
Урология - Symptoms and syndroms
.pdf
Zimnitsky test
Urine is gathered every three hours during 24 hours beginning from the morning. Than urine density is measured.
Normally volume of each portion ranges from
50 to 200-300 ml, day diuresis prevail over night, variation of density is not less than 1216 (for example the least density is 1006, the greatest density is 1020.

Straight X-ray
Preparation of the patient
No food and fluids should be given to the patient for at least 6 hours bebore.
A purgative is given at the night before.
Enema is sometimes prescribed but it is probably less effective.

Plain film of the abdomen is taken of the kidney, ureter and bladder region (KUB region)
KIDNEY – size can be assessed from this film.
Congenital absence kidney can be diagnosed.
An enlarged kidney from hydronephrosis, polycystic disease or renal cancer can be diagnosed.
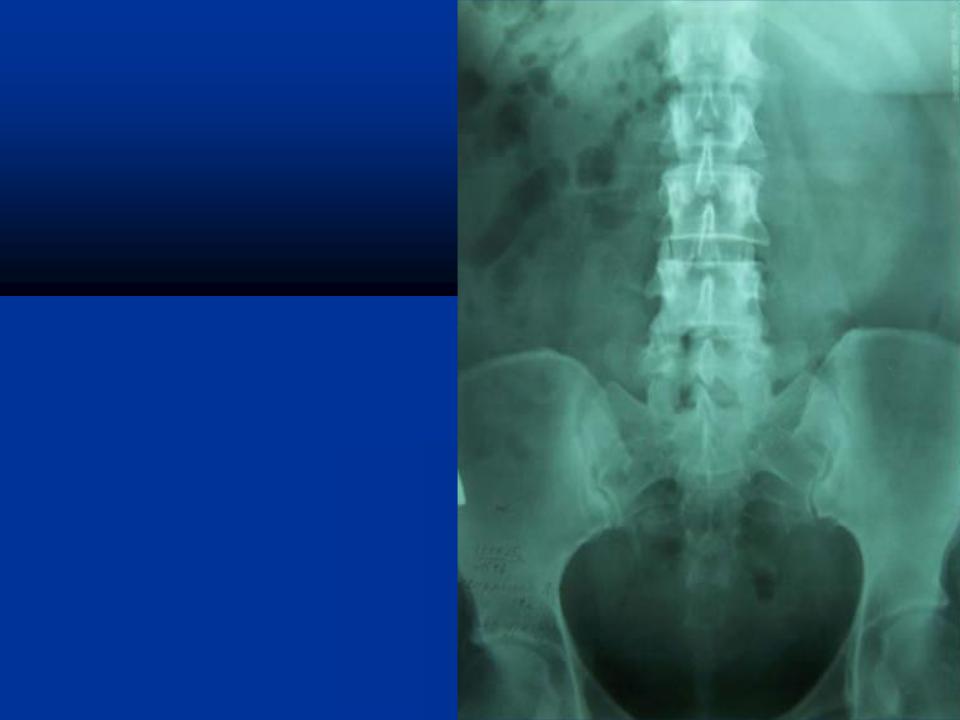
A normal kidney extends from the top of the 1st to the bottom of the 3rd or middle of the 4th lumbar vertebra.
In 90% of cases the right kidney is lower than the left because of displacement by the liver.
Localised swelling as may be caused by a carbuncle, a tubercular cyst, a simple cyst or a tumor can be diagnosed.

