
- •Preface
- •Part IV. Basic Single Equation Analysis
- •Chapter 18. Basic Regression Analysis
- •Equation Objects
- •Specifying an Equation in EViews
- •Estimating an Equation in EViews
- •Equation Output
- •Working with Equations
- •Estimation Problems
- •References
- •Chapter 19. Additional Regression Tools
- •Special Equation Expressions
- •Robust Standard Errors
- •Weighted Least Squares
- •Nonlinear Least Squares
- •Stepwise Least Squares Regression
- •References
- •Chapter 20. Instrumental Variables and GMM
- •Background
- •Two-stage Least Squares
- •Nonlinear Two-stage Least Squares
- •Limited Information Maximum Likelihood and K-Class Estimation
- •Generalized Method of Moments
- •IV Diagnostics and Tests
- •References
- •Chapter 21. Time Series Regression
- •Serial Correlation Theory
- •Testing for Serial Correlation
- •Estimating AR Models
- •ARIMA Theory
- •Estimating ARIMA Models
- •ARMA Equation Diagnostics
- •References
- •Chapter 22. Forecasting from an Equation
- •Forecasting from Equations in EViews
- •An Illustration
- •Forecast Basics
- •Forecasts with Lagged Dependent Variables
- •Forecasting with ARMA Errors
- •Forecasting from Equations with Expressions
- •Forecasting with Nonlinear and PDL Specifications
- •References
- •Chapter 23. Specification and Diagnostic Tests
- •Background
- •Coefficient Diagnostics
- •Residual Diagnostics
- •Stability Diagnostics
- •Applications
- •References
- •Part V. Advanced Single Equation Analysis
- •Chapter 24. ARCH and GARCH Estimation
- •Basic ARCH Specifications
- •Estimating ARCH Models in EViews
- •Working with ARCH Models
- •Additional ARCH Models
- •Examples
- •References
- •Chapter 25. Cointegrating Regression
- •Background
- •Estimating a Cointegrating Regression
- •Testing for Cointegration
- •Working with an Equation
- •References
- •Binary Dependent Variable Models
- •Ordered Dependent Variable Models
- •Censored Regression Models
- •Truncated Regression Models
- •Count Models
- •Technical Notes
- •References
- •Chapter 27. Generalized Linear Models
- •Overview
- •How to Estimate a GLM in EViews
- •Examples
- •Working with a GLM Equation
- •Technical Details
- •References
- •Chapter 28. Quantile Regression
- •Estimating Quantile Regression in EViews
- •Views and Procedures
- •Background
- •References
- •Chapter 29. The Log Likelihood (LogL) Object
- •Overview
- •Specification
- •Estimation
- •LogL Views
- •LogL Procs
- •Troubleshooting
- •Limitations
- •Examples
- •References
- •Part VI. Advanced Univariate Analysis
- •Chapter 30. Univariate Time Series Analysis
- •Unit Root Testing
- •Panel Unit Root Test
- •Variance Ratio Test
- •BDS Independence Test
- •References
- •Part VII. Multiple Equation Analysis
- •Chapter 31. System Estimation
- •Background
- •System Estimation Methods
- •How to Create and Specify a System
- •Working With Systems
- •Technical Discussion
- •References
- •Vector Autoregressions (VARs)
- •Estimating a VAR in EViews
- •VAR Estimation Output
- •Views and Procs of a VAR
- •Structural (Identified) VARs
- •Vector Error Correction (VEC) Models
- •A Note on Version Compatibility
- •References
- •Chapter 33. State Space Models and the Kalman Filter
- •Background
- •Specifying a State Space Model in EViews
- •Working with the State Space
- •Converting from Version 3 Sspace
- •Technical Discussion
- •References
- •Chapter 34. Models
- •Overview
- •An Example Model
- •Building a Model
- •Working with the Model Structure
- •Specifying Scenarios
- •Using Add Factors
- •Solving the Model
- •Working with the Model Data
- •References
- •Part VIII. Panel and Pooled Data
- •Chapter 35. Pooled Time Series, Cross-Section Data
- •The Pool Workfile
- •The Pool Object
- •Pooled Data
- •Setting up a Pool Workfile
- •Working with Pooled Data
- •Pooled Estimation
- •References
- •Chapter 36. Working with Panel Data
- •Structuring a Panel Workfile
- •Panel Workfile Display
- •Panel Workfile Information
- •Working with Panel Data
- •Basic Panel Analysis
- •References
- •Chapter 37. Panel Estimation
- •Estimating a Panel Equation
- •Panel Estimation Examples
- •Panel Equation Testing
- •Estimation Background
- •References
- •Part IX. Advanced Multivariate Analysis
- •Chapter 38. Cointegration Testing
- •Johansen Cointegration Test
- •Single-Equation Cointegration Tests
- •Panel Cointegration Testing
- •References
- •Chapter 39. Factor Analysis
- •Creating a Factor Object
- •Rotating Factors
- •Estimating Scores
- •Factor Views
- •Factor Procedures
- •Factor Data Members
- •An Example
- •Background
- •References
- •Appendix B. Estimation and Solution Options
- •Setting Estimation Options
- •Optimization Algorithms
- •Nonlinear Equation Solution Methods
- •References
- •Appendix C. Gradients and Derivatives
- •Gradients
- •Derivatives
- •References
- •Appendix D. Information Criteria
- •Definitions
- •Using Information Criteria as a Guide to Model Selection
- •References
- •Appendix E. Long-run Covariance Estimation
- •Technical Discussion
- •Kernel Function Properties
- •References
- •Index
- •Symbols
- •Numerics
110—Chapter 21. Time Series Regression
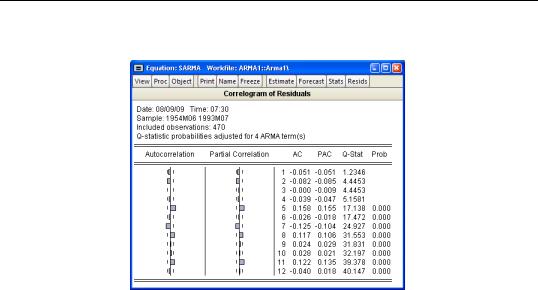
For the example seasonal ARMA model, the 12-period residual correlogram looks as follows:
The correlogram has a significant spike at lag 5, and all subsequent Q-statistics are highly significant. This result clearly indicates the need for respecification of the model.
References
Box, George E. P. and Gwilym M. Jenkins (1976). Time Series Analysis: Forecasting and Control, Revised Edition, Oakland, CA: Holden-Day.
Fair, Ray C. (1984). Specification, Estimation, and Analysis of Macroeconometric Models, Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press.
Greene, William H. (2008). Econometric Analysis, 6th Edition, Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Hamilton, James D. (1994a). Time Series Analysis, Princeton University Press.
Hayashi, Fumio. (2000). Econometrics, Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Johnston, Jack and John Enrico DiNardo (1997). Econometric Methods, 4th Edition, New York: McGrawHill.
Rao, P. and Z. Griliches (1969). “Small Sample Properties of Several Two-Stage Regression Methods in the Context of Auto-Correlated Errors,” Journal of the American Statistical Association, 64, 253–272.
