
QUiz
.docx
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 4.2, page 63 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
4. |
|
A component |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(b) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 4.2, page 63 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
5. |
|
Requirements creep can be addressed by |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 4.2, page 66 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
6. |
|
Attrition of key personnel can be addressed by |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 4.2, page 66 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
7. |
|
Round-trip engineering |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 4.2, page 64 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
8. |
|
Intermediate releases in groups of usage scenarios |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 4.2, page 65 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
9. |
|
The architecture-first approach |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 4.2, page 63 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
10. |
|
Obsolete principles of conventional project management include |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
Component-based development |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(b) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 4.2, page 63 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
2. |
|
Configurable processes that are economically scalable |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(d) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 4.2, page 65 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
3. |
|
Iterative life-cycle processes that confront risk early |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 4.2, page 63 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
4. |
|
Model-based development |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(b) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 4.3, page 68 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
5. |
|
A demonstration-based approach |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 4.2, page 65 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
6. |
|
Objective quality control |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 4.2, page 65 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
7. |
|
The architecture-first approach |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(b) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 4.2, page 63 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
8. |
|
All of the following are true except |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
0.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 4.2, page 64 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
9. |
|
Change-management environments |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 4.2, page 63 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
10. |
|
The author's top 10 principles |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
Unsuccessful projects are typically characterized by |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(c) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See chapter 5, page 73 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
2. |
|
The elaboration phase |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 5.1, page 77, and section 5.3, pages 77-8 in the textbook. |
|
|
|
3. |
|
In iterative processes, which of the following are true?
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Correct answer is |
(a) |
|
|
Your score on this question is: |
10.00 |
|
|
Feedback: |
See section 5.1-3, pages 76-8 in the textbook. |
|

 (a) is
any collection of modules
(a) is
any collection of modules
 (b) is
a cohesive set of preexisting lines of code with defined interface
and behavior
(b) is
a cohesive set of preexisting lines of code with defined interface
and behavior
 (c) renders
ideas of coupling and cohesion obsolete
(c) renders
ideas of coupling and cohesion obsolete
 (d) must
always exist when a design is contemplated
(d) must
always exist when a design is contemplated (a) demonstration-based
review
(a) demonstration-based
review
 (b) early
architecture performance feedback
(b) early
architecture performance feedback
 (c) incremental
releases
(c) incremental
releases
 (d) component-based
development
(d) component-based
development (a) successful
early iterations and trustworthy management
(a) successful
early iterations and trustworthy management
 (b) giving
most of the responsibility to a project's average
performers
(b) giving
most of the responsibility to a project's average
performers
 (c) a
very structured environment
(c) a
very structured environment
 (d) hiring
the best candidates
(d) hiring
the best candidates (a) requires
automation
(a) requires
automation
 (b) is
necessary for an integrated environment
(b) is
necessary for an integrated environment
 (c) discourages
change
(c) discourages
change
 (d) eliminates
the need for change management
(d) eliminates
the need for change management (a) eliminate
the need for use cases
(a) eliminate
the need for use cases
 (b) are
only required for baselines
(b) are
only required for baselines
 (c) demonstrate
an evolving understanding of system requirements
(c) demonstrate
an evolving understanding of system requirements
 (d) have
nothing to do with use cases
(d) have
nothing to do with use cases (a) implies
that balance must be achieved among driving design requirements,
design decisions, and life-cycle plans before resources are
committed for full-scale development
(a) implies
that balance must be achieved among driving design requirements,
design decisions, and life-cycle plans before resources are
committed for full-scale development
 (b) keeps
projects from being done concurrently
(b) keeps
projects from being done concurrently
 (c) has
little impact on project planning
(c) has
little impact on project planning
 (d) only
applies to the first two iterations of a project
(d) only
applies to the first two iterations of a project (a) "Design
without documentation is not design."
(a) "Design
without documentation is not design."
 (b) "People
and time are not interchangeable."
(b) "People
and time are not interchangeable."
 (c) "Realize
that software's entropy increases."
(c) "Realize
that software's entropy increases."
 (d) "Expect
mediocrity."
