
- •Preface
- •Introduction
- •Lesson Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Course Objectives
- •Course Agenda
- •Appendixes Used in the Course
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Oracle Database 11g: Focus Areas
- •Oracle Database 11g
- •Oracle Fusion Middleware
- •Oracle Enterprise Manager Grid Control 10g
- •Oracle BI Publisher
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Relational and Object Relational Database Management Systems
- •Data Storage on Different Media
- •Relational Database Concept
- •Definition of a Relational Database
- •Data Models
- •Entity Relationship Model
- •Relating Multiple Tables
- •Relational Database Terminology
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using SQL to Query Your Database
- •SQL Statements
- •Development Environments for SQL
- •Lesson Agenda
- •The Human Resources (HR) Schema
- •Tables Used in the Course
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Oracle Database 11g Documentation
- •Additional Resources
- •Summary
- •Practice I: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Capabilities of SQL SELECT Statements
- •Basic SELECT Statement
- •Selecting All Columns
- •Selecting Specific Columns
- •Writing SQL Statements
- •Column Heading Defaults
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Arithmetic Expressions
- •Using Arithmetic Operators
- •Operator Precedence
- •Defining a Null Value
- •Null Values in Arithmetic Expressions
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Defining a Column Alias
- •Using Column Aliases
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Concatenation Operator
- •Literal Character Strings
- •Using Literal Character Strings
- •Alternative Quote (q) Operator
- •Duplicate Rows
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Displaying the Table Structure
- •Using the DESCRIBE Command
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 1: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Limiting Rows Using a Selection
- •Limiting the Rows That Are Selected
- •Using the WHERE Clause
- •Character Strings and Dates
- •Comparison Operators
- •Using Comparison Operators
- •Range Conditions Using the BETWEEN Operator
- •Membership Condition Using the IN Operator
- •Pattern Matching Using the LIKE Operator
- •Combining Wildcard Characters
- •Using the NULL Conditions
- •Defining Conditions Using the Logical Operators
- •Using the AND Operator
- •Using the OR Operator
- •Using the NOT Operator
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Rules of Precedence
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using the ORDER BY Clause
- •Sorting
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Substitution Variables
- •Using the Single-Ampersand Substitution Variable
- •Character and Date Values with Substitution Variables
- •Specifying Column Names, Expressions, and Text
- •Using the Double-Ampersand Substitution Variable
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using the DEFINE Command
- •Using the VERIFY Command
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 2: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •SQL Functions
- •Two Types of SQL Functions
- •Single-Row Functions
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Character Functions
- •Case-Conversion Functions
- •Using Case-Conversion Functions
- •Character-Manipulation Functions
- •Using the Character-Manipulation Functions
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Number Functions
- •Using the ROUND Function
- •Using the TRUNC Function
- •Using the MOD Function
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Working with Dates
- •RR Date Format
- •Using the SYSDATE Function
- •Arithmetic with Dates
- •Using Arithmetic Operators with Dates
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Date-Manipulation Functions
- •Using Date Functions
- •Using ROUND and TRUNC Functions with Dates
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 3: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Conversion Functions
- •Implicit Data Type Conversion
- •Explicit Data Type Conversion
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using the TO_CHAR Function with Dates
- •Elements of the Date Format Model
- •Using the TO_CHAR Function with Dates
- •Using the TO_CHAR Function with Numbers
- •Using the TO_NUMBER and TO_DATE Functions
- •Using the TO_CHAR and TO_DATE Function with RR Date Format
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Nesting Functions
- •Lesson Agenda
- •General Functions
- •NVL Function
- •Using the NVL Function
- •Using the NVL2 Function
- •Using the NULLIF Function
- •Using the COALESCE Function
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Conditional Expressions
- •CASE Expression
- •Using the CASE Expression
- •DECODE Function
- •Using the DECODE Function
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 4: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •What Are Group Functions?
