
- •Preface
- •Introduction
- •Lesson Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Course Objectives
- •Course Agenda
- •Appendixes Used in the Course
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Oracle Database 11g: Focus Areas
- •Oracle Database 11g
- •Oracle Fusion Middleware
- •Oracle Enterprise Manager Grid Control 10g
- •Oracle BI Publisher
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Relational and Object Relational Database Management Systems
- •Data Storage on Different Media
- •Relational Database Concept
- •Definition of a Relational Database
- •Data Models
- •Entity Relationship Model
- •Relating Multiple Tables
- •Relational Database Terminology
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using SQL to Query Your Database
- •SQL Statements
- •Development Environments for SQL
- •Lesson Agenda
- •The Human Resources (HR) Schema
- •Tables Used in the Course
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Oracle Database 11g Documentation
- •Additional Resources
- •Summary
- •Practice I: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Capabilities of SQL SELECT Statements
- •Basic SELECT Statement
- •Selecting All Columns
- •Selecting Specific Columns
- •Writing SQL Statements
- •Column Heading Defaults
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Arithmetic Expressions
- •Using Arithmetic Operators
- •Operator Precedence
- •Defining a Null Value
- •Null Values in Arithmetic Expressions
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Defining a Column Alias
- •Using Column Aliases
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Concatenation Operator
- •Literal Character Strings
- •Using Literal Character Strings
- •Alternative Quote (q) Operator
- •Duplicate Rows
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Displaying the Table Structure
- •Using the DESCRIBE Command
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 1: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Limiting Rows Using a Selection
- •Limiting the Rows That Are Selected
- •Using the WHERE Clause
- •Character Strings and Dates
- •Comparison Operators
- •Using Comparison Operators
- •Range Conditions Using the BETWEEN Operator
- •Membership Condition Using the IN Operator
- •Pattern Matching Using the LIKE Operator
- •Combining Wildcard Characters
- •Using the NULL Conditions
- •Defining Conditions Using the Logical Operators
- •Using the AND Operator
- •Using the OR Operator
- •Using the NOT Operator
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Rules of Precedence
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using the ORDER BY Clause
- •Sorting
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Substitution Variables
- •Using the Single-Ampersand Substitution Variable
- •Character and Date Values with Substitution Variables
- •Specifying Column Names, Expressions, and Text
- •Using the Double-Ampersand Substitution Variable
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using the DEFINE Command
- •Using the VERIFY Command
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 2: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •SQL Functions
- •Two Types of SQL Functions
- •Single-Row Functions
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Character Functions
- •Case-Conversion Functions
- •Using Case-Conversion Functions
- •Character-Manipulation Functions
- •Using the Character-Manipulation Functions
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Number Functions
- •Using the ROUND Function
- •Using the TRUNC Function
- •Using the MOD Function
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Working with Dates
- •RR Date Format
- •Using the SYSDATE Function
- •Arithmetic with Dates
- •Using Arithmetic Operators with Dates
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Date-Manipulation Functions
- •Using Date Functions
- •Using ROUND and TRUNC Functions with Dates
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 3: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Conversion Functions
- •Implicit Data Type Conversion
- •Explicit Data Type Conversion
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using the TO_CHAR Function with Dates
- •Elements of the Date Format Model
- •Using the TO_CHAR Function with Dates
- •Using the TO_CHAR Function with Numbers
- •Using the TO_NUMBER and TO_DATE Functions
- •Using the TO_CHAR and TO_DATE Function with RR Date Format
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Nesting Functions
- •Lesson Agenda
- •General Functions
- •NVL Function
- •Using the NVL Function
- •Using the NVL2 Function
- •Using the NULLIF Function
- •Using the COALESCE Function
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Conditional Expressions
- •CASE Expression
- •Using the CASE Expression
- •DECODE Function
- •Using the DECODE Function
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 4: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •What Are Group Functions?
