
- •Preface
- •Introduction
- •Lesson Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Course Objectives
- •Course Agenda
- •Appendixes Used in the Course
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Oracle Database 11g: Focus Areas
- •Oracle Database 11g
- •Oracle Fusion Middleware
- •Oracle Enterprise Manager Grid Control 10g
- •Oracle BI Publisher
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Relational and Object Relational Database Management Systems
- •Data Storage on Different Media
- •Relational Database Concept
- •Definition of a Relational Database
- •Data Models
- •Entity Relationship Model
- •Relating Multiple Tables
- •Relational Database Terminology
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using SQL to Query Your Database
- •SQL Statements
- •Development Environments for SQL
- •Lesson Agenda
- •The Human Resources (HR) Schema
- •Tables Used in the Course
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Oracle Database 11g Documentation
- •Additional Resources
- •Summary
- •Practice I: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Capabilities of SQL SELECT Statements
- •Basic SELECT Statement
- •Selecting All Columns
- •Selecting Specific Columns
- •Writing SQL Statements
- •Column Heading Defaults
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Arithmetic Expressions
- •Using Arithmetic Operators
- •Operator Precedence
- •Defining a Null Value
- •Null Values in Arithmetic Expressions
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Defining a Column Alias
- •Using Column Aliases
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Concatenation Operator
- •Literal Character Strings
- •Using Literal Character Strings
- •Alternative Quote (q) Operator
- •Duplicate Rows
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Displaying the Table Structure
- •Using the DESCRIBE Command
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 1: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Limiting Rows Using a Selection
- •Limiting the Rows That Are Selected
- •Using the WHERE Clause
- •Character Strings and Dates
- •Comparison Operators
- •Using Comparison Operators
- •Range Conditions Using the BETWEEN Operator
- •Membership Condition Using the IN Operator
- •Pattern Matching Using the LIKE Operator
- •Combining Wildcard Characters
- •Using the NULL Conditions
- •Defining Conditions Using the Logical Operators
- •Using the AND Operator
- •Using the OR Operator
- •Using the NOT Operator
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Rules of Precedence
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using the ORDER BY Clause
- •Sorting
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Substitution Variables
- •Using the Single-Ampersand Substitution Variable
- •Character and Date Values with Substitution Variables
- •Specifying Column Names, Expressions, and Text
- •Using the Double-Ampersand Substitution Variable
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using the DEFINE Command
- •Using the VERIFY Command
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 2: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •SQL Functions
- •Two Types of SQL Functions
- •Single-Row Functions
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Character Functions
- •Case-Conversion Functions
- •Using Case-Conversion Functions
- •Character-Manipulation Functions
- •Using the Character-Manipulation Functions
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Number Functions
- •Using the ROUND Function
- •Using the TRUNC Function
- •Using the MOD Function
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Working with Dates
- •RR Date Format
- •Using the SYSDATE Function
- •Arithmetic with Dates
- •Using Arithmetic Operators with Dates
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Date-Manipulation Functions
- •Using Date Functions
- •Using ROUND and TRUNC Functions with Dates
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 3: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Conversion Functions
- •Implicit Data Type Conversion
- •Explicit Data Type Conversion
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using the TO_CHAR Function with Dates
- •Elements of the Date Format Model
- •Using the TO_CHAR Function with Dates
- •Using the TO_CHAR Function with Numbers
- •Using the TO_NUMBER and TO_DATE Functions
- •Using the TO_CHAR and TO_DATE Function with RR Date Format
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Nesting Functions
- •Lesson Agenda
- •General Functions
- •NVL Function
- •Using the NVL Function
- •Using the NVL2 Function
- •Using the NULLIF Function
- •Using the COALESCE Function
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Conditional Expressions
- •CASE Expression
- •Using the CASE Expression
- •DECODE Function
- •Using the DECODE Function
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 4: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •What Are Group Functions?
- •Types of Group Functions
- •Group Functions: Syntax
- •Using the AVG and SUM Functions
- •Using the MIN and MAX Functions
- •Using the COUNT Function
- •Using the DISTINCT Keyword
- •Group Functions and Null Values
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Creating Groups of Data
- •Creating Groups of Data: GROUP BY Clause Syntax
- •Using the GROUP BY Clause
- •Grouping by More than One Column
- •Using the GROUP BY Clause on Multiple Columns
- •Illegal Queries Using Group Functions
- •Restricting Group Results
- •Restricting Group Results with the HAVING Clause
- •Using the HAVING Clause
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Nesting Group Functions
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 5: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Types of Joins
- •Joining Tables Using SQL:1999 Syntax
- •Qualifying Ambiguous Column Names
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Creating Natural Joins
- •Retrieving Records with Natural Joins
- •Creating Joins with the USING Clause
- •Joining Column Names
- •Retrieving Records with the USING Clause
- •Using Table Aliases with the USING Clause
- •Creating Joins with the ON Clause
- •Retrieving Records with the ON Clause
- •Creating Three-Way Joins with the ON Clause
- •Applying Additional Conditions to a Join
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Joining a Table to Itself
- •Self-Joins Using the ON Clause
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Nonequijoins
- •Retrieving Records with Nonequijoins
- •Lesson Agenda
- •INNER Versus OUTER Joins
- •LEFT OUTER JOIN
- •RIGHT OUTER JOIN
- •FULL OUTER JOIN
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Cartesian Products
- •Generating a Cartesian Product
- •Creating Cross Joins
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 6: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using a Subquery to Solve a Problem
- •Subquery Syntax
- •Using a Subquery
- •Guidelines for Using Subqueries
- •Types of Subqueries
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Single-Row Subqueries
- •Executing Single-Row Subqueries
- •Using Group Functions in a Subquery
- •The HAVING Clause with Subqueries
- •What Is Wrong with This Statement?
