
- •Preface
- •Introduction
- •Lesson Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Course Objectives
- •Course Agenda
- •Appendixes Used in the Course
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Oracle Database 11g: Focus Areas
- •Oracle Database 11g
- •Oracle Fusion Middleware
- •Oracle Enterprise Manager Grid Control 10g
- •Oracle BI Publisher
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Relational and Object Relational Database Management Systems
- •Data Storage on Different Media
- •Relational Database Concept
- •Definition of a Relational Database
- •Data Models
- •Entity Relationship Model
- •Relating Multiple Tables
- •Relational Database Terminology
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using SQL to Query Your Database
- •SQL Statements
- •Development Environments for SQL
- •Lesson Agenda
- •The Human Resources (HR) Schema
- •Tables Used in the Course
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Oracle Database 11g Documentation
- •Additional Resources
- •Summary
- •Practice I: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Capabilities of SQL SELECT Statements
- •Basic SELECT Statement
- •Selecting All Columns
- •Selecting Specific Columns
- •Writing SQL Statements
- •Column Heading Defaults
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Arithmetic Expressions
- •Using Arithmetic Operators
- •Operator Precedence
- •Defining a Null Value
- •Null Values in Arithmetic Expressions
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Defining a Column Alias
- •Using Column Aliases
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Concatenation Operator
- •Literal Character Strings
- •Using Literal Character Strings
- •Alternative Quote (q) Operator
- •Duplicate Rows
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Displaying the Table Structure
- •Using the DESCRIBE Command
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 1: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Limiting Rows Using a Selection
- •Limiting the Rows That Are Selected
- •Using the WHERE Clause
- •Character Strings and Dates
- •Comparison Operators
- •Using Comparison Operators
- •Range Conditions Using the BETWEEN Operator
- •Membership Condition Using the IN Operator
- •Pattern Matching Using the LIKE Operator
- •Combining Wildcard Characters
- •Using the NULL Conditions
- •Defining Conditions Using the Logical Operators
- •Using the AND Operator
- •Using the OR Operator
- •Using the NOT Operator
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Rules of Precedence
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using the ORDER BY Clause
- •Sorting
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Substitution Variables
- •Using the Single-Ampersand Substitution Variable
- •Character and Date Values with Substitution Variables
- •Specifying Column Names, Expressions, and Text
- •Using the Double-Ampersand Substitution Variable
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using the DEFINE Command
- •Using the VERIFY Command
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 2: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •SQL Functions
- •Two Types of SQL Functions
- •Single-Row Functions
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Character Functions
- •Case-Conversion Functions
- •Using Case-Conversion Functions
- •Character-Manipulation Functions
- •Using the Character-Manipulation Functions
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Number Functions
- •Using the ROUND Function
- •Using the TRUNC Function
- •Using the MOD Function
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Working with Dates
- •RR Date Format
- •Using the SYSDATE Function
- •Arithmetic with Dates
- •Using Arithmetic Operators with Dates
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Date-Manipulation Functions
- •Using Date Functions
- •Using ROUND and TRUNC Functions with Dates
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 3: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Conversion Functions
- •Implicit Data Type Conversion
- •Explicit Data Type Conversion
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using the TO_CHAR Function with Dates
- •Elements of the Date Format Model
- •Using the TO_CHAR Function with Dates
- •Using the TO_CHAR Function with Numbers
- •Using the TO_NUMBER and TO_DATE Functions
- •Using the TO_CHAR and TO_DATE Function with RR Date Format
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Nesting Functions
- •Lesson Agenda
- •General Functions
- •NVL Function
- •Using the NVL Function
- •Using the NVL2 Function
- •Using the NULLIF Function
- •Using the COALESCE Function
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Conditional Expressions
- •CASE Expression
- •Using the CASE Expression
- •DECODE Function
- •Using the DECODE Function
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 4: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •What Are Group Functions?