- •Types of Group Functions
- •Group Functions: Syntax
- •Using the AVG and SUM Functions
- •Using the MIN and MAX Functions
- •Using the COUNT Function
- •Using the DISTINCT Keyword
- •Group Functions and Null Values
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Creating Groups of Data
- •Creating Groups of Data: GROUP BY Clause Syntax
- •Using the GROUP BY Clause
- •Grouping by More than One Column
- •Using the GROUP BY Clause on Multiple Columns
- •Illegal Queries Using Group Functions
- •Restricting Group Results
- •Restricting Group Results with the HAVING Clause
- •Using the HAVING Clause
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Nesting Group Functions
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 5: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Types of Joins
- •Joining Tables Using SQL:1999 Syntax
- •Qualifying Ambiguous Column Names
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Creating Natural Joins
- •Retrieving Records with Natural Joins
- •Creating Joins with the USING Clause
- •Joining Column Names
- •Retrieving Records with the USING Clause
- •Using Table Aliases with the USING Clause
- •Creating Joins with the ON Clause
- •Retrieving Records with the ON Clause
- •Creating Three-Way Joins with the ON Clause
- •Applying Additional Conditions to a Join
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Joining a Table to Itself
- •Self-Joins Using the ON Clause
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Nonequijoins
- •Retrieving Records with Nonequijoins
- •Lesson Agenda
- •INNER Versus OUTER Joins
- •LEFT OUTER JOIN
- •RIGHT OUTER JOIN
- •FULL OUTER JOIN
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Cartesian Products
- •Generating a Cartesian Product
- •Creating Cross Joins
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 6: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using a Subquery to Solve a Problem
- •Subquery Syntax
- •Using a Subquery
- •Guidelines for Using Subqueries
- •Types of Subqueries
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Single-Row Subqueries
- •Executing Single-Row Subqueries
- •Using Group Functions in a Subquery
- •The HAVING Clause with Subqueries
- •What Is Wrong with This Statement?
- •No Rows Returned by the Inner Query
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Multiple-Row Subqueries
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Null Values in a Subquery
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 7: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Set Operators
- •Set Operator Guidelines
- •The Oracle Server and Set Operators
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Tables Used in This Lesson
- •Lesson Agenda
- •UNION Operator
- •Using the UNION Operator
- •UNION ALL Operator
- •Using the UNION ALL Operator
- •Lesson Agenda
- •INTERSECT Operator
- •Using the INTERSECT Operator
- •Lesson Agenda
- •MINUS Operator
- •Using the MINUS Operator
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Matching the SELECT Statements
- •Matching the SELECT Statement: Example
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using the ORDER BY Clause in Set Operations
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 8: Overview

Group Functions: Syntax
|
|
|
SELECT |
group_function(column), ... |
|
FROM |
table |
|
[WHERE |
condition] |
|
[ORDER BY |
column]; |
|
|
|
|
Group Functions: Syntax |
Copyright © 2009, Oracle. All rights reserved. |
Academy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oracle |
|
The group function is placed after the SELECT keyword. You may have multiple group functions separated by commas.
Guidelines for using the group functions:
• DISTINCT makes the function consider only nonduplicate values; ALL makes it consider every |
||||
|
|
|
|
Only |
|
value, including duplicates. The default is ALL and therefore does not need to be specified. |
|||
• |
The data types for the functions with an&expr argume t may be CHAR, VARCHAR2, NUMBER, |
|||
• |
or DATE. |
Internal |
|
|
|
|
Use |
||
All group functions ignore ull values. To substitute a value for null values, use the NVL, NVL2, |
||||
|
or COALESCE functions. |
|
|
|
Oracle |
|
|
||
Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals I 5 - 6
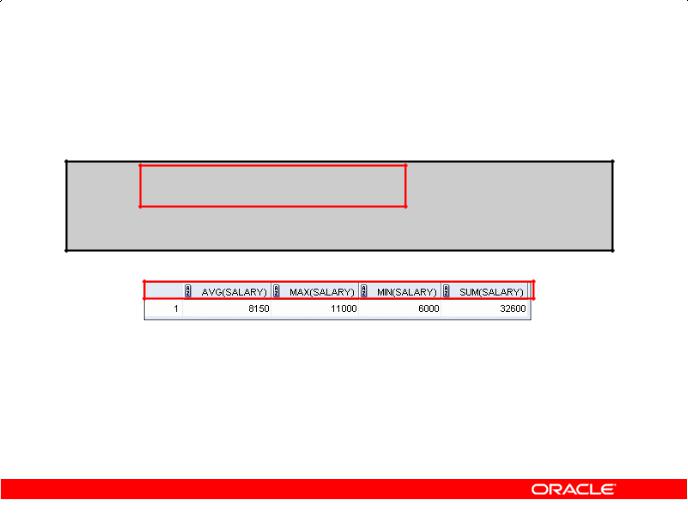
Using the AVG and SUM Functions
You can use AVG and SUM for numeric data.
