
- •Quick Quiz 13.1
- •Quick Quiz 13.2
- •Quick Quiz 13.3
- •Quick Quiz 13.4
- •Quick Quiz 13.5
- •Quick Quiz 13.6
- •Course of lectures «Contemporary Physics: Part1»
- •Magnetic Fields and Forces
- •Magnetic Fields and Forces
- •Magnetic Fields and Forces
- •Magnetic Force Acting on a Current-
- •Magnetic Force Acting on a Current-
- •Magnetic Force Acting on a Current-
- •Magnetic Force Acting on a Current-
- •Magnetic Force Acting on a Current-
- •Magnetic Force Acting on a Current-
- •Torque on a Current Loop in a Uniform
- •Torque on a Current Loop in a Uniform
- •Torque on a Current Loop in a Uniform
- •Motion of a Charged Particle in a Uniform
- •Motion of a Charged Particle in a Uniform
- •Applications Involving Charged Particles
- •Applications Involving Charged Particles
- •Applications Involving Charged Particles
- •The Hall Effect
- •The Hall Effect
- •The Hall Effect
- •The Biot–Savart Law
- •The Biot–Savart Law
- •TheMagnetic Force Between
- •TheMagnetic Force Between
- •The Magnetic Field of a Solenoid
- •The Magnetic Field of a Solenoid
- •Magnetic Flux
- •Gauss’s Law in Magnetism
- •Displacement Current and the General
- •Displacement Current and the General
- •Homework:
- •Quick Quiz 14.1
- •Quick Quiz 14.2
- •Quick Quiz 14.3
- •Quick Quiz 14.4
- •Quick Quiz 14.5

The Magnetic Force Between
Magnetic Force Between
Two Parallel Conductors
The force between two parallel wires is used to define the ampere as follows: 
When the magnitude of the force per unit length between two long parallel wires that carry identical currents and are separated by 1 m is 2·10-7 N/m, the current in each wire is defined to be 1 A.
The SI unit of charge, the coulomb, is defined in terms of the ampere:
When a conductor carries a steady current of 1 A, the quantity of charge that flows through a cross section of the conductor in 1 s is 1 C.

 Ampère’s Law
Ampère’s Law

 Ampère’s Law
Ampère’s Law
The line integral of B·ds around any closed path equals μ0I, where I is the total steady current
passing through any surface bounded by the closed path. 

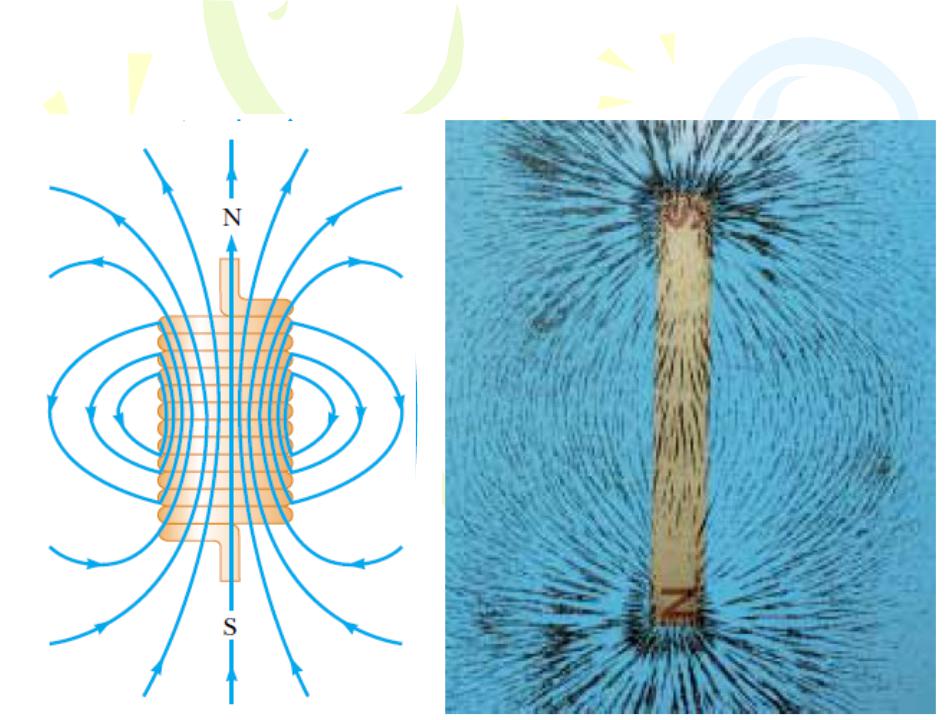
The Magnetic Field of a Solenoid
A solenoid is a long wire wound in the form of a helix.

The Magnetic Field of a Solenoid

Magnetic Flux

Gauss’s Law in Magnetism
Gauss’s law in magnetism states that 
the net magnetic flux through any closed surface is always zero:

Displacement Current and the General
Form of Ampère’s Law
Show that Ampère’s law in this form is valid only if any electric fields present are constant in time.

Displacement Current and the General
Form of Ampère’s Law
Magnetic fields are produced both by conduction currents and by time-varying electric fields.

Homework:
Magnetism in Matter
