
- •Reznichenko Valery
- •Lecture 1. Introduction
- •Lecture 1. Introduction
- •Lecture 1. Introduction
- •Lecture 1. Introduction
- •Lecture 1. Introduction
- •Lecture 1. Introduction
- •Lecture 1. Introduction
- •Lecture 1. Introduction
- •Lecture 1. Introduction
- •Lecture 1. Introduction
- •Lecture 1. Introduction
- •Lecture 1. Introduction
- •Lecture 1. Introduction
- •Lecture 1. Introduction
- •Lecture 1. Introduction
- •Lecture 1. Introduction

Reznichenko Valery
Organization of data and knowledge bases
Lecture.1 Introduction
National Aviation University Computer Sciences Faculty Department of software engineering
1

Lecture 1. Introduction
CONTENTS
File systems and data bases
Definitions of DB and DBMS
Advantages of DB usage
DBMS languages
DBMS users
Basic requirements to database systems
CSF NAU |
2 |
Lecture 1. Introduction
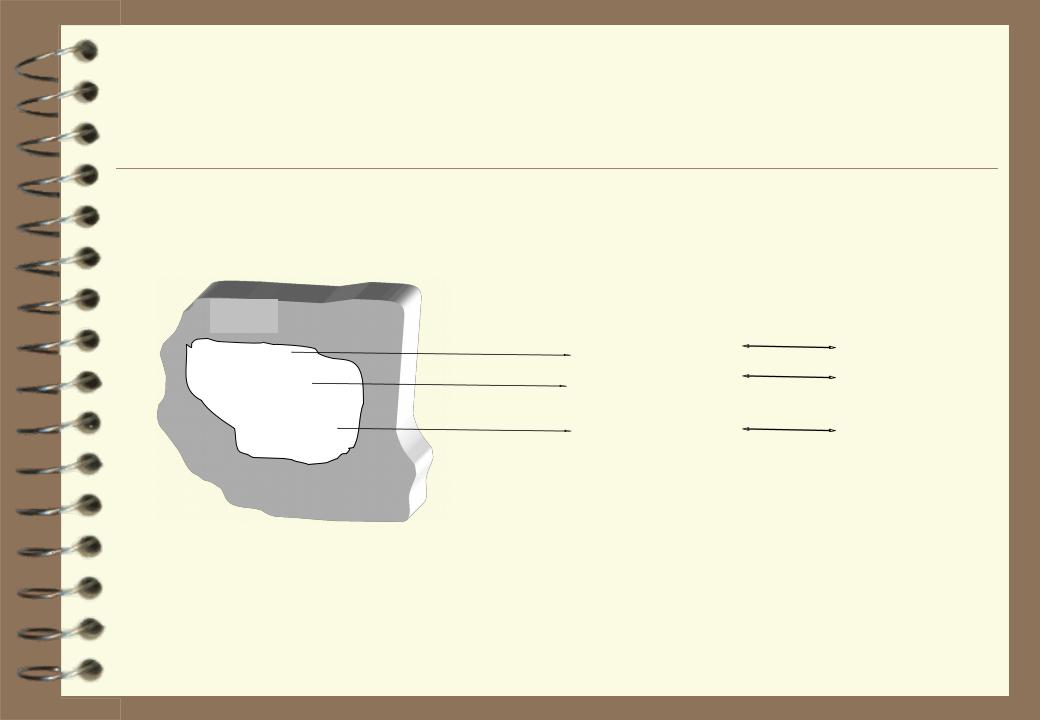
File Systems
AD
Task 1 |
Program-1 |
File-1 |
|
Program-2 |
File-2 |
||
Task 2 |
|||
… |
|
||
… |
|
||
Task N |
Program-N |
File-N |
CSF NAU |
3 |

