
Let
.docx|
What is the goal of software engineering? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(b) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section top of the course notes. |
|
|
|
2. |
|
Which of the following is true about the probable effect of adding new programmers to a software project? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(b) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 1.1 of the course notes. See section 1.5 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
3. |
|
It has been said that software should be engineered like bridges. Of the following, which best describes the value of this analogy? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 1.2 of the course notes. See section 1.1 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
4. |
|
Which of the following is true of software today? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
You did not answer this question. |
|
|
Correct answer is |
(b) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 1.2 of the course notes. |
|
|
|
5. |
|
Which of the following normally happens during the implementation phase of software development? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(b) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 1.3 of the course notes. See section 1.3 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
6. |
|
In which of the following phases of software development is fixing a fault normally less costly than in any of the others? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 1.3 of the course notes. See 1.3-1.4 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
7. |
|
Over the entire life cycle of a software product, which phase typically takes the most time? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 1.3 of the course notes. See 1.3 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
8. |
|
Which of the following is characteristic of internal software development? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 1.4 of the course notes. See section 2.1 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
9. |
|
In a software product development context, the developer is the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 1.4 of the course notes. See section 2.1 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
10. |
|
In the context of software engineering, what is a product? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(d) |
|
Which of the following statements are true of problem identification?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
7.14 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.1.1 of the course notes. See section 2.2 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
2. |
|
Who should be involved in requirements testing for a software project? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(b) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
7.14 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.1.2 of the course notes. See section 2.2 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
3. |
|
For a software development project, who participates in design phase testing? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.1.3 of the course notes. See section 2.4 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
4. |
|
Which of the following are produced during the implementation phase of software development?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(d) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
7.14 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.1.4 of the course notes. See section 2.5 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
5. |
|
In software development, which of the following testing approaches are used in integration testing?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
7.14 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.1.5 of the course notes. See section 2.6 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
6. |
|
Which of the following is true of maintenance in software development? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.1.6 of the course notes. See section 2.7 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
7. |
|
A build-and-fix model for software development is appropriate in which of the following instances? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
7.14 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.2.1 of the course notes. |
|
|
|
8. |
|
Until the 1980s, the only widely accepted life-cycle model of software development was the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
7.14 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.2.2 of the course notes. See section 3.1 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
9. |
|
Which of the following are true of the typical rapid prototype?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.2.3 of the course notes. See sections 3.3, 9.3 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
10. |
|
When the incremental model is being used, work on specifications for a new increment should |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
7.14 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 3.4.1 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
11. |
|
Which of the following are true of the synchronize-and-stabilize model of software development?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
7.14 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.2.5 of the course notes. See section 3.5 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
12. |
|
A feature of the spiral model that distinguishes it from other life-cycle models is the |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
7.14 |

 (a)
The replacement of hand coding by automatic programming
(a)
The replacement of hand coding by automatic programming
 (b)
The production of fault-free software that satisfies the user's
needs and that is delivered on time and within budget
(b)
The production of fault-free software that satisfies the user's
needs and that is delivered on time and within budget
 (c)
The development of software that conforms to international
standards
(c)
The development of software that conforms to international
standards
 (d)
The application of engineering techniques to software production
(d)
The application of engineering techniques to software production
 (a)
Production will generally be sped up because programmers are
generally most productive when they first start on a project.
(a)
Production will generally be sped up because programmers are
generally most productive when they first start on a project.
 (b)
Production will generally be slowed because of the need for
training and additional coordination.
(b)
Production will generally be slowed because of the need for
training and additional coordination.
 (c)
Production will generally be sped up because new programmers
generally bring bright new implementation ideas to a project.
(c)
Production will generally be sped up because new programmers
generally bring bright new implementation ideas to a project.
 (d)
Production will generally be sped up because of the decrease in
pressure on the programmers already working on the project.
(d)
Production will generally be sped up because of the decrease in
pressure on the programmers already working on the project.
 (a)
Building software is so different from building bridges that the
analogy should be totally rejected.
(a)
Building software is so different from building bridges that the
analogy should be totally rejected.
 (b)
Building software is quite similar to building bridges, so many
aspects of software design and development should be closely
modeled on bridge design and construction.
(b)
Building software is quite similar to building bridges, so many
aspects of software design and development should be closely
modeled on bridge design and construction.
 (c)
Software design and development should be planned with the same
care that is put into designing and building bridges.
(c)
Software design and development should be planned with the same
care that is put into designing and building bridges.
 (d)
Software crashes are never as important as bridge failures, so the
analogy is meaningless.
(d)
Software crashes are never as important as bridge failures, so the
analogy is meaningless.
 (a)
Most software being written currently is for educational and
entertainment purposes.
(a)
Most software being written currently is for educational and
entertainment purposes.
 (b)
Software is ubiquitous and its quality often crucial.
(b)
Software is ubiquitous and its quality often crucial.
 (c)
Most software being written currently is for private businesses
and government organizations.
(c)
Most software being written currently is for private businesses
and government organizations.
 (d)
Software quality is steadily increasing.
(d)
Software quality is steadily increasing.
 (a)
Modules are coded and then the modular architecture is
revised.
(a)
Modules are coded and then the modular architecture is
revised.
 (b)
Modules are coded and tested.
