
QUiz
.docx
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 7.2, page 113 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
5. |
|
Software architecture |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(d) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See chapter 7, page 109 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
6. |
|
Walker Royce, the textbook's author, defines a model as a relatively independent abstraction of a system and defines a view as a subset of a model that abstracts a specific, relevant perspective. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(d) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.3.1 of the course notes. See chapter 7, page 110 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
7. |
|
Stable software architectures |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 7.1, page 115 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
8. |
|
An architecture baseline |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(d) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See chapter 7, page 9, Key Points in the textbook. |
|
|
|
9. |
|
Software architecture is an important part of the modern software process. Of the following statements about it, which is true? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(d) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.3.1 of the course notes. See chapter 7, page 109 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
10. |
|
Architecture-first development |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
What is considered in the environment workflow? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 8.1, page 120, and Glossary, page 393 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
2. |
|
The design workflow includes the activities associated with |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 8.1, page 120, and Glossary, page 392 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
3. |
|
What is vertical prototyping? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.4.1 of the course notes. |
|
|
|
4. |
|
What differentiates the life-cycle phases of the modern process from the life-cycle phases of the conventional process? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See chapter 8, page 118 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
5. |
|
What represents a major challenge for project management in the modern process? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(d) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.4.1 of the course notes. |
|
|
|
6. |
|
How many iterations of each workflow should be present in each phase? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(d) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 8.1, page 119 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
7. |
|
What characterizes a software process workflow?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 8.1, page 118 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
8. |
|
An iteration is defined as |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(d) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 8.2, page 121, and Glossary, page 393 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
9. |
|
Is there an order in which the workflows should be executed? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See chapter 8 and section 8.1, pages 117-18 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
10. |
|
What is a possible use for horizontal prototyping? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
What is horizontal prototyping? |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(b) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.4.1 of the course notes. |
|
|
|
2. |
|
What is true about iterations and workflows?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(d) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 2.4.1 of the course notes. |
|
|
|
3. |
|
What characterizes a software process workflow?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(d) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |

 (a) it
is not complete unless it contains all design models
(a) it
is not complete unless it contains all design models
 (b) it
cannot have supplementary material
(b) it
cannot have supplementary material
 (c) it
encompasses a design view, a process view, a use case view, a
component view, and a deployment view
(c) it
encompasses a design view, a process view, a use case view, a
component view, and a deployment view
 (d) it
does not require effort beyond preparing models, which are
prepared as part of the process
(d) it
does not require effort beyond preparing models, which are
prepared as part of the process (a) can
be performed by inexperienced people
(a) can
be performed by inexperienced people
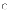 (b) is
a very exact science
(b) is
a very exact science
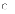 (c) is
a paper-only exercise and can't be demonstrated
(c) is
a paper-only exercise and can't be demonstrated
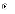 (d) has
very fuzzy guidelines
(d) has
very fuzzy guidelines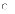 (a) Shaw
and Garlan's architectural definition is closer to a view than a
model.
(a) Shaw
and Garlan's architectural definition is closer to a view than a
model.
 (b) Shaw
and Garlan's architectural approach has nothing to do with a view
or a model.
(b) Shaw
and Garlan's architectural approach has nothing to do with a view
or a model.
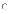 (c) Shaw
and Garlan's view is not particularly abstract.
(c) Shaw
and Garlan's view is not particularly abstract.
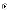 (d) Shaw
and Garlan's architectural definition is closer to a model than a
view.
(d) Shaw
and Garlan's architectural definition is closer to a model than a
view.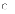 (a) can
never be changed
(a) can
never be changed
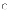 (b) must
be developed before the project is started
(b) must
be developed before the project is started
 (c) are
developed iteratively
(c) are
developed iteratively
 (d) are
developed only in the inception phase after a few iterations
(d) are
developed only in the inception phase after a few iterations (a) is
a paper document
(a) is
a paper document
 (b) is
extracted from requirements models
(b) is
extracted from requirements models
 (c) is
the ultimate goal of the construction phase
(c) is
the ultimate goal of the construction phase
 (d) is
a collection of information across all the engineering sets
(d) is
a collection of information across all the engineering sets (a) The
concept of "architecture" isn't very precise, so system
components can be represented in any way that is
convenient.
(a) The
concept of "architecture" isn't very precise, so system
components can be represented in any way that is
convenient.
 (b) Almost
everyone agrees that the Unified Modeling Language definition of
software architecture is the best.
(b) Almost
everyone agrees that the Unified Modeling Language definition of
software architecture is the best.
 (c) It
should always be represented in Unified Modeling Language
constructs as long as what is being created is object-oriented
software.
(c) It
should always be represented in Unified Modeling Language
constructs as long as what is being created is object-oriented
software.
 (d) Not
everyone agrees on the definition of or notation for software
architecture.
