
MSQexam
.docxView Assessment Result
Начало формы
|
|
|
|
Family Name: |
Alzhanov |
|
Given Name: |
Ermek |
|
Login: |
erdau |
|
E-mail: |
11075@iitu.kz |
|
Status: |
Enrolled |
|
|
Assessment Name: |
Exam 1 Multiple-Choice |
|
Instance: |
1 |
|
|
Section: |
SSD9-19424359_Information Systems - 5B070300 - IS 0907 |
|
During: |
Fall 2012 |
|
Section Status: |
Active |
|
|
For course: |
Software Specification, Testing anf Maintenance |
|
(SSD9) |
|
|
Corresponding to: |
SSD9 |
|
At: |
International University of Information Technology (IITU) |
|
|
|
|
|
Your performance was as follows: |
|
|
You took 22 minutes on this assessment from Fri Oct 12 2012 05:36:11 GMT+0600 to Fri Oct 12 2012 05:57:19 GMT+0600. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. |
|
What is the goal of software engineering? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section top of the course notes. |
|
|
|
2. |
|
Which of the following is true of software today? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(d) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 1.2 of the course notes. |
|
|
|
3. |
|
In which of the following phases of software development is fixing a fault normally less costly than in any of the others? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(d) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 1.3 of the course notes. See 1.3-1.4 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
4. |
|
In the context of software engineering, what is a system? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(d) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
5.56 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 1.4 of the course notes. See section 1.7 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
5. |
|
Which of the following statements are true of problem identification?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
5.56 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.1.1 of the course notes. See section 2.2 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
6. |
|
Which of the following is true of the requirements document for a software project? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(d) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.1.2 of the course notes. See section 2.2 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
7. |
|
Which of the following defines traceability of the design document? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(b) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
5.56 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.1.3 of the course notes. See section 2.4 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
8. |
|
Which of the following are produced during the implementation phase of software development?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.1.4 of the course notes. See section 2.5 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
9. |
|
In a software development project, acceptance testing is performed by the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
5.56 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.1.5 of the course notes. See section 2.6 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
10. |
|
Regression testing for a software development project is testing to determine whether |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.1.6 of the course notes. See section 2.7 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
11. |
|
Which of the following is true of the build-and-fix model of software development? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(d) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.2.1 of the course notes. |
|
|
|
12. |
|
Until the 1980s, the only widely accepted life-cycle model of software development was the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(b) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
5.56 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.2.2 of the course notes. See section 3.1 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
13. |
|
Rapid prototyping should be used for what purpose? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 9.3 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
14. |
|
Which of the following disadvantages does the incremental model have?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.2.4 of the course notes. See section 3.4.1 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
15. |
|
Which of the following are true of the synchronize-and-stabilize model of software development?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(d) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
5.56 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.2.5 of the course notes. See section 3.5 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
16. |
|
Which of the following activities are included in a cycle of the spiral?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.2.6 of the course notes. See section 3.6 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
17. |
|
A feature of the fountain model and other object-oriented models is |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(d) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
5.56 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.2.7 of the course notes. See section 3.7 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
18. |
|
An open modular architecture for software is a requirement of the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(d) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
5.56 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.2.4, of the course notes. See section 3.4, 3.8 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
Go to top of assessment. |
|
|
Total score: 44.44 |
|
|
© Copyright 2007 iCarnegie, Inc. All rights reserved. |
Конец формы
View Assessment Result
Начало формы
|
|
|
|
Family Name: |
Bekarystanov |
|
Given Name: |
Talgat |
|
Login: |
tbekarys |
|
E-mail: |
10926@iitu.kz |
|
Status: |
Enrolled |
|
|
Assessment Name: |
Exam 1 Multiple-Choice |
|
Instance: |
1 |

 (a)
The application of engineering techniques to software
production
(a)
The application of engineering techniques to software
production
 (b)
The replacement of hand coding by automatic programming
(b)
The replacement of hand coding by automatic programming
 (c)
The production of fault-free software that satisfies the user's
needs and that is delivered on time and within budget
(c)
The production of fault-free software that satisfies the user's
needs and that is delivered on time and within budget
 (d)
The development of software that conforms to international
standards
(d)
The development of software that conforms to international
standards
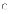 (a)
Most software being written currently is for private businesses
and government organizations.
(a)
Most software being written currently is for private businesses
and government organizations.
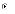 (b)
Software quality is steadily increasing.
(b)
Software quality is steadily increasing.
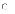 (c)
Most software being written currently is for educational and
entertainment purposes.
(c)
Most software being written currently is for educational and
entertainment purposes.
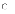 (d)
Software is ubiquitous and its quality often crucial.
(d)
Software is ubiquitous and its quality often crucial.
