
- •Ssd2: Introduction to Computer Systems contents
- •Prerequisites
- •Course Textbook
- •Hardware/Software Requirements
- •The purpose of ssd2 is for students to
- •Students successfully completing ssd2 will be able to
- •1.1 Overview of Computer Systems
- •1.1.1 Components of a Computer System
- •Hardware System
- •Software System—Operating System Software and Application Software
- •Network System
- •1.2 Evolution of Computer Systems
- •1.2.1 Brief History
- •1200S—Manual Calculating Devices
- •1600S—Mechanical Calculators
- •1800S—Punched Cards
- •1940S—Vacuum Tubes
- •1950S—Transistors
- •1960S—Integrated Circuits
- •1970S to Present—Microprocessor
- •Pace of Advancement
- •1.2.2 Applications of Computer Systems
- •In Education Multimedia-Facilitated Learning
- •Simulation-Based Education
- •Intelligent Machine-Based Training
- •Interactive Learning
- •In Business Supply Chain Management
- •Project Management
- •Customer Relationship Management
- •Sales and Marketing Using Electronic Commerce
- •Manufacturing Research
- •In Entertainment Movies
- •Video Games
- •1.3 Data Representation in a Computer System
- •1.3.1 Bits and Bytes
- •Data Representation Using Binary Digits
- •Increasing Need for Bytes
- •1.3.2 Number Systems
- •Decimal
- •Hexadecimal
- •Learning Exercise
- •2.1 Processor and Memory
- •2.1.1 Processor Basics
- •Processor
- •Instruction Execution with the cpu
- •Performance: Factors and Measures
- •Types of Processors
- •2.1.2 Types of Memory
- •Cmos Memory
- •Summary
- •2.1.3 Lab: Benchmarking (Optional)
- •2.2 Peripherals
- •2.2.1 Connecting Peripherals
- •Expansion Slots and Cards
- •Usb and FireWire
- •Comparing Different Ports
- •2.2.2 Buses
- •2.2.3 Input/Output Devices
- •Input Devices
- •Cameras
- •Digital Camcorders
- •Scanners
- •Output Devices: Monitors and Projectors
- •Crt Monitors
- •Lcd Monitors
- •Projectors
- •Output Devices: Printers
- •Ink Printers
- •Dye-Sublimation Printers
- •Laser Printers
- •Comparing Printers
- •2.3 Storage Devices
- •2.3.1 Disk Controller Interfaces
- •Ide Interface
- •Eide Master/Slave
- •2.3.2 Mass Storage
- •How Mass Storage Devices Differ from ram
- •Disk Drive Reliability
- •Optical Media: cDs versus dvDs
- •Magnetic Media
- •Optical versus Magnetic
- •Solid State
- •Comparing Storages
- •2.4 Putting Together the Hardware Components
- •2.4.1 How Components Work Together
- •2.4.2 Lab: Researching a Computer System
- •2.4.3 Lab: Online Configuration
- •2.5 Improving Computer Performance
- •2.5.1 Moore's Law
- •2.5.2 Bottlenecks
- •Bottlenecks—Slowing a Process
- •Typical Bottlenecks
- •Eliminating Bottlenecks
- •2.5.3 Throughput and Latency
- •Unit 3. Operating System Software
- •3.1 Structure
- •3.1.1 Layers of Software
- •Layers and Process Management
- •Encapsulation and Abstraction
- •Layers of Software
- •3.1.2 The bios: Life at the Bottom
- •The Role of the bios
- •Changing bios Settings
- •3.1.3 Process Control
- •3.1.4 Lab: The Task Manager
- •3.2 Device Management and Configuration
- •3.2.1 Interrupt Handling
- •Interrupts
- •Interrupt Priority and Nested Interrupts
- •Traps and Faults
- •3.2.2 Hardware Attributes
- •Installing Drivers
- •Changing a Driver's Configuration
- •3.2.3 Configuration
- •3.2.4 Lab: Device Management
- •3.3 Resource Sharing
- •3.3.1 Virtual Memory
- •Managing Memory
- •Relocation
- •Virtual Memory
- •3.3.2 File and Printer Sharing
- •Printers
- •3.4 File Systems
- •3.4.1 File Organization
- •Folders
- •Shortcuts
- •File Names and Types
- •3.4.2 File Allocation Table and nt File System