(b)
Modules are coded and tested.
 (c)
Modules are coded but not tested.
(c)
Modules are coded but not tested.
 (d)
Modules and architecture are documented.
(d)
Modules and architecture are documented.
 (a)
The maintenance phase
(a)
The maintenance phase
 (b)
The implementation phase
(b)
The implementation phase
 (c)
The design phases
(c)
The design phases
 (d)
The integration phase
(d)
The integration phase
 (a)
Implementation
(a)
Implementation
 (b)
Design
(b)
Design
 (c)
Maintenance
(c)
Maintenance
 (d)
Specification
(d)
Specification
 (a)
The client and the developer are in the same organization.
(a)
The client and the developer are in the same organization.
 (b)
The developer and the user are in independent organizations.
(b)
The developer and the user are in independent organizations.
 (c)
The client and the developer are in independent
organizations.
(c)
The client and the developer are in independent
organizations.
 (d)
The client and the user are in independent organizations.
(d)
The client and the user are in independent organizations.
 (a)
individual or organization that creates the software product
(a)
individual or organization that creates the software product
 (b)
audience for the product
(b)
audience for the product
 (c)
individual or organization that specifies the software
product
(c)
individual or organization that specifies the software
product
 (d)
individual or organization that pays for the product
(d)
individual or organization that pays for the product
 (a)
Any document directed to the client that is produced during
software development
(a)
Any document directed to the client that is produced during
software development
 (b)
Any nontrivial piece of hardware on which software is to be
developed
(b)
Any nontrivial piece of hardware on which software is to be
developed
 (c)
The output of a life-cycle phase
(c)
The output of a life-cycle phase
 (d)
Any nontrivial piece of software
(d)
Any nontrivial piece of software
 (a)
I only
(a)
I only
 (b)
I and III only
(b)
I and III only
 (c)
I and II only
(c)
I and II only
 (d)
II only
(d)
II only
 (a)
The developer's SQA group and the client's SQA group
(a)
The developer's SQA group and the client's SQA group
 (b)
The developer's SQA group, the client, and the user
(b)
The developer's SQA group, the client, and the user
 (c)
The client's SQA group, the developer and the user
(c)
The client's SQA group, the developer and the user
 (d)
The developer's SQA group and the client's management
(d)
The developer's SQA group and the client's management
 (a)
The developer's SQA group and the design team
(a)
The developer's SQA group and the design team
 (b)
The client, the user, and the developer
(b)
The client, the user, and the developer
 (c)
The design team and the client
(c)
The design team and the client
 (d)
The client's SQA group and the design team
(d)
The client's SQA group and the design team
 (a)
I only
(a)
I only
 (b)
I and II only
(b)
I and II only
 (c)
I and III only
(c)
I and III only
 (d)
I, II, and III
(d)
I, II, and III
 (a)
III only
(a)
III only
 (b)
II and III only
(b)
II and III only
 (c)
I, II, and III
(c)
I, II, and III
 (d)
I and II only
(d)
I and II only
 (a)
It is an integral part of the software process.
(a)
It is an integral part of the software process.
 (b)
It is typically performed by the user.
(b)
It is typically performed by the user.
 (c)
It is something to be avoided, wherever and whenever
possible.
(c)
It is something to be avoided, wherever and whenever
possible.
 (d)
It typically begins a few years after the original delivery.
(d)
It typically begins a few years after the original delivery.
 (a)
The product is small and the requirements are simple and well
defined.
(a)
The product is small and the requirements are simple and well
defined.
 (b)
The customer cannot enunciate the requirements.
(b)
The customer cannot enunciate the requirements.
 (c)
The product will have a short lifetime.
(c)
The product will have a short lifetime.
 (d)
The customer is willing to pay the money.
(d)
The customer is willing to pay the money.
 (a)
Waterfall model
(a)
Waterfall model
 (b)
Rapid prototyping model
(b)
Rapid prototyping model
 (c)
Spiral model
(c)
Spiral model
 (d)
Build-and-fix model
(d)
Build-and-fix model
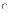 (a)
I only
(a)
I only
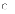 (b)
I and II only
(b)
I and II only
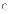 (c)
I and III only
(c)
I and III only
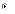 (d)
I, II, and III
(d)
I, II, and III
 (a)
be delayed until detailed design of the previous increment is
completed
(a)
be delayed until detailed design of the previous increment is
completed
 (b)
begin as soon as specifications for the previous increment are
completed
(b)
begin as soon as specifications for the previous increment are
completed
 (c)
be delayed until architectural design of the previous increment is
completed
(c)
be delayed until architectural design of the previous increment is
completed
 (d)
begin as soon as requirements for the previous increment are
completed
(d)
begin as soon as requirements for the previous increment are
completed
 (a)
I and III only
(a)
I and III only
 (b)
I, II, and III
(b)
I, II, and III
 (c)
II only
(c)
II only
 (d)
I only
(d)
I only
 (a)
use of risk analysis prior to each phase
(a)
use of risk analysis prior to each phase
 (b)
presence of feedback between phases
(b)
presence of feedback between phases
 (c)
appropriateness of use for both internal and contract software
development
(c)
appropriateness of use for both internal and contract software
development
 (d)
applicability to both small and large-scale software products
(d)
applicability to both small and large-scale software products