(d) Not
everyone agrees on the definition of or notation for software
architecture. (a) relies
on project management's understanding of all technical details of
architectural description
(a) relies
on project management's understanding of all technical details of
architectural description
 (b) is
less critical to project success in modern project
management
(b) is
less critical to project success in modern project
management
 (c) is
critical to project success and software management
(c) is
critical to project success and software management
 (d) is
a relatively straightforward and not particularly difficult
undertaking
(d) is
a relatively straightforward and not particularly difficult
undertaking (a) Installation
of the programming environment
(a) Installation
of the programming environment
 (b) Planning
and control of the external conditions that could affect the
project
(b) Planning
and control of the external conditions that could affect the
project
 (c) Evolution
of the maintenance environment and automation of the production of
the artifact sets
(c) Evolution
of the maintenance environment and automation of the production of
the artifact sets
 (d) Definition
of the architecture objectives
(d) Definition
of the architecture objectives (a) testing
components
(a) testing
components
 (b) planning
the content of the release
(b) planning
the content of the release
 (c) modeling
the solution and evolving the architecture
(c) modeling
the solution and evolving the architecture
 (d) maintaining
the software change-order database
(d) maintaining
the software change-order database (a) The
development of prototypes that demonstrate the exact functionality
of a product for only a small section of the entire
product
(a) The
development of prototypes that demonstrate the exact functionality
of a product for only a small section of the entire
product
 (b) The
development of prototypes that include stubs for the parts of the
system not yet implemented
(b) The
development of prototypes that include stubs for the parts of the
system not yet implemented
 (c) The
development of prototypes layer by layer
(c) The
development of prototypes layer by layer
 (d) The
development of prototypes that start from the user interface and
work their way down into the system
(d) The
development of prototypes that start from the user interface and
work their way down into the system (a) The
phases can be executed in any order, as opposed to the sequential
order of the conventional process.
(a) The
phases can be executed in any order, as opposed to the sequential
order of the conventional process.
 (b) The
phases are defined in terms of the artifact sets that have to be
produced rather than in terms of activities.
(b) The
phases are defined in terms of the artifact sets that have to be
produced rather than in terms of activities.
 (c) The
phases represent states of the project rather than a sequence of
activities.
(c) The
phases represent states of the project rather than a sequence of
activities.
 (d) The
phases include management activities, which are not considered in
the conventional process.
(d) The
phases include management activities, which are not considered in
the conventional process. (a) To
decide what workflow to perform in each iteration
(a) To
decide what workflow to perform in each iteration
 (b) To
decide the order in which the workflows are going to be
performed
(b) To
decide the order in which the workflows are going to be
performed
 (c) To
decide the artifacts to be built in each iteration
(c) To
decide the artifacts to be built in each iteration
 (d) To
decide what tasks and components are going to be part of each
iteration
(d) To
decide what tasks and components are going to be part of each
iteration (a) There
should always be at least two iterations of each
workflow.
(a) There
should always be at least two iterations of each
workflow.
 (b) Usually
three iterations of each workflow are enough.
(b) Usually
three iterations of each workflow are enough.
 (c) The
number of iterations depends on the size of the team working in
the phase.
(c) The
number of iterations depends on the size of the team working in
the phase.
 (d) The
activities of each workflow may require more than one iteration in
order to achieve the desired results.
(d) The
activities of each workflow may require more than one iteration in
order to achieve the desired results.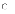 (a) II
only
(a) II
only
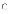 (b) I
and II only
(b) I
and II only
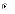 (c) II
and III only
(c) II
and III only
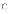 (d) I,
II, and III
(d) I,
II, and III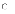 (a) the
phases that make up the life-cycle process
(a) the
phases that make up the life-cycle process
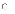 (b) the
effort involved in each phase of the process
(b) the
effort involved in each phase of the process
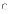 (c) the
set of all software process workflows
(c) the
set of all software process workflows
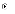 (d) a
distinct sequence of activities within a phase, resulting in a
release
(d) a
distinct sequence of activities within a phase, resulting in a
release (a) No,
the workflows are performed concurrently even though internally
they are composed of mostly sequential activities.
(a) No,
the workflows are performed concurrently even though internally
they are composed of mostly sequential activities.
 (b) Yes,
the workflows should be executed in the order in which they are
presented in the text book.
(b) Yes,
the workflows should be executed in the order in which they are
presented in the text book.
 (c) Yes,
but the deployment workflow cannot begin until all the other
workflows are complete.
(c) Yes,
but the deployment workflow cannot begin until all the other
workflows are complete.
 (d) Yes,
but the management workflow has to be complete before starting
work on any other workflow.
(d) Yes,
but the management workflow has to be complete before starting
work on any other workflow. (a) Demonstration
of user interfaces when the actual working functions haven't yet
been implemented
(a) Demonstration
of user interfaces when the actual working functions haven't yet
been implemented
 (b) Demonstration
and testing of all the file conversion features of a text
editor
(b) Demonstration
and testing of all the file conversion features of a text
editor
 (c) Demonstration
of proper communication between two systems
(c) Demonstration
of proper communication between two systems
 (d) Demonstration
of the complete "move" features of a graphics editor
(d) Demonstration
of the complete "move" features of a graphics editor (a) The
development of prototypes that are developed by multiple teams
working concurrently
(a) The
development of prototypes that are developed by multiple teams
working concurrently
 (b) The
development of prototypes that demonstrate a broad spectrum of the
product's features without extensive functionality behind each
function
(b) The
development of prototypes that demonstrate a broad spectrum of the
product's features without extensive functionality behind each
function
 (c) The
development of prototypes that only consider user interface
aspects
(c) The
development of prototypes that only consider user interface
aspects
 (d) The
development of prototypes that cover a branch of the system,
showing the complete functionality behind each function
(d) The
development of prototypes that cover a branch of the system,
showing the complete functionality behind each function (a) I
only
(a) I
only
 (b) III
only
(b) III
only
 (c) I
and II only
(c) I
and II only
 (d) I
and III only
(d) I
and III only (a) II
only
(a) II
only
 (b) I,
II, and III
(b) I,
II, and III
 (c) I
and II only
(c) I
and II only
 (d) II
and III only
(d) II
and III only