- •Clusters and File Allocation Tables
- •Nt File System
- •Unit 4. Application Software
- •4.1 Software Basics
- •4.2 Using Software Systems
- •4.2.1 Lab: dos Commands
- •4.2.2 Lab: Macros
- •4.2.3 Lab: Embedding Application Objects
- •4.3 Batch Script Files
- •4.3.1 Advanced Command-Line Functions
- •Dos Command Syntax
- •Review of File System Commands
- •Wildcard Characters
- •Redirection and Piping
- •4.3.2 Batch File Commands
- •Batch Files
- •Commands
- •4.3.3 Lab: Creating a Batch File
- •Example of a Batch File
- •Example of a Batch File with Arguments
- •4.4 Databases
- •4.4.1 Lab: Searching the Library of Congress
- •4.5 Software Engineering
- •4.5.1 Issues in Large-Scale Software Development
- •The Software Development Process
- •Define or Redefine the Problem
- •Plan a Solution to the Problem
- •Code the Solution
- •Evaluate and Test Everything
- •4.5.2 Open Source Model
- •Free Software
- •4.5.3 Tools for Software Creation and Management
- •Editors
- •Compilers
- •Debuggers
- •Integrated Development Environments (idEs)
- •Unit 5. Network Systems
- •5.1 Internet Basics
- •5.1.1 Mime Types
- •5.1.2 Internet Languages
- •JavaScript
- •5.2 Local and Wide Area Networks
- •5.3 Communication Strategies
- •5.3.1 Client-Server Framework
- •5.3.2 Peer-to-Peer Connectivity
- •5.4 Data Transfer Technologies
- •5.5 Internet Architecture
- •5.5.1 Routers and tcp/ip
- •Internet Protocol
- •Routers
- •Transmission Control Protocol
- •5.5.2 Domain Name Service
- •Domain Name Service
- •5.5.3 Connectivity
- •Conventional Analog Phone Lines
- •Isdn: Integrated Services Digital Network
- •Cable Modem
- •XDsl: Digital Subscriber Line
- •Dedicated High Speed Lines
- •5.5.4 Internet Service Providers
- •Unit 6. Computer Security
- •6.1 Security Threats
- •6.1.1 Intruders: Who, Why, and How?
- •6.1.2 Identity Theft and Privacy Violation
- •Password Cracking
- •Packet sniffing
- •Social Engineering/Fraud
- •Spoofing
- •Port Scanning
- •6.1.3 Malicious Software
- •Trojan Horse
- •Prevention
- •Detection
- •Counter Measures
- •6.1.4 Denial of Service
- •Network Connectivity
- •Network Bandwidth
- •Other Resource Consumption Attacks
- •Distributed Denial of Service Attack
- •Prevention
- •6.2 Security Technologies
- •6.2.1 Encryption
- •Substitution Cipher
- •Transmitting the Key
- •Private Key Encryption Scheme
- •Public Key Encryption Scheme
- •Hybrid Encryption Schemes
- •6.2.2 Applications of Encryption
- •Hard Drives
- •Dvd Movies
- •Cellular Phones
- •6.2.3 Authentication
- •Strong Passwords
- •Smart Cards
- •Biometrics
- •Digital Signatures
- •Digital Certificates and Certificate Authorities
- •Ssl Protocol
- •6.3 Prevention, Detection, and Recovery
- •6.3.1 Firewall
- •Application Gateway
- •Packet Filter
- •Application Gateway versus Packet Filter
- •Intruder Attacks Prevented by Firewall
- •Setting up a Firewall
- •6.3.2 Intrusion Detection Tools
- •Intrusion Detection Systems
- •Network Monitoring Tools
- •Anti-Virus Software
- •6.3.3 Data Recovery
- •6.3.4 Summary of Security Tips
3.4.1 File Organization
Files
Folders
Drives
Paths
Shortcuts
File Names and Types
One of the main things computers are used for is storing and retrieving information. The information is stored in one or more "files," which in turn are organized into "folders." The Microsoft Windows file system supports four kinds of entities: files, folders, drives, and shortcuts. The figure below illustrates how files are organized from the perspective of a Windows operating system user.
