
- •Credits
- •Foreword
- •About the Authors
- •About the Reviewers
- •www.PacktPub.com
- •Table of Contents
- •Preface
- •Introducing SFML
- •Downloading and installation
- •A minimal example
- •A few notes on C++
- •Developing the first game
- •The Game class
- •Game loops and frames
- •Input over several frames
- •Vector algebra
- •Frame-independent movement
- •Fixed time steps
- •Other techniques related to frame rates
- •Displaying sprites on the screen
- •File paths and working directories
- •Real-time rendering
- •Adapting the code
- •Summary
- •Defining resources
- •Resources in SFML
- •Textures
- •Images
- •Fonts
- •Shaders
- •Sound buffers
- •Music
- •A typical use case
- •Graphics
- •Audio
- •Acquiring, releasing, and accessing resources
- •An automated approach
- •Finding an appropriate container
- •Loading from files
- •Accessing the textures
- •Error handling
- •Boolean return values
- •Throwing exceptions
- •Assertions
- •Generalizing the approach
- •Compatibility with sf::Music
- •A special case – sf::Shader
- •Summary
- •Entities
- •Aircraft
- •Alternative entity designs
- •Rendering the scene
- •Relative coordinates
- •SFML and transforms
- •Scene graphs
- •Scene nodes
- •Node insertion and removal
- •Making scene nodes drawable
- •Drawing entities
- •Connecting entities with resources
- •Aligning the origin
- •Scene layers
- •Updating the scene
- •One step back – absolute transforms
- •The view
- •Viewport
- •View optimizations
- •Resolution and aspect ratio
- •View scrolling
- •Zoom and rotation
- •Landscape rendering
- •SpriteNode
- •Landscape texture
- •Texture repeating
- •Composing our world
- •World initialization
- •Loading the textures
- •Building the scene
- •Update and draw
- •Integrating the Game class
- •Summary
- •Polling events
- •Window events
- •Joystick events
- •Keyboard events
- •Mouse events
- •Getting the input state in real time
- •Events and real-time input – when to use which
- •Delta movement from the mouse
- •Playing nice with your application neighborhood
- •A command-based communication system
- •Introducing commands
- •Receiver categories
- •Command execution
- •Command queues
- •Handling player input
- •Commands in a nutshell
- •Implementing the game logic
- •A general-purpose communication mechanism
- •Customizing key bindings
- •Why a player is not an entity
- •Summary
- •Defining a state
- •The state stack
- •Adding states to StateStack
- •Handling updates, input, and drawing
- •Input
- •Update
- •Draw
- •Delayed pop/push operations
- •The state context
- •Integrating the stack in the Application class
- •Navigating between states
- •Creating the game state
- •The title screen
- •Main menu
- •Pausing the game
- •The loading screen – sample
- •Progress bar
- •ParallelTask
- •Thread
- •Concurrency
- •Task implementation
- •Summary
- •The GUI hierarchy, the Java way
- •Updating the menu
- •The promised key bindings
- •Summary
- •Equipping the entities
- •Introducing hitpoints
- •Storing entity attributes in data tables
- •Displaying text
- •Creating enemies
- •Movement patterns
- •Spawning enemies
- •Adding projectiles
- •Firing bullets and missiles
- •Homing missiles
- •Picking up some goodies
- •Collision detection and response
- •Finding the collision pairs
- •Reacting to collisions
- •An outlook on optimizations
- •An interacting world
- •Cleaning everything up
- •Out of view, out of the world
- •The final update
- •Victory and defeat
- •Summary
- •Defining texture atlases
- •Adapting the game code
- •Low-level rendering
- •OpenGL and graphics cards
- •Understanding render targets
- •Texture mapping
- •Vertex arrays
- •Particle systems
- •Particles and particle types
- •Particle nodes
- •Emitter nodes
- •Affectors
- •Embedding particles in the world
- •Animated sprites
- •The Eagle has rolled!