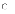 (a)
The implementation phase
(a)
The implementation phase
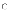 (b)
The integration phase
(b)
The integration phase
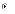 (c)
The maintenance phase
(c)
The maintenance phase
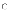 (d)
The design phases
(d)
The design phases
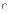 (a)
Any set of hardware components on which a software product will
run
(a)
Any set of hardware components on which a software product will
run
 (b)
Any software product that can be used without any other
software
(b)
Any software product that can be used without any other
software
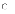 (c)
A combination of software products
(c)
A combination of software products
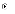 (d)
The combination of hardware and software that runs the product
(d)
The combination of hardware and software that runs the product
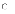 (a)
I and III only
(a)
I and III only
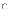 (b)
II only
(b)
II only
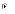 (c)
I only
(c)
I only
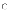 (d)
I and II only
(d)
I and II only
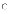 (a)
It includes detailed cost estimates.
(a)
It includes detailed cost estimates.
 (b)
It is a legally binding contract between the client and the
developer.
(b)
It is a legally binding contract between the client and the
developer.
 (c)
It will not change through the life cycle of the software
product.
(c)
It will not change through the life cycle of the software
product.
 (d)
It is a basis for the specification document.
(d)
It is a basis for the specification document.
 (a)
Each design choice, except choices of low-level detail, must be
attributed to a particular member of the design team.
(a)
Each design choice, except choices of low-level detail, must be
attributed to a particular member of the design team.
 (b)
Each design choice, except choices of low-level detail, must be
linked to statements in the specifications document, and each
statement in the specification document must be reflected in some
aspect of the design.
(b)
Each design choice, except choices of low-level detail, must be
linked to statements in the specifications document, and each
statement in the specification document must be reflected in some
aspect of the design.
 (c)
Each design choice, except choices of low-level detail, must be
described by the relevant data structures and algorithms.
(c)
Each design choice, except choices of low-level detail, must be
described by the relevant data structures and algorithms.
 (d)
Each design choice, except choices of low-level detail, must be
linked to statements in the requirements document and each
statement in the requirements document must be reflected in some
aspect of the design.
(d)
Each design choice, except choices of low-level detail, must be
linked to statements in the requirements document and each
statement in the requirements document must be reflected in some
aspect of the design.
 (a)
I only
(a)
I only
 (b)
I and II only
(b)
I and II only
 (c)
I, II, and III
(c)
I, II, and III
 (d)
I and III only
(d)
I and III only
 (a)
client on the client's hardware with actual data
(a)
client on the client's hardware with actual data
 (b)
client on the developer's hardware with actual data
(b)
client on the developer's hardware with actual data
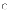 (c)
developer on the client's hardware with actual data
(c)
developer on the client's hardware with actual data
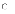 (d)
client on the client's hardware with test data
(d)
client on the client's hardware with test data
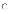 (a)
a component that was unchanged during changes to other components
still performs correctly
(a)
a component that was unchanged during changes to other components
still performs correctly
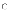 (b)
a module or product hasn't lost code
(b)
a module or product hasn't lost code
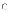 (c)
any modules inside a changed component still communicate
correctly
(c)
any modules inside a changed component still communicate
correctly
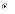 (d)
a problem that instigated an attempted fix has indeed been fixed
(d)
a problem that instigated an attempted fix has indeed been fixed
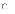 (a)
It is a good choice for large-scale software products.
(a)
It is a good choice for large-scale software products.
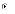 (b)
It is never justified given the modern tools that are now
available.
(b)
It is never justified given the modern tools that are now
available.
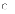 (c)
It has been a widely used life-cycle model since the 1980s.
(c)
It has been a widely used life-cycle model since the 1980s.
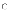 (d)
It is considered to be an incomplete life-cycle model.
(d)
It is considered to be an incomplete life-cycle model.
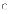 (a)
Spiral model
(a)
Spiral model
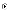 (b)
Waterfall model
(b)
Waterfall model
 (c)
Build-and-fix model
(c)
Build-and-fix model
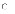 (d)
Rapid prototyping model
(d)
Rapid prototyping model
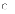 (a)
Eliciting requirements from the user
(a)
Eliciting requirements from the user
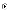 (b)
To transition into the final product with a minimum of
recoding
(b)
To transition into the final product with a minimum of
recoding
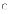 (c)
As a substitute for specifications
(c)
As a substitute for specifications
 (d)
As a substitute for design documents
(d)
As a substitute for design documents
 (a)
I, II, and III
(a)
I, II, and III
 (b)
I and III only
(b)
I and III only
 (c)
II and III only
(c)
II and III only
 (d)
I only
(d)
I only
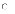 (a)
I, II, and III
(a)
I, II, and III
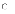 (b)
II only
(b)
II only
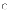 (c)
I only
(c)
I only
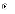 (d)
I and III only
(d)
I and III only
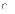 (a)
I and II only
(a)
I and II only
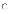 (b)
II and III only
(b)
II and III only
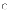 (c)
I, II, and III
(c)
I, II, and III
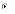 (d)
II only
(d)
II only
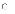 (a)
shorter overall development times
(a)
shorter overall development times
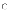 (b)
ease of application
(b)
ease of application
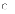 (c)
greater acceptability by clients
(c)
greater acceptability by clients
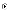 (d)
overlap between development phases
(d)
overlap between development phases
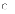 (a)
synchronize-and-stabilize model
(a)
synchronize-and-stabilize model
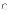 (b)
fountain model
(b)
fountain model
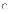 (c)
waterfall model
(c)
waterfall model
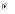 (d)
incremental model
(d)
incremental model