
- •Table of Contents
- •Preface
- •What This Book Covers
- •What You Need for This Book
- •Conventions
- •Reader Feedback
- •Customer Support
- •Errata
- •Questions
- •The Need for Cryptography
- •Privacy
- •Security
- •A History of the Internet
- •Holding the Internet Together
- •The Creation of ICANN
- •ICANN Bypassed
- •The Root Name Servers
- •Running the Top-Level Domains
- •History of Internet Engineering
- •The Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF)
- •RFCs—Requests For Comments
- •IETF and Crypto
- •The War on Crypto
- •Dual Use
- •Public Cryptography
- •The Escrowed Encryption Standard
- •Export Laws
- •The Summer of '97
- •The EFF DES Cracker
- •Echelon
- •The End of the Export Restrictions
- •Free Software
- •Free as in Verifiable
- •The Open Source Movement
- •The History of Openswan
- •IETF Troubles over DNS
- •Super FreeS/WAN
- •The Arrival of Openswan
- •NETKEY
- •Further Reading
- •Using Openswan
- •Copyright and License Conditions
- •Writing and Contributing Code
- •Legality of Using Openswan
- •International Agreements
- •International Law and Hosting Openswan
- •Unrecognized International Claims
- •Patent Law
- •Expired and Bogus Patents
- •Useful Legal Links
- •Summary
- •A Very Brief Overview of Cryptography
- •Valid Packet Rewriting
- •Ciphers
- •Algorithms
- •Uniqueness
- •Public-Key Algorithms
- •Exchanging Public Keys
- •Digital Signatures
- •Diffie-Hellman Key Exchange
- •Avoiding the Man in the Middle
- •Session Keys
- •Crypto Requirements for IPsec
- •IPsec: A Suite of Protocols
- •Kernel Mode: Packet Handling
- •Authentication Header (AH)
- •Encapsulated Security Payload (ESP)
- •Transport and Tunnel Mode
- •Choosing the IPsec Mode and Type
- •The Kernel State
- •Encryption Details
- •Manual Keying
- •Final Note on Protocols and Ports
- •Usermode: Handling the Trust Relationships
- •The IKE Protocol
- •Phase 1: Creating the ISAKMP SA
- •Phase 2: Quick Mode
- •The NAT Problem
- •Summary
- •Linux Distributions
- •Debian
- •SuSE
- •Slackware
- •Gentoo
- •Linux 'Router' Distributions
- •Deciding on the Userland
- •Pluto
- •Racoon
- •Isakmpd
- •More Reasons to Pick Pluto
- •Choosing the Kernel IPsec Stack
- •KLIPS, the Openswan Stack
- •ipsecX Interfaces
- •First Packet Caching
- •Path MTU Discovery
- •KLIPS' Downside
- •NETKEY, the 2.6 IPsec Stack
- •The USAGI / SuSE IPsec Stack
- •Making the Choice
- •GPL Compliance and KLIPS
- •Binary Installation of the Openswan Userland
- •Checking for Old Versions
- •Installing the Binary Package for Openswan
- •Building from Source
- •Using RPM-based Distributions
- •Rebuilding the Openswan Userland
- •Building src.rpm from Scratch
- •Openswan Options
- •Building the Openswan Userland from Source
- •Downloading the Source Code
- •Configuring the Userland Tools
- •Optional Features
- •Compile Flags
- •File Path Options
- •Obscure Pluto Options
- •Compiling and Installing
- •Binary Installation of KLIPS
- •Building KLIPS from Source
- •Kernel Prerequisites
- •Identifying your Kernel's Abilities
- •Using Both KLIPS and NETKEY
- •The Kernel Build Options
- •Required Kernel Options
- •Desired Options
- •NETKEY Stack Options
- •KLIPS Stack Options
- •L2TP Options
- •Patching the Kernel