- •Post effects and shaders
- •Fullscreen post effects
- •Shaders
- •The bloom effect
- •Summary
- •Music themes
- •Loading and playing
- •Use case – In-game themes
- •Sound effects
- •Loading, inserting, and playing
- •Removing sounds
- •Use case – GUI sounds
- •Sounds in 3D space
- •The listener
- •Attenuation factor and minimum distance
- •Positioning the listener
- •Playing spatial sounds
- •Use case – In-game sound effects
- •Summary
- •Playing multiplayer games
- •Interacting with sockets
- •Socket selectors
- •Custom protocols
- •Data transport
- •Network architectures
- •Peer-to-peer
- •Client-server architecture
- •Authoritative servers
- •Creating the structure for multiplayer
- •Working with the Server
- •Server thread
- •Server loop
- •Peers and aircraft
- •Hot Seat
- •Accepting new clients
- •Handling disconnections
- •Incoming packets
- •Studying our protocol
- •Understanding the ticks and updates
- •Synchronization issues
- •Taking a peek in the other end – the client
- •Client packets
- •Transmitting game actions via network nodes
- •The new pause state
- •Settings
- •The new Player class
- •Latency
- •Latency versus bandwidth
- •View scrolling compensation
- •Aircraft interpolation
- •Cheating prevention
- •Summary
- •Index
Keeping Track of Your Textures – Resource Management
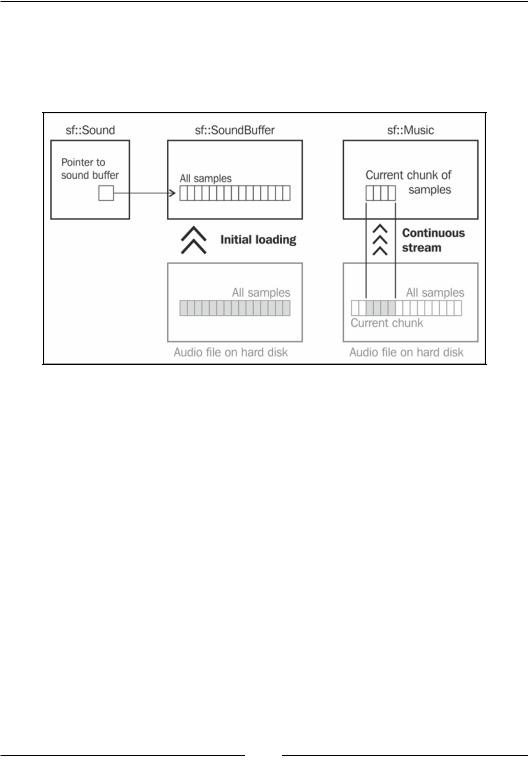
The difference between sound buffers and music is shown in the following diagram. On the left, you see a sound buffer object, which loads the whole audio data from the hard disk at once. It can be played using a separate sound object. On the right, a music object streams from the hard disk, that is, it continuously loads small chunks. It can be played on its own.
A typical use case
Now we have seen what kinds of different resources there are, but we do not know yet how to apply this knowledge to our game. While the approach you have seen in Chapter 1, Making a Game Tick, may work for simple examples, it does not scale well to a bigger project. As our game grows, we have to reflect about how the resources are going to be used. This is explained in the next sections.
Graphics
In our game, a crucial part will be the visual representation of the world and different objects in it. We need to think about how we get from an image on the hard disk to its visualization on the screen.
•Game entities such as the player's airplane, enemies, or the landscape are represented with sprites and possibly texts. They do not own the heavy textures and fonts; instead they use the front-end classes to refer to them.
[ 34 ]
www.it-ebooks.info

Chapter 2
•As a consequence, the resources (textures and fonts) need to be accessible by the entities. We must make sure that the resource objects stay alive as long as any front-end object refers to them, so we have to find an appropriate scope to declare the resources.
•A sprite in the airplane must somehow get a reference to the texture stored outside. Therefore, we have to transport this information via constructor parameter to the airplane class.
Audio
Another important resource is audio, which can be divided into sound effects and background music. We have to consider how to make both of them audible in the final application, when all we start with is a bunch of audio files in a directory:
•Sound effects are not tied to a specific game entity such as an airplane; they persist independently of the object that causes them. Imagine an airplane that explodes and creates an explosion sound. When we destroy the plane object, we still want the explosion to be audible for some time. As a result, we do not store sf::Sound instances in the game entities, but in an object which remains alive throughout a mission. The same applies to the underlying sf::SoundBuffer objects which are used by sf::Sound.
•For music themes, the semantics are similar. It may even occur that the same theme is played across multiple missions. Ideally, the sf::Music objects exist in a scope that outlives a single mission.
•Although the game entities do not own sound effects, they are supposed to play them. As a consequence, we shall provide an interface that allows playing new sound effects.
Acquiring, releasing, and accessing resources
Once we have decided which resources are required by the application, the next step is to investigate how long and by whom they are used. This allows us to decide how the resources are stored in the application, as well as who is responsible of loading and releasing them.
•We want to load the resource in advance, for example, at the time the game starts or the player begins a new mission. In contrast to loading on demand (as soon as a resource is needed), this approach has the advantage that possible loading times occur in the beginning and not during a game. Therefore, the game itself remains fluent and is not interrupted because of resources.
[ 35 ]
www.it-ebooks.info
