
- •Table of Contents
- •Foreword
- •Chapter 1. A Quick Walk Through
- •Workfile: The Basic EViews Document
- •Viewing an individual series
- •Looking at different samples
- •Generating a new series
- •Looking at a pair of series together
- •Estimating your first regression in EViews
- •Saving your work
- •Forecasting
- •What’s Ahead
- •Chapter 2. EViews—Meet Data
- •The Structure of Data and the Structure of a Workfile
- •Creating a New Workfile
- •Deconstructing the Workfile
- •Time to Type
- •Identity Noncrisis
- •Dated Series
- •The Import Business
- •Adding Data To An Existing Workfile—Or, Being Rectangular Doesn’t Mean Being Inflexible
- •Among the Missing
- •Quick Review
- •Appendix: Having A Good Time With Your Date
- •Chapter 3. Getting the Most from Least Squares
- •A First Regression
- •The Really Important Regression Results
- •The Pretty Important (But Not So Important As the Last Section’s) Regression Results
- •A Multiple Regression Is Simple Too
- •Hypothesis Testing
- •Representing
- •What’s Left After You’ve Gotten the Most Out of Least Squares
- •Quick Review
- •Chapter 4. Data—The Transformational Experience
- •Your Basic Elementary Algebra
- •Simple Sample Says
- •Data Types Plain and Fancy
- •Numbers and Letters
- •Can We Have A Date?
- •What Are Your Values?
- •Relative Exotica
- •Quick Review
- •Chapter 5. Picture This!
- •A Simple Soup-To-Nuts Graphing Example
- •A Graphic Description of the Creative Process
- •Picture One Series
- •Group Graphics
- •Let’s Look At This From Another Angle
- •To Summarize
- •Categorical Graphs
- •Togetherness of the Second Sort
- •Quick Review and Look Ahead
- •Chapter 6. Intimacy With Graphic Objects
- •To Freeze Or Not To Freeze Redux
- •A Touch of Text
- •Shady Areas and No-Worry Lines
- •Templates for Success
- •Point Me The Way
- •Your Data Another Sorta Way
- •Give A Graph A Fair Break
- •Options, Options, Options
- •Quick Review?
- •Chapter 7. Look At Your Data
- •Sorting Things Out
- •Describing Series—Just The Facts Please
- •Describing Series—Picturing the Distribution
- •Tests On Series
- •Describing Groups—Just the Facts—Putting It Together
- •Chapter 8. Forecasting
- •Just Push the Forecast Button
- •Theory of Forecasting
- •Dynamic Versus Static Forecasting
- •Sample Forecast Samples
- •Facing the Unknown
- •Forecast Evaluation
- •Forecasting Beneath the Surface
- •Quick Review—Forecasting
- •Chapter 9. Page After Page After Page
- •Pages Are Easy To Reach
- •Creating New Pages
- •Renaming, Deleting, and Saving Pages
- •Multi-Page Workfiles—The Most Basic Motivation
- •Multiple Frequencies—Multiple Pages
- •Links—The Live Connection
- •Unlinking
- •Have A Match?
- •Matching When The Identifiers Are Really Different
- •Contracted Data
- •Expanded Data
- •Having Contractions
- •Two Hints and A GotchYa
- •Quick Review
- •Chapter 10. Prelude to Panel and Pool
- •Pooled or Paneled Population
- •Nuances
- •So What Are the Benefits of Using Pools and Panels?
- •Quick (P)review
- •Chapter 11. Panel—What’s My Line?
- •What’s So Nifty About Panel Data?
- •Setting Up Panel Data
- •Panel Estimation
- •Pretty Panel Pictures
- •More Panel Estimation Techniques
- •One Dimensional Two-Dimensional Panels
- •Fixed Effects With and Without the Social Contrivance of Panel Structure
- •Quick Review—Panel
- •Chapter 12. Everyone Into the Pool
- •Getting Your Feet Wet
- •Playing in the Pool—Data
- •Getting Out of the Pool
- •More Pool Estimation
- •Getting Data In and Out of the Pool
- •Quick Review—Pools
- •Chapter 13. Serial Correlation—Friend or Foe?
- •Visual Checks
- •Testing for Serial Correlation
- •More General Patterns of Serial Correlation
- •Correcting for Serial Correlation
- •Forecasting
- •ARMA and ARIMA Models
- •Quick Review
- •Chapter 14. A Taste of Advanced Estimation
- •Weighted Least Squares
- •Heteroskedasticity
- •Nonlinear Least Squares
- •Generalized Method of Moments
- •Limited Dependent Variables
- •ARCH, etc.