STONES – majority of the urinary calculi are radio-opaque except the pure uric acid stone.
Numerous small calcific bodies in the parenchyma of the kidney may suggest tuberculosis or nephro-calcinosis caused by hyperparathyroidism.
About 7% of malignant renal tumors contain some calcification.
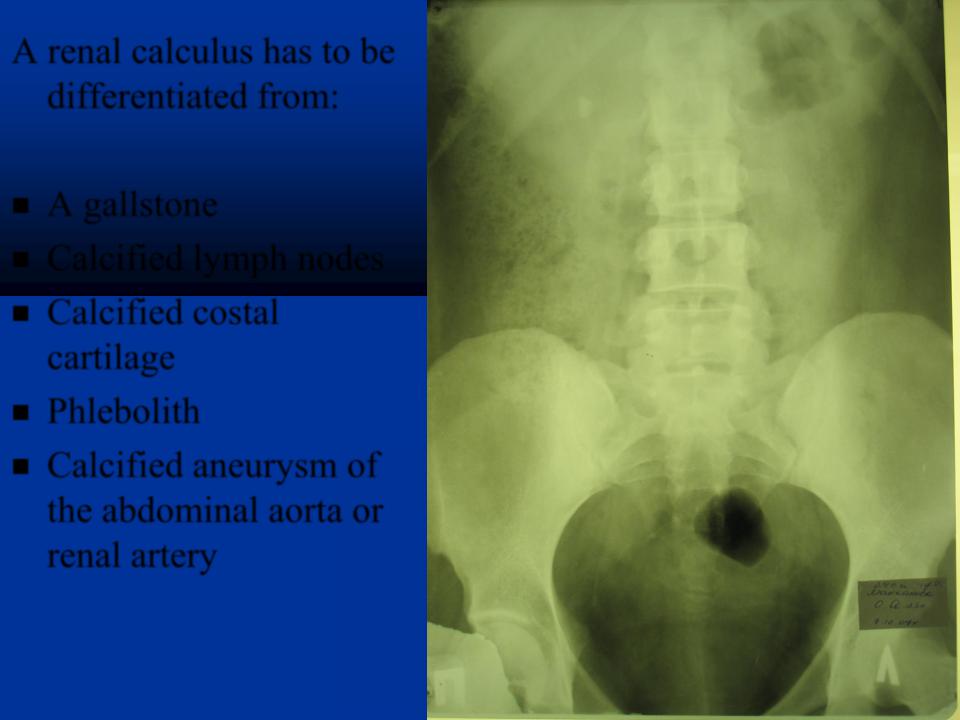
A renal calculus has to be differentiated from:
A gallstone
Calcified lymph nodes
Calcified costal cartilage
Phlebolith
Calcified aneurysm of the abdominal aorta or renal artery

The characteristics of a renal stone are:
A renal calculus moves with respiration which can be verified by taking two exposures, one at full inspiration and the other at full expiration.
Density of a renal stone is uniform whereas gallstones are less dense in the centre.
Renal stones take the shape of the renal pelvis and calyces.

Ureteric stone is usually oval and lies in the line of the ureter.
Vesical calculi are seen just above the symphysis pubis.
The prostatic calculi appear as small dots behind the symphysis pubis.
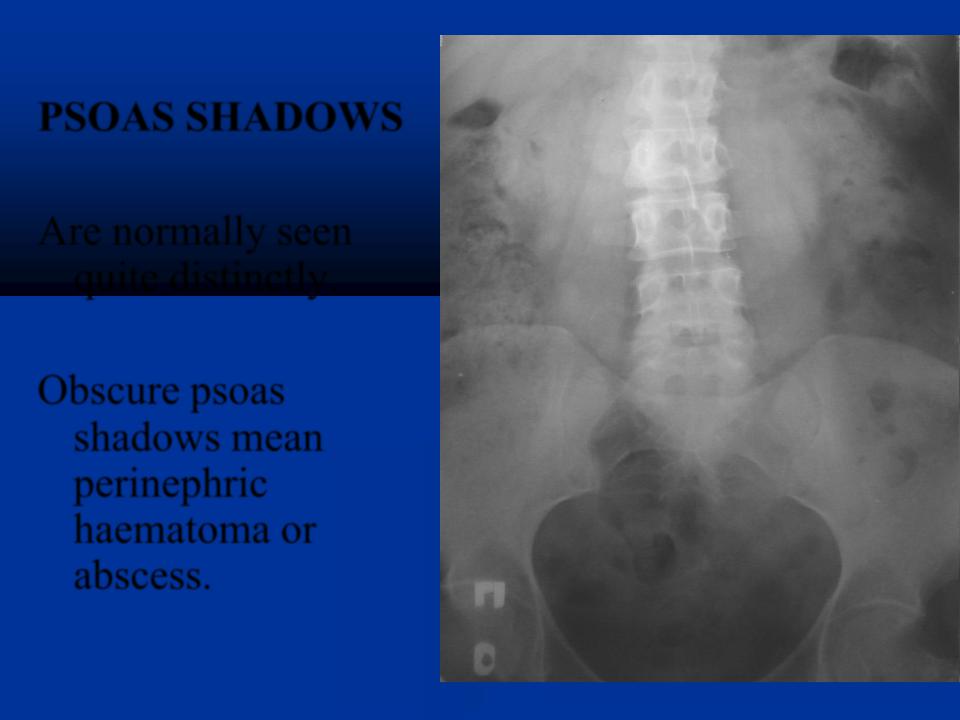
PSOAS SHADOWS
Are normally seen quite distinctly.
Obscure psoas shadows mean perinephric haematoma or abscess.

BONES – should be carefully noticed to detect any arthritic change or presence of metastases.
Arthritic changes may well lead to radicular pain which may mimic a renal pain.