- •No Rows Returned by the Inner Query
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Multiple-Row Subqueries
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Null Values in a Subquery
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 7: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Set Operators
- •Set Operator Guidelines
- •The Oracle Server and Set Operators
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Tables Used in This Lesson
- •Lesson Agenda
- •UNION Operator
- •Using the UNION Operator
- •UNION ALL Operator
- •Using the UNION ALL Operator
- •Lesson Agenda
- •INTERSECT Operator
- •Using the INTERSECT Operator
- •Lesson Agenda
- •MINUS Operator
- •Using the MINUS Operator
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Matching the SELECT Statements
- •Matching the SELECT Statement: Example
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using the ORDER BY Clause in Set Operations
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 8: Overview

Objectives
After completing this lesson, you should be able to do the following:
•Identify the available group functions
•Describe the use of group functions
•Group data by using the GROUP BY clause
•Include or exclude grouped rows by using the HAVING clause
Objectives |
Copyright © 2009, Oracle. All rights reserved. |
Academy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oracle |
|
This lesson further addresses functions. It focuses on obtaining summary information (such as averages) for groups of rows. It discusses how to group rows in a table into smaller sets and how to specify search criteria for groups of rows.
& |
Only |
Internal |
|
Use |
|
Oracle |
|
Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals I 5 - 2

Lesson Agenda
•Group functions:
–Types and syntax
–Use AVG, SUM, MIN, MAX, COUNT
–Use DISTINCT keyword within group functions
–NULL values in a group function
•Grouping rows:
–GROUP BY clause
–HAVING clause
•Nesting group functions
|
Copyright © 2009, Oracle. All rights reserved. |
Academy |
||
|
|
|||
|
|
Oracle |
||
& |
Only |
|
||
|
Internal |
|
|
|
|
Use |
|
||
Oracle |
|
|
|
|
Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals I 5 - 3
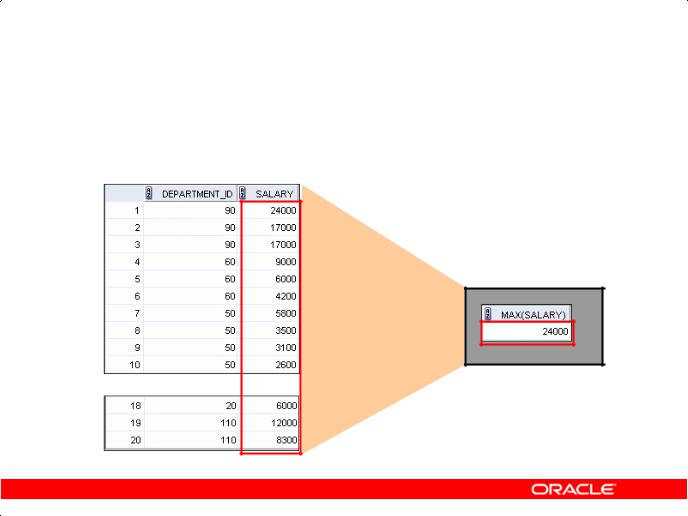
What Are Group Functions?
Group functions operate on sets of rows to give one result per group.
EMPLOYEES
|
Maximum salary in |
|
||
|
EMPLOYEES table |
|
||
… |
|
|
|
Academy |
What Are Group Functions? |
Copyright © 2009, Oracle. All rights reserved. |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
Oracle |
||
Unlike single-row functions, group functions operate on sets of rows to give one result per group. |
||||
These sets may comprise the entire table or the table split into groups. |
||||
|
& |
Only |
|
|
Internal |
|
|
|
|
Oracle |
Use |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals I 5 - 4
Types of Group Functions
• |
AVG |
|
||
• |
COUNT |
|
||
• |
MAX |
|
||
• |
MIN |
|
|
|
|
|
Group |
||
|
||||
• |
STDDEV |
|
|
|
|
|
functions |
||
•SUM
•VARIANCE
Types of Group Functions |
Copyright © 2009, Oracle. All rights reserved. |
Academy |
|
|
Each of the functions accepts an argument. The following table id ntifies the options that you can use in the syntax:
|
Function |
|
Desc iption |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Only |
|
|
Oracle |
|
|
AVG([DISTINCT|ALL]n) |
Average va ue of n, ignoring null values |
|
|
COUNT({*|[DISTINCT|ALL]expr& |
Number of rows, where expr evaluates to |
|
|
|
Internal |
Minimum value of expr, ignoring null values |
|
}) |
|
something other than null (count all selected |
|
|
Use |
|
|
|
|
rows using *, including duplicates and rows |
|
|
|
with nulls) |
|
MAX([DISTINCT|ALL]expr) |
Maximum value of expr, ignoring null values |
|
|
|
|
|
|
MIN([DIST NCT|ALL]expr) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Oracle |
|
|
|
STDDEV([DISTINCT|ALL]x) |
Standard deviation of n, ignoring null values |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SUM([DISTINCT|ALL]n) |
Sum values of n, ignoring null values |
|
|
|
|
|
|
VARIANCE([DISTINCT|ALL]x) |
Variance of n, ignoring null values |
|
|
|
|
|
Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals I 5 - 5