- •Types of Group Functions
- •Group Functions: Syntax
- •Using the AVG and SUM Functions
- •Using the MIN and MAX Functions
- •Using the COUNT Function
- •Using the DISTINCT Keyword
- •Group Functions and Null Values
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Creating Groups of Data
- •Creating Groups of Data: GROUP BY Clause Syntax
- •Using the GROUP BY Clause
- •Grouping by More than One Column
- •Using the GROUP BY Clause on Multiple Columns
- •Illegal Queries Using Group Functions
- •Restricting Group Results
- •Restricting Group Results with the HAVING Clause
- •Using the HAVING Clause
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Nesting Group Functions
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 5: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Types of Joins
- •Joining Tables Using SQL:1999 Syntax
- •Qualifying Ambiguous Column Names
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Creating Natural Joins
- •Retrieving Records with Natural Joins
- •Creating Joins with the USING Clause
- •Joining Column Names
- •Retrieving Records with the USING Clause
- •Using Table Aliases with the USING Clause
- •Creating Joins with the ON Clause
- •Retrieving Records with the ON Clause
- •Creating Three-Way Joins with the ON Clause
- •Applying Additional Conditions to a Join
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Joining a Table to Itself
- •Self-Joins Using the ON Clause
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Nonequijoins
- •Retrieving Records with Nonequijoins
- •Lesson Agenda
- •INNER Versus OUTER Joins
- •LEFT OUTER JOIN
- •RIGHT OUTER JOIN
- •FULL OUTER JOIN
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Cartesian Products
- •Generating a Cartesian Product
- •Creating Cross Joins
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 6: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using a Subquery to Solve a Problem
- •Subquery Syntax
- •Using a Subquery
- •Guidelines for Using Subqueries
- •Types of Subqueries
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Single-Row Subqueries
- •Executing Single-Row Subqueries
- •Using Group Functions in a Subquery
- •The HAVING Clause with Subqueries
- •What Is Wrong with This Statement?
- •No Rows Returned by the Inner Query
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Multiple-Row Subqueries
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Null Values in a Subquery
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 7: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Set Operators
- •Set Operator Guidelines
- •The Oracle Server and Set Operators
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Tables Used in This Lesson
- •Lesson Agenda
- •UNION Operator
- •Using the UNION Operator
- •UNION ALL Operator
- •Using the UNION ALL Operator
- •Lesson Agenda
- •INTERSECT Operator
- •Using the INTERSECT Operator
- •Lesson Agenda
- •MINUS Operator
- •Using the MINUS Operator
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Matching the SELECT Statements
- •Matching the SELECT Statement: Example
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using the ORDER BY Clause in Set Operations
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 8: Overview

Oracle Enterprise Manager Grid Control 10g
•Efficient Oracle Fusion Middleware management
•Simplifying application and infrastructure life cycle management
•Improved database administration and application management capabilities
|
Copyright © 2009, Oracle. All rights reserved. |
Academy |
Oracle Enterprise Manager Grid Control 10g |
||
Spanning applications, middleware, and database management, Oracle Enterprise Manager Grid |
||
Control 10g delivers integrated enterprise management for Ora le and non-Oracle systems. |
||
|
Oracle |
|
Oracle Enterprise Manager Grid Control 10g features adv nced Oracle Fusion Middleware |
||
management capabilities for the services that business applications rely upon, including SOA, |
||
Business Activity Monitoring, and Identity Management. |
|
|
• Wide-ranging management functionality&for your applications including service-level |
||
management, application perform nce management, configuration management, and change |
||
automation |
Only |
|
• Built-in grid automationInternalcapabilitiesUsemeans that information technology responds proactively to fluctuating demand and implements new services more quickly so that businesses can thrive.
• In-depth diagnostics and readily available remediation across a range of applications including custom-built applications, Oracle E-Business Suite, PeopleSoft, Siebel, Oracle Fusion
OracleMiddlewar , Oracle Database, and underlying infrastructure
• Extensive life cycle management capabilities extends grid computing by providing solutions for the entire application and infrastructure life cycle, including test, stage, and production through operations. It has simplified patch management with synchronized patching, additional operating system support, and conflict detection features.
Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals I I - 13
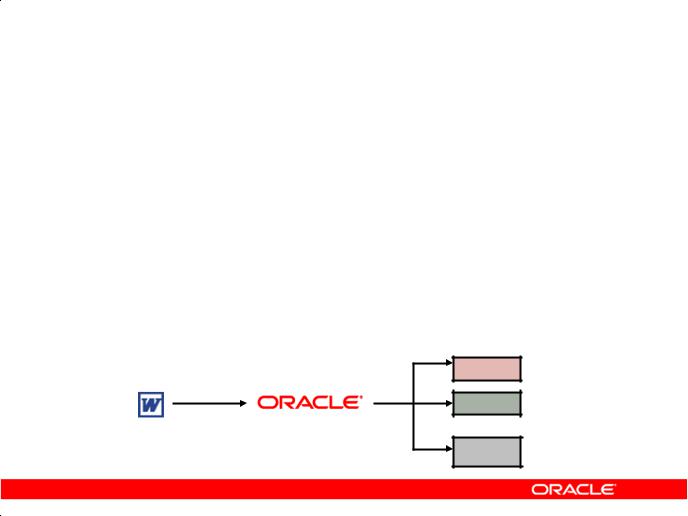
Oracle BI Publisher
•Provides a central architecture for authoring, managing, and delivering information in secure and multiple formats
•Reduces complexity and time to develop, test, and deploy all kinds of reports
–Financial Reports, Invoices, Sales or Purchase orders, XML, and EDI/EFT(eText documents)
•Enables flexible customizations
–For example, a Microsoft Word document report can be generated in multiple formats such as PDF, HTML, Excel,
RTF, and so on. |
|
|
|
BI PUBLISHER |
|
HTML |
||
Microsoft Word |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
Excel |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Copyright © 2009, Oracle. All rights reserved. |
Academy |
|||
Oracle BI Publisher |
|
|
|
|
|
Oracle Database 11g also includes Oracle BI Publisher—the ent rprise reporting solution from |
|||||
Oracle. Oracle BI Publisher (formerly known as XML Publisher) offers the most efficient and |
|||||
scalable reporting solution available for complex, dist ibuted environments. |
|||||
Oracle BI Publisher reduces the high costs associated with the development, customization, and |
|||||
|
|
Oracle |
|||
maintenance of business documents, while increasing the efficiency of reports management. By |
|||||
using a set of familiar desktop tools, users&can create and mai |
tain their own report formats based on |
||||
data queries created by the IT staff or developers. |
Only |
||||
|
|
|
|||
Oracle BI Publisher report fo mats can be de igned using Microsoft Word or Adobe Acrobat—tools |
|||||
that most users are already familiar with. Oracle BI Publisher also enables you to bring in data from |
|||||
multiple data sources i o a single outputUsedocument. You can deliver reports via printer, email, or |
|||||
fax. You can publish your report to a portal. You can even allow users to collaboratively edit and |
|||||
Internal |
|
|
|
|
|
manage reports on the Web-based Distributed Authoring and Versioning (WebDav) Web servers. |
|||||
Oracle |
|
|
|
|
|
Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals I I - 14

Lesson Agenda
•Course objectives, course agenda, and appendixes used in this course
•Overview of Oracle Database 11g and related products
•Overview of relational database management concepts and terminologies
•Introduction to SQL and its development environments
•The HR schema and the tables used in this course
•Oracle Database 11g documentation and additional resources
|
Copyright © 2009, Oracle. All rights reserved. |
Academy |
||
|
|
|||
|
|
Oracle |
||
& |
Only |
|
||
|
Internal |
|
|
|
|
Use |
|
||
Oracle |
|
|
|
|
Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals I I - 15

Relational and Object Relational
Database Management Systems
•Relational model and object relational model
•User-defined data types and objects
•Fully compatible with relational database
•Supports multimedia and large objects
•High-quality database server features
Relational and Object Relational Database Management SystemsAcademy
The Oracle server supports both the relational andOraclethe object re ational database models.
The Oracle server extends the data-modeling capabilities to support an object relational database model that provides object-oriented programming, complex data types, complex business objects, and full compatibility with the relational world.
It includes several features for improved performance& Onlyand fu ctionality of the OLTP applications,
supports client/server and W b-based applications that are distributed and multitiered.
such as better sharing of run-time data structures, larger buffer caches, and deferrable constraints. Data warehouse applicationsInternalbenefit from enhancements such as parallel execution of insert, update, and delete operations; partitioni g; a dUseparallel-aware query optimization. The Oracle model
For more information about the relational and object relational model, see the
Concepts 11g Release 1 (11.1) manual.
Oracle
Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals I I - 16
