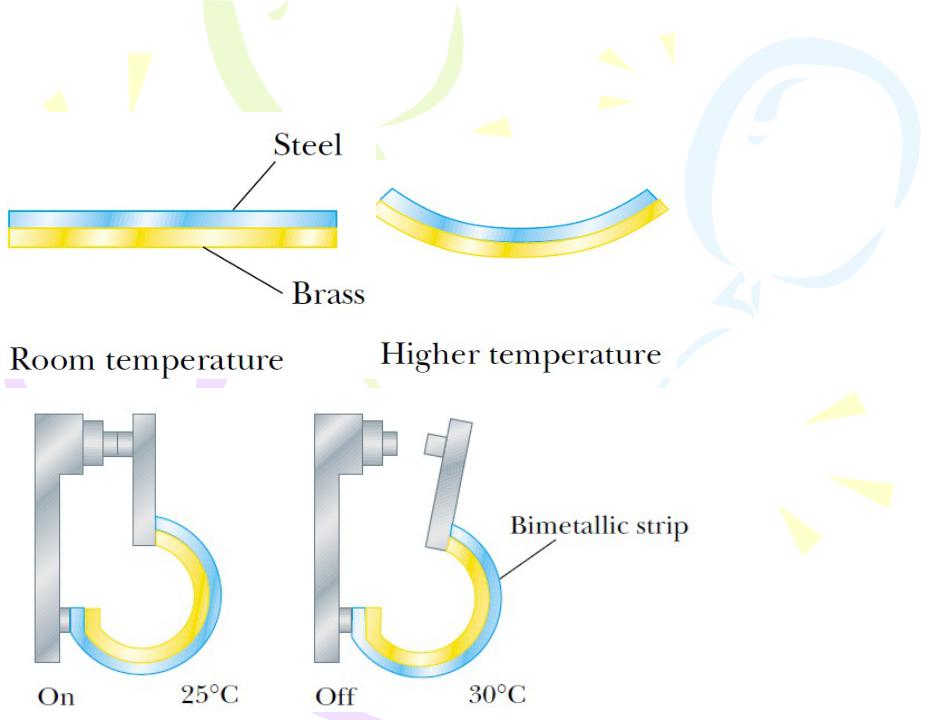
Figure 9.1 (a) A bimetallic strip bends as the temperature changes because the two metals have different expansion coefficients. (b) A bimetallic strip used in a thermostat to break or make electrical contact.

The Unusual Behavior of Water
Figure 9.2 The variation in the density of water at atmospheric pressure with temperature. The inset at the right shows that the maximum density of water occurs at 4°C.

Macroscopic Description of an
Ideal Gas
It is convenient to express the amount of gas in a given volume in terms of the number of moles n. One mole of any substance is that amount of the substance that contains Avogadro’s number NA = 6.022 ) 1023 of
constituent particles (atoms or molecules).
(9.4)
Macroscopic Description of an
Ideal Gas
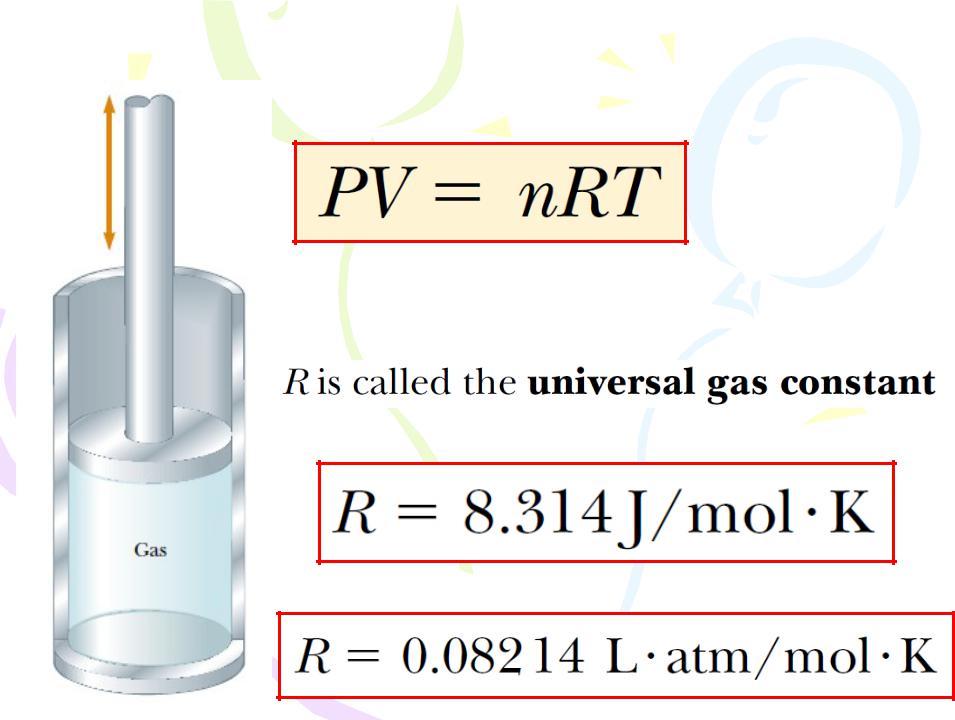
(9.5)
Equation of state for an ideal gas

Macroscopic Description of an
Ideal Gas
Figure 9.4 A bottle of champagne is shaken and opened. Liquid spews out of the opening. A common misconception is that the pressure inside the bottle is increased due to the shaking.