SELECT AVG(salary), MAX(salary),
MIN(salary), SUM(salary)
FROM employees
WHERE job_id LIKE '%REP%';
|
Copyright © 2009, Oracle. All rights reserved. |
Academy |
|||
|
|
|
|||
Using the AVG and SUM Functions |
Oracle |
||||
|
You can use the AVG, SUM, MIN, and |
||||
|
MAX functions against the columns that can store numeric data. |
||||
|
The example in the slide displays the average, highest, lowest, and sum of monthly salaries for all |
||||
|
sales representatives. |
|
Only |
|
|
|
|
& |
|
|
|
|
Internal |
|
|
|
|
Oracle |
Use |
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
||
Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals I 5 - 7
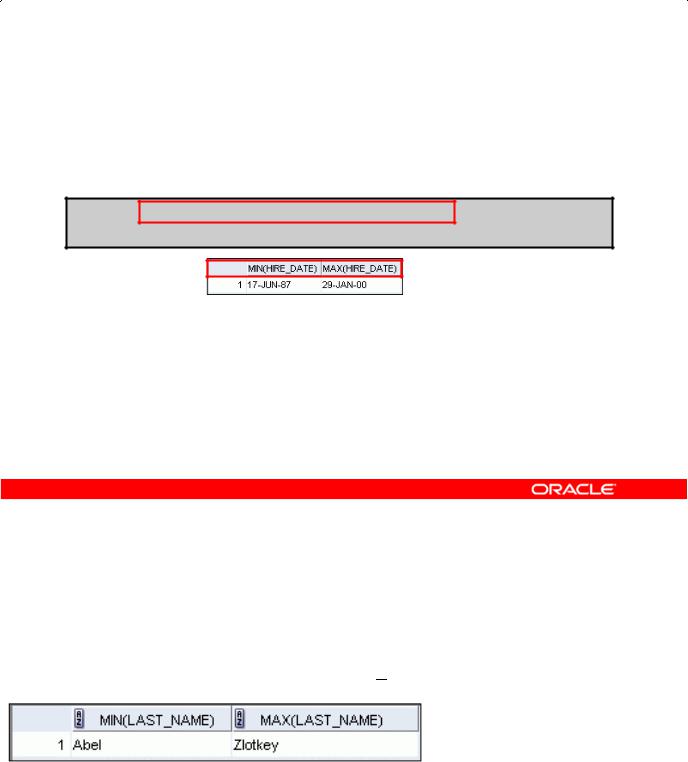
Using the MIN and MAX Functions
You can use MIN and MAX for numeric, character, and date data types.
SELECT MIN(hire_date), MAX(hire_date)
FROM employees;
|
Copyright © 2009, Oracle. All rights reserved. |
Academy |
|
|
|
||
Using the MIN and MAX Functions |
Oracle |
||
|
|
||
You can use the MAX and MIN functions for numeric, character, and date data types. The example in the slide displays the most junior and most senior employees.
The following example displays the employee last name th t is first and the employee last name that
is last in an alphabetic list of all employees: |
Only |
& |
|
SELECT MIN(last_name), MAX(last ame) |
|
FROM employees; |
|
Internal |
|
Use |
|
Note: The , , , and functions can be used only with numeric data types.
OracleAVG SUM VARIANCE STDDEV
MAX and MIN cannot be used with LOB or LONG data types.
Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals I 5 - 8

Using the COUNT Function
COUNT(*) returns the number of rows in a table:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1 |
|
SELECT |
COUNT(*) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
FROM |
employees |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
WHERE |
department_id = 50; |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
COUNT(expr) returns the number of rows with non-null values |
|||||||
|
|
|
for expr: |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
SELECT |
COUNT(commission_pct) |
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
FROM |
employees |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
WHERE |
department_id = 80; |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Copyright © 2009, Oracle. All rights reserved. |
|
|
||
Using the COUNT Function |
|
|
Academy |
|||||||
|
The COUNT function has three formats: |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
||||||
|
• |
COUNT(*) |
|
|
Oracle |
|||||
|
• |
COUNT(expr) |
||||||||
|
• |
COUNT(DISTINCT expr) |
||||||||
COUNT(*) returns the number of rows in a table that satisfy the criteria of the SELECT statement, |
|
including duplicate rows and rows containing&null values in a y of the columns. If a WHERE clause is |
|
included in the SELECT statement, COUNT(*) returns the number of rows that satisfy the condition |
|
in the WHERE clause. |
Only |
|
|
In contrast, COUNT(expr) tu ns the number of non-null values that are in the column identified |
||
by expr. |
Use |
|
COUNT(DISTINCTInternalexpr) returns the number of unique, non-null values that are in the column |
||
Oracle |
||
identified by |
xpr. |
|
Examples: |
|
|
1. |
The example in the slide displays the number of employees in department 50. |
|
2. |
The example in the slide displays the number of employees in department 80 who can earn a |
|
|
commission. |
|
Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals I 5 - 9