- •Maximum Likelihood—Rolling Your Own
- •System Estimation
- •Vector Autoregressions—VAR
- •Quick Review?
- •Chapter 15. Super Models
- •Your First Homework—Bam, Taken Up A Notch!
- •Looking At Model Solutions
- •More Model Information
- •Your Second Homework
- •Simulating VARs
- •Rich Super Models
- •Quick Review
- •Chapter 16. Get With the Program
- •I Want To Do It Over and Over Again
- •You Want To Have An Argument
- •Program Variables
- •Loopy
- •Other Program Controls
- •A Rolling Example
- •Quick Review
- •Appendix: Sample Programs
- •Chapter 17. Odds and Ends
- •How Much Data Can EViews Handle?
- •How Long Does It Take To Compute An Estimate?
- •Freeze!
- •A Comment On Tables
- •Saving Tables and Almost Tables
- •Saving Graphs and Almost Graphs
- •Unsubtle Redirection
- •Objects and Commands
- •Workfile Backups
- •Updates—A Small Thing
- •Updates—A Big Thing
- •Ready To Take A Break?
- •Help!
- •Odd Ending
- •Chapter 18. Optional Ending
- •Required Options
- •Option-al Recommendations
- •More Detailed Options
- •Window Behavior
- •Font Options
- •Frequency Conversion
- •Alpha Truncation
- •Spreadsheet Defaults
- •Workfile Storage Defaults
- •Estimation Defaults
- •File Locations
- •Graphics Defaults
- •Quick Review
- •Index
- •Symbols
ARCH, etc.—351
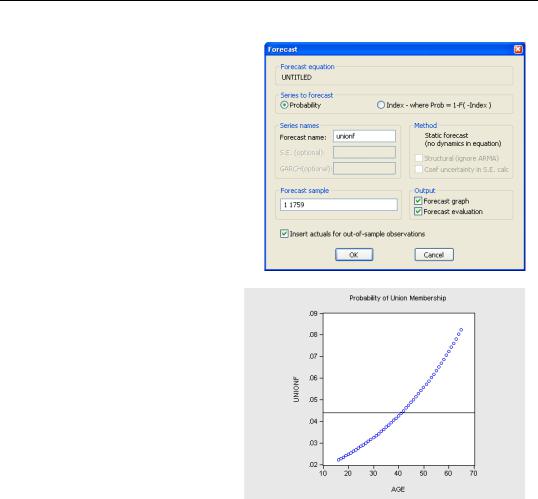
Logit’s Forecast dialog offers a choice of predicting the index s, or the probability. Here we predict the probability.
The graph shown to the right plots the probability of union membership as a function of age. For comparison purposes, we’ve added a horizontal line marking the unconditional probability of union membership. A 60 year old is about three times as likely to be in a union as is a 20 year old.
ARCH, etc.
Have you tried About EViews on the Help menu and then clicked the  button? Only one Nobel prize winner (so far!) appears in the credits list. Which brings us to the topic of autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity, or ARCH. ARCH, and members of the extended ARCH family, model time-varying variances of the error term. The simplest ARCH model is: yt = aˆ + bˆ xt + et
button? Only one Nobel prize winner (so far!) appears in the credits list. Which brings us to the topic of autoregressive conditional heteroskedasticity, or ARCH. ARCH, and members of the extended ARCH family, model time-varying variances of the error term. The simplest ARCH model is: yt = aˆ + bˆ xt + et
jt2= g0 + g1e2t – 1
In this ARCH(1) model, the variance of this period’s error term depends on the squared residual from the previous period.
352—Chapter 14. A Taste of Advanced Estimation
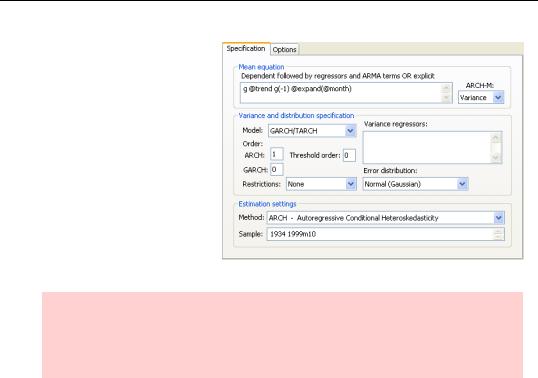
The residuals from the currency data used earlier showed noticeably persistent volatility, a sign of a potential ARCH effect. In EViews, all the action in specifying ARCH takes place in the Specification tab of the Equation Estimation dialog. To get to the right version of the Specification tab, choose ARCH -
Autoregressive Conditional Heteroskedasticity in the
Method dropdown of the Estimation settings field.