- •Types of Group Functions
- •Group Functions: Syntax
- •Using the AVG and SUM Functions
- •Using the MIN and MAX Functions
- •Using the COUNT Function
- •Using the DISTINCT Keyword
- •Group Functions and Null Values
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Creating Groups of Data
- •Creating Groups of Data: GROUP BY Clause Syntax
- •Using the GROUP BY Clause
- •Grouping by More than One Column
- •Using the GROUP BY Clause on Multiple Columns
- •Illegal Queries Using Group Functions
- •Restricting Group Results
- •Restricting Group Results with the HAVING Clause
- •Using the HAVING Clause
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Nesting Group Functions
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 5: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Types of Joins
- •Joining Tables Using SQL:1999 Syntax
- •Qualifying Ambiguous Column Names
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Creating Natural Joins
- •Retrieving Records with Natural Joins
- •Creating Joins with the USING Clause
- •Joining Column Names
- •Retrieving Records with the USING Clause
- •Using Table Aliases with the USING Clause
- •Creating Joins with the ON Clause
- •Retrieving Records with the ON Clause
- •Creating Three-Way Joins with the ON Clause
- •Applying Additional Conditions to a Join
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Joining a Table to Itself
- •Self-Joins Using the ON Clause
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Nonequijoins
- •Retrieving Records with Nonequijoins
- •Lesson Agenda
- •INNER Versus OUTER Joins
- •LEFT OUTER JOIN
- •RIGHT OUTER JOIN
- •FULL OUTER JOIN
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Cartesian Products
- •Generating a Cartesian Product
- •Creating Cross Joins
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 6: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using a Subquery to Solve a Problem
- •Subquery Syntax
- •Using a Subquery
- •Guidelines for Using Subqueries
- •Types of Subqueries
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Single-Row Subqueries
- •Executing Single-Row Subqueries
- •Using Group Functions in a Subquery
- •The HAVING Clause with Subqueries
- •What Is Wrong with This Statement?
- •No Rows Returned by the Inner Query
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Multiple-Row Subqueries
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Null Values in a Subquery
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 7: Overview
- •Objectives
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Set Operators
- •Set Operator Guidelines
- •The Oracle Server and Set Operators
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Tables Used in This Lesson
- •Lesson Agenda
- •UNION Operator
- •Using the UNION Operator
- •UNION ALL Operator
- •Using the UNION ALL Operator
- •Lesson Agenda
- •INTERSECT Operator
- •Using the INTERSECT Operator
- •Lesson Agenda
- •MINUS Operator
- •Using the MINUS Operator
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Matching the SELECT Statements
- •Matching the SELECT Statement: Example
- •Lesson Agenda
- •Using the ORDER BY Clause in Set Operations
- •Quiz
- •Summary
- •Practice 8: Overview

Oracle Database 11g: Focus Areas
Information Application
Management Development
Copyright © 2009, Oracle. All rights reserved. |
Academy |
Oracle Database 11g: Focus Areas |
|
Oracle Database 11g offers extensive features across the following focus areas: |
|
• Infrastructure Grids: The Infrastructure Grid technology of Oracle enables pooling of low-cost
servers and storage to form systems that deliver the highest quality of service in terms of |
||
manageability, high availability, and performance. Oracle Database 11g consolidates and |
||
extends the benefits of grid computing. ApartOraclefrom taking full advantage of grid computing, |
||
Oracle Database 11g has unique change assurance features to manage changes in a controlled |
||
and cost effective manner. |
& |
Only |
|
||
|
|
|
• Information Management: Or cle Database 11g extends the existing information management |
||
capabilities in content management, information integration, and information life cycle |
||
management areas. Oracle provides content management of advanced data types such as |
||
|
Use |
|
Extensible Markup Language (XML), text, spatial, multimedia, medical imaging, and semantic |
||
Internal |
|
|
technologies. |
|
|
Oracle |
|
|
• Application Development: Oracle Database 11g has capabilities to use and manage all the major application development environments such as PL/SQL, Java/JDBC, .NET and Windows, PHP, SQL Developer, and Application Express.
Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals I I - 9

|
|
|
|
Academy |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Copyright © 2009, Oracle. All rights reserved. |
|
||
Oracle Database 11g |
|
|
|
||
|
Organizations need to support multiple terabytes of information for users who demand fast and |
||||
|
high-quality service: |
Oracle |
|||
secure access to business applications round-the-clock. The database systems must be reliable and
must be able to recover quickly in the event of any kind of f ilure. Oracle Database 11g is designed
along the following feature areas to help organizations manage infrastructure grids easily and deliver |
|
& |
Only |
• Manageability: By using some of the change assurance, management automation, and fault |
|
Internal |
|
diagnostics features, the datab se dministrators (DBAs) can increase their productivity, reduce |
|
costs, minimize errors, and maximize quality of service. Some of the useful features that |
|
Use |
|
promote better management are Databa e Replay facility, the SQL Performance Analyzer, and the Automatic SQL Tuning facility.
• High availability: By using the high availability features, you can reduce the risk of down time
and data loss. These features improves online operations and enable faster database upgrades. Oracle
Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals I I - 10

Academy
• Performance: By using capabilities such as SecureFiles, compr ssion for online transaction
processing (OLTP), Real Application ClustersOracle(RAC) optimizations, Result Caches and so on, you can greatly improve the performance of your d t b se. Oracle Database 11g enables organizations to manage large, scalable transactional and data warehousing systems that deliver fast data access using low-cost modular storage.
• Security: Oracle Database 11g helps organizations protect their information with unique secure |
|
& |
|
configurations, data encryption nd masking, and sophisticated auditing capabilities. It delivers a |
|
|
Only |
secure and scalableInternalplatform for reliUseble and fast access to all types of information by using the industry-standard interfaces.
•Information integra ion: Oracle Database 11g has many features to better integrate data throughout the e terprise. It also supports advanced information life cycle management capabilities. This helps you manage the changing data in your database.
Oracle
Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals I I - 11
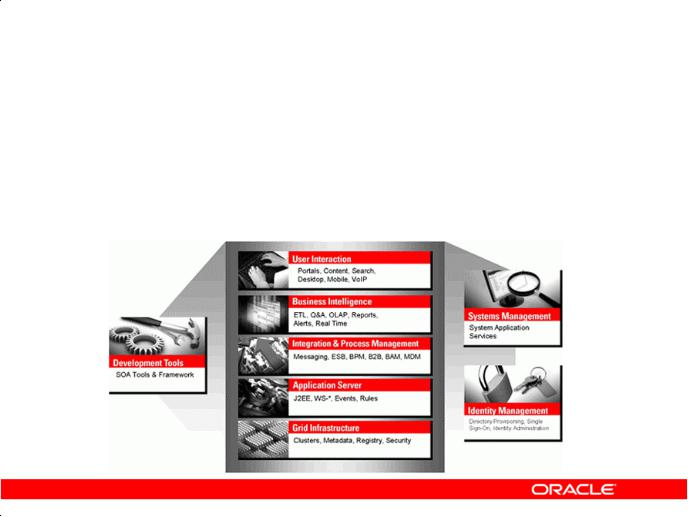
Oracle Fusion Middleware
Portfolio of leading, standards-based, and customer-proven software products that spans a range of tools and services from J2EE and developer tools, through integration services, business intelligence, collaboration, and content management
Academy
Oracle Fusion Middleware is a comprehensive and well-integrat d family of products that offers complete support for development, deployment, and management of Service-Oriented Architecture (SOA). SOA facilitates the development of modular business services that can be easily integrated
and reused, thereby reducing development and maintenance costs, and providing higher quality of |
||
|
|
Only |
services. Oracle Fusion Middleware’s pluggableOraclearchitecture enables you to leverage your |
||
|
& |
|
investments in any existing application, system, or technology. Its unbreakable core technology |
||
|
Internal |
|
minimizes the disruption caused by pl nned or unplanned outages. |
||
|
Use |
|
Some of the products from the Oracle Fusion Middl ware family include: |
||
• |
Enterprise Application Se ver: Application Server |
|
• |
Integration and Proc ss Management: BPEL Process Manager, Oracle Business Process |
|
Analysis Suite
• Development Tools: Oracle Application Development Framework, JDeveloper, SOA Suite Oracle• Business Int lligence: Oracle Business Activity Monitoring, Oracle Data Integrator
• Systems Management: Enterprise Manager
• Identity Management: Oracle Identity Management
• Content Management: Oracle Content Database Suite
• User Interaction: Portal, WebCenter
Oracle Database 11g: SQL Fundamentals I I - 12