(d) "Expect
mediocrity." (a) requires
code generators
(a) requires
code generators
 (b) is
necessary to reduce the amount of human-generated
code
(b) is
necessary to reduce the amount of human-generated
code
 (c) eliminates
source lines of code (SLOC) as a metric
(c) eliminates
source lines of code (SLOC) as a metric
 (d) can
be used any time there is a code library available
(d) can
be used any time there is a code library available (a) mean
that the process chosen must work for all contemplated
projects
(a) mean
that the process chosen must work for all contemplated
projects
 (b) violate
the 80/20 rule
(b) violate
the 80/20 rule
 (c) hardly
ever yield a return on the effort expended
(c) hardly
ever yield a return on the effort expended
 (d) mean
that a common process spirit, extensive process automation, and
architectural patterns and components can be reused
(d) mean
that a common process spirit, extensive process automation, and
architectural patterns and components can be reused (a) increase
predictability and avoid expensive downstream scrap and
rework
(a) increase
predictability and avoid expensive downstream scrap and
rework
 (b) put
priority on early delivery to increase stakeholder
confidence
(b) put
priority on early delivery to increase stakeholder
confidence
 (c) cannot
address all stakeholder concerns
(c) cannot
address all stakeholder concerns
 (d) are
easier for inexperienced managers to apply
(d) are
easier for inexperienced managers to apply (a) requires
visual modeling and risk control
(a) requires
visual modeling and risk control
 (b) requires
object-oriented methods and rigorous notation
(b) requires
object-oriented methods and rigorous notation
 (c) requires
visual modeling and round-trip engineering
(c) requires
visual modeling and round-trip engineering
 (d) requires
complementary tools and integrated environments
(d) requires
complementary tools and integrated environments (a) allows
for early elimination of architectural defects
(a) allows
for early elimination of architectural defects
 (b) requires
architectural defects to be tolerated for early
releases
(b) requires
architectural defects to be tolerated for early
releases
 (c) makes
architectural defects inevitable
(c) makes
architectural defects inevitable
 (d) eliminates
the need for a beta test
(d) eliminates
the need for a beta test (a) is
independent of process and is applied directly to evolving
artifacts
(a) is
independent of process and is applied directly to evolving
artifacts
 (b) only
applies to project management
(b) only
applies to project management
 (c) requires
well-defined measures derived directly from evolving
artifacts
(c) requires
well-defined measures derived directly from evolving
artifacts
 (d) is
only important at baselines
(d) is
only important at baselines (a) keeps
projects from being done concurrently
(a) keeps
projects from being done concurrently
 (b) implies
that balance must be achieved among driving design requirements,
design decisions, and life-cycle plans before resources are
committed for full-scale development
(b) implies
that balance must be achieved among driving design requirements,
design decisions, and life-cycle plans before resources are
committed for full-scale development
 (c) only
applies to the first two iterations of a project
(c) only
applies to the first two iterations of a project
 (d) has
little impact on project planning
(d) has
little impact on project planning (a) The
iterative life-cycle process addresses risk management.
(a) The
iterative life-cycle process addresses risk management.
 (b) The
architecture-first approach addresses the central design element
of the spiral method.
(b) The
architecture-first approach addresses the central design element
of the spiral method.
 (c) Change
management is the manual element of modern
process.
(c) Change
management is the manual element of modern
process.
 (d) Component-based
development addresses technology elements of the spiral method.
(d) Component-based
development addresses technology elements of the spiral method. (a) require
objectively controlled baselines
(a) require
objectively controlled baselines
 (b) are
too expensive for small projects
(b) are
too expensive for small projects
 (c) rely
on guidelines derived from the experience of experts
(c) rely
on guidelines derived from the experience of experts
 (d) are
only important for baselines
(d) are
only important for baselines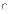 (a) map
directly to cost model parameters
(a) map
directly to cost model parameters
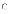 (b) have
no economic implications for software development costs
(b) have
no economic implications for software development costs
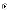 (c) have
a one-to-one relationship with cost model parameters
(c) have
a one-to-one relationship with cost model parameters
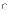 (d) have
no relationship with cost model parameters
(d) have
no relationship with cost model parameters (a) a
jump right to coding
(a) a
jump right to coding
 (b) too
much analysis
(b) too
much analysis
 (c) a
failure to find a balance between research and
production
(c) a
failure to find a balance between research and
production
 (d) conventional
software processes
(d) conventional
software processes (a) is
the second phase of a life cycle and focuses on the elaboration of
an architecture baseline consistent with a production plan and a
requirements vision
(a) is
the second phase of a life cycle and focuses on the elaboration of
an architecture baseline consistent with a production plan and a
requirements vision
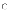 (b) concentrates
on research aspects of a project in every iteration of a project's
life cycle
(b) concentrates
on research aspects of a project in every iteration of a project's
life cycle
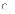 (c) happens
only once in the lifetime of a software project—during the first
life-cycle iteration
(c) happens
only once in the lifetime of a software project—during the first
life-cycle iteration
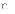 (d) cannot
be started before the inception phase is complete
(d) cannot
be started before the inception phase is complete (a) I
and II only
(a) I
and II only
 (b) I
and III only
(b) I
and III only
 (c) I,
II, and III
(c) I,
II, and III
 (d) II
and III only
(d) II
and III only