Hint: Unlike nearly all other EViews estimation procedures, ARCH requires a continuous sample. Define an appropriate sample in the Specification tab. If your sample includes a break, EViews will give an error message. In this example, we had to use a subset of our data to accommodate the continuous sample requirement.
ARCH, etc.—353
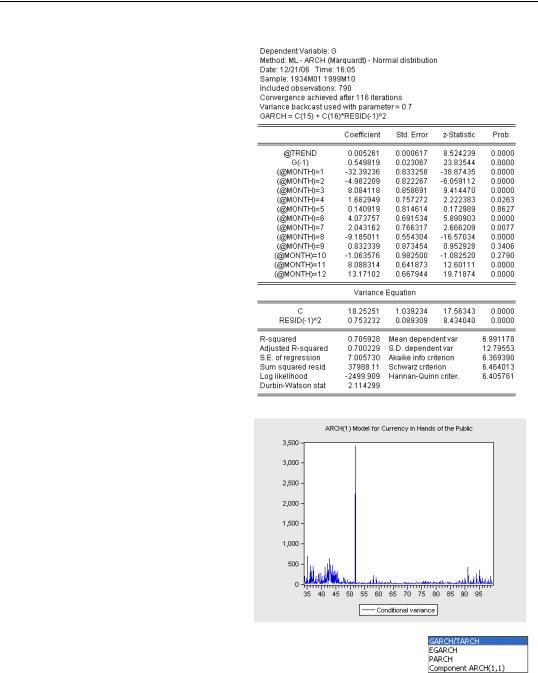
ARCH coefficients appear below the structural coefficients. The ARCH coefficient—our estimated g1 —is
both large, 0.75, and statistically significant, t = 8.4 .
In addition to the usual results, the
View menu offers Garch Graph.
Garch Graph provides a plot of the predicted conditional variance or the conditional standard deviation.
Selecting Garch Graph/Conditional Variance, we see that higher variances occur early and late in the sample, plus an enormous spike in 1952.
Perhaps the variance spike is really
there, or perhaps ARCH(1) isn’t the best model. EViews offers a wide choice from the extended ARCH family. The Model dropdown offers four broad choices. Each broad choice is further refined with various
options. Most simply, you can specify the order of the ARCH or GARCH (Generalized ARCH) model in the dialog fields just below Model.
354—Chapter 14. A Taste of Advanced Estimation
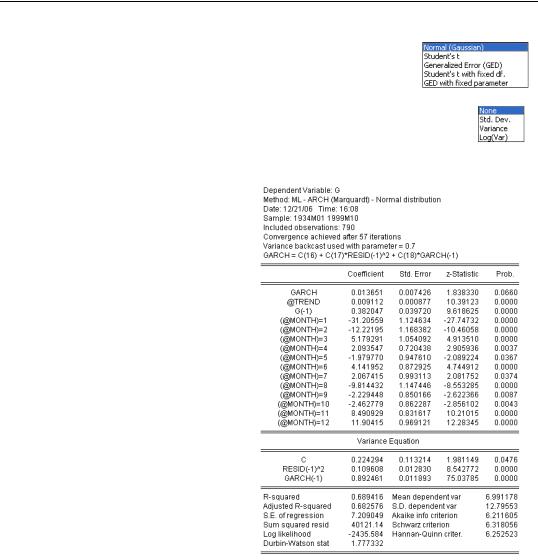
You can also choose from a variety of error distributions using the
Error distribution dropdown.
One of the most interesting applications of ARCH is to put the timevarying variance back into the structural equation. This is called ARCH-in-
mean, or ARCH-M, and is added to the specification using the ARCH-M dropdown menu in the upper right of the Specification tab.
Here we’ve changed the model to GARCH(1,1) and entered the variance in the structural equation. EViews labels the structural coefficient of the ARCH-M effect GARCH. Notice that the structural effect of ARCH-M is almost significant at the five percent level.