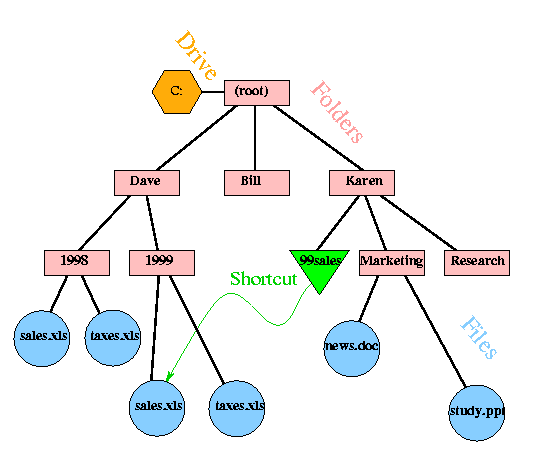
Figure 1 File organization in a Windows operating system
Files
Each file contains some data. When a file is associated with a particular application, such as Microsoft Word, Excel, or Power Point, it is often called a document. Every file has a name. In Windows, file names can be up to 255 characters long and can contain letters, numbers, and certain special characters, including spaces. Although Windows allows use of both uppercase and lowercase letters in a file name, the distinction is ignored by the file system. Thus if you create a file namedFriends, you can also access it as friends or FRIENDS or even fRiEnDs. Other operating systems, such as Unix/Linux, are sensitive to capitalization. In these operating systems, the files Friends.txt and friends.txt are different.
Every file also has a set of properties associated with it. The most important property is the file type, which indicates to the operating system what application to use to open the file. Other properties include the size of the file, the date and time the file was created, and the date and time the file was last modified. You can view a file's properties by clicking with the right mouse button the file icon and selecting Properties on the pop-up menu. If you have access to a Windows machine, try this now. Another way to see file types and sizes is to go to the View menu in the Folder window and click Details.
Folders
Files reside in folders, which are sometimes called directories. Folders have names and properties too. And, like files, every folder has a residency: it is located in another folder called its parent. This gives the file system a hierarchical structure, like a family tree. That is where the term "parent" comes from. Another good analogy is a company organization chart, where every employee has a boss above him, except for the president at the top. The top of the folder hierarchy is called the root.
The file system will not permit two items in a folder to have the same name. You can verify this by creating two files in your working folder called file1 and file2. If you then try to change the name of file2 to file1, you will get an error message, and the change will not be completed. In the diagram above, there are two files named sales.xls, but they are in different folders.
Drives
Folders are housed in the computer drive. A computer can have many drives, drive A, drive C, drive D, drive E, etc. One way to access the drives is by double-clicking on the icon named "My Computer" on your Desktop. This icon is normally located in the upper-left corner of the Desktop. After you double-clicked on the My Computer icon, you will see that each drive is labeled by an icon that indicates the type of medium the drive uses. For example, the hard drive icon is a picture of a hard drive, and the optical drive icon is a picture of a CD-ROM. Clicking a drive's icon will take you to the root directory of that drive.
Paths
Since items in different folders can have the same name and folders can be nested within other folders, we need a way to instruct the operating system or an application exactly which object (that is, which file or folder) we are referring to. We can do this by specifying the complete path to the object, from the root directory. The first sales file in the diagram above can be reached via the path C:\Dave\1998\sales.xls. As you can see, a path contains a drive designator and a sequence of folder names separated by backslashes—and then, if we are referring to a file, the name of the file itself. The path to the root directory on this drive is written C:\ . You can get Windows to display the full path in the title bar of a folder window by going to the View menu and selecting Options. Then go to theView tab and select the check box labeled Display full paths in the title bar.
