
Interpolated shading is
Phong and Gouraud shading+
Flat Shading
Phong Shading
Gouraud shading
Matting is
Separating a desired foreground image from background of constant or almost constant color+
Shading model
Defining shape of curve
The same as Smoothing
Transmissionis
Lightpassesthrough the object+
the component of reflected light that scattersin the material’s interior (after transmission) before exiting againLight absorbed by the object
Light reflected by the object
Forward Kinematics: Basic idea
Specify how joints should move
Specify where character should go, then deduce joint motion
Record motions of real people/objects, then transfer to digital characters
Specify how end effector should move
Sub-surface Scattering is
Component of reflected light that scattersin the material’s interior (after transmission) before exiting again +
Light absorbed by the object
Light reflected by the object
Lightpassesthrough the object
Main Idea : Flat shading
Draw all points with identical color/intensity+
Draw all points with random color/intensity
Interpolate color/intensity from vertices
Approach of Interpolative Shading
Main Idea: Flat shading
Draw all triangle points p with identical colour/intensity+
Draw all triangle points p with identical colour
Draw all triangle points p with identical intensity
Specular Reflection is
Represents shiny component of reflected light, caused by mirror-like reflection off of smooth or polished surfaces (plastics, polished metal, etc.)+
Represents ambient component of reflected light
Represents mirror component of reflected light
Ray tracing is
ray tracing is a technique for generating an image by tracing the path of light through pixelsin an image plane and simulating the effects of its encounters with virtual objects.+
ray tracing is a technique for generating a pixels by tracing the path of light through image
ray tracing is a technique for planning an image by tracing the path of light through pixels
Motion Capture: Basic idea
Motion capture is the process of recording the movement of objects or people.+
Motion capture is the process of playing the movement of objects or people
Motion capture is the process of moving the objects or people
“Pure” translation Equation
 +
+Vector is
A vector describes a length and a direction(A vector is a quantity or phenomenon that has two independent properties: magnitude and direction.)+
A vector describes a scalar coordinate
A vector describes a direction coordinate
General Linear 2D Transformations: Common Equation
 +
+
Computer graphic is
The science of turning the rules of geometry and physics into (digital) pictures that mean something to people+
The science of turning the rules of geometry pictures that mean something to people
The science geometry and physics into (digital) pictures that mean something to people
Amount of algorithms of Computing Ray-Triangle Intersection(select 1 option according the course)
2+
5
3
Ellipse: Full equation of Parametric Representation
 +
+
Main Idea of Flat shading
Draw all triangle points p with identical colour/intensity+
Draw all triangle points p with identical colour
Draw all triangle points p with identical intensity
From Camera to Canonical view: Equation of transformation.
 +
+Matting is
Matting refers to the problem of accurate foreground estimation in images and video. It is one of the key techniques in many image editing and film production applications+
Matting refers to the advantages of accurate foreground estimation in images and video. It is one of the key techniques in many image editing and film production applications
Matting refers to the problem of not foreground estimation in images and video. It is one of the key techniques in many image editing and film production applications
Equation of Plane in Homogeneous Coordinates
 +
+
Ray Tracing: which one is not Advantages
Highly customize, can model shadows, arbitrary reflection, parallelizable, allows trading off speed for accuracy – advantages+
Highly not customizable
Not arbitrary reflection
“+”of Keyframe Animation
Very expressive, Animator has full control of animation+
Very expensive, Animator has full control of animation
Very expensive, Animator has not to control of animation
Inverse Kinematics is
Specify where character should go, then deduce joint motion+
Specify where people should go, then deduce joint motion
Specify where character should go, then apply joint motion
Implicit Equation of Normal Vectors
 ,
,
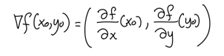 +
+Phong model: equation of ambient component.
 +
+“+” of Key-Framing with Forward Kinematics
Very easy to specify & implement+
Very hard to specify & implement
Very easy to specify &work with
Rasterization is
The task of taking an image described in a vector graphics format (shapes) and converting it into a raster image (pixels or dots) for output on a video display or printer, or for storage in a bitmap file format.+
The task of taking an image described in a hard graphics format (shapes) and converting it into a raster image (pixels or dots) for output on a video display or printer, or for storage in a bitmap file format.
The task of taking a pixel described in a vector graphics format (shapes) and converting it into a raster image (pixels or dots) for output on a video display or printer, or for storage in a bitmap file format.