Lecture 1. Introduction
File System Drawbacks
Data depends on programs
Inflexibility of data structure
Static data
Absence of integration
Data inconsistency
Inefficient concurrent access
Inefficient storage and processing
CSF NAU |
4 |
Lecture 1. Introduction
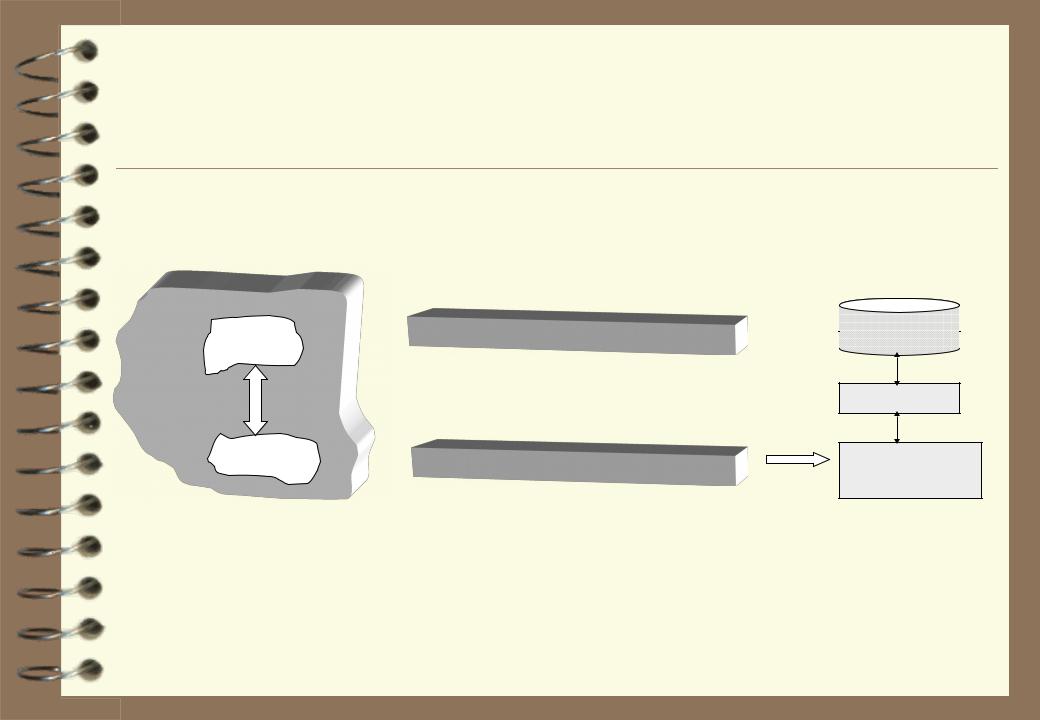
Data Base Approach
AD
Data
Tasks
 Information model of AD
Information model of AD
 Functional model of AD
Functional model of AD




 DB
DB



DBMS
Application
CSF NAU |
5 |

Lecture 1. Introduction
Data Base Definition
The database (DB) is a large set of complex- structured data, that assume:
the integrated storage,
centralized management and
sharing.
CSF NAU |
6 |

Lecture 1. Introduction
DBMS Definition
Data Base Management System (DBMS) is a
software for EFFECTIVE, CONVENIENT, and SAFETY creation and maintenance of data in a database, for organization of search data and outputing them.
CSF NAU |
7 |

Lecture 1. Introduction
DB Advantages
Integrated data storage
Centralized management
Common usage (sharing)
Data independence
Data integrity
Data security
Effective data access management
Data recovery
CSF NAU |
8 |

Lecture 1. Introduction
Centralized DB Management
DB schema design
Development data storage structures
DB restructuring and reorganization
Supporting DB back-up and recovery mechanisms
Data protection mechanisms
DB Adjustments
Regular observations
CSF NAU |
9 |

Lecture 1. Introduction
Data Independence in DB
The data independence is a status, when the application programs are completely independent from data storage, access and representation
Logical independence
Physical independence
CSF NAU |
10 |