- •NAT-Traversal Patch
- •KLIPS Compile Shortcut
- •Activating KLIPS
- •Determining the Stack in Use
- •Building KLIPS into the Linux Kernel Source Tree
- •Building a Standard Kernel
- •NAT Traversal
- •Patching KLIPS into the Linux Kernel
- •Verifying the Installation
- •Summary
- •Manual versus Automatic
- •PSK versus RSA
- •Pitfalls of Debugging IPsec
- •Pre-Flight Check
- •The ipsec verify Command
- •NAT and Masquerading
- •Checking External Commands
- •Opportunistic Encryption
- •The ipsec livetest Command
- •Configuration of Openswan
- •The ipsec.conf File
- •Host-to-Host Tunnel
- •Left and Right
- •The type Options
- •The auto Option
- •The rsasigkey Options
- •Bringing Up the IPsec Tunnels
- •Listing IPsec Connections
- •Testing the IPsec Tunnel
- •Connecting Subnets Through an IPsec Connection
- •Testing Subnet Connections
- •Testing Properly
- •Encrypting the Host and the Network Behind It
- •Employing Advanced Routing
- •Creating More Tunnels
- •Avoiding Duplication
- •The Also Keyword
- •KLIPS and the ipsecX Interfaces
- •Pre-Shared Keys (PSKs)
- •Proper Secrets
- •Dynamic IP Addresses
- •Hostnames
- •Roadwarriors
- •Multiple Roadwarrior Connections
- •Dynamic IP and PSKs
- •Mixing PSK and RSA
- •Connection Management
- •Subnet Extrusion
- •NAT Traversal
- •Deprecated Syntax
- •Confirming a Functional NAT-T
- •Dead Peer Detection
- •DPD Works Both Ways
- •Configuring DPD
- •Buggy Cisco Routers
- •Ciphers and Algorithms
- •Using ike= to Specify Phase 1 Parameters
- •Using esp= to Specify Phase 2 Parameters
- •Defaults and Strictness
- •Unsupported Ciphers and Algorithms
- •Aggressive Mode
- •XAUTH
- •XAUTH Gateway (Server Side)
- •XAUTH Client (Supplicant Side)
- •Fine Tuning
- •Perfect Forward Secrecy
- •Rekeying
- •Key Rollover
- •Summary
- •X.509 Certificates Explained
- •X.509 Objects
- •X.509 Packing
- •Types of Certificates
- •Passphrases, PIN Codes, and Interactivity
- •IKE and Certificates
- •Using the Certificate DN as ID for Openswan
- •Generating Certificates with OpenSSL
- •Setting the Time
- •Configuring OpenSSL
- •Be Consistent with All Certificates
- •OpenSSL Commands for Common Certificate Actions
- •Configuring Apache for IPsec X.509 Files
- •Creating X.509-based Connections
- •Using a Certificate Authority
- •Using Multiple CAs
- •Sending and Receiving Certificate Information
- •Creating your own CA using OpenSSL
- •Creating Host Certificates with Your Own CA
- •Host Certificates for Microsoft Windows (PKCS#12)
- •Certificate Revocation
- •Dynamic CRL Fetching
- •Configuring CRL
- •Online Certificate Status Protocol (OCSP)
- •Summary
- •History of Opportunistic Encryption
- •Trusting Third Parties
- •Trusting the DNS?
- •OE in a Nutshell
- •An OE Security Gateway
- •DNS Key Records
- •Forward and Reverse Zones
- •The OE DNS Records
- •Different Types of OE
- •Policy Groups
- •Internal States
- •Configuring OE
- •Configuring Policies
- •Full OE or Initiate-Only
- •Generating Correct DNS Records
- •Name Server Updates
- •Verifying Your OE Setup
- •Testing Your OE Setup
- •The trap eroute
- •The pass eroute
- •The hold eroute
- •Manipulating OE Connections Manually
- •Advanced OE Setups
- •Caveats
- •Summary
- •Where to Firewall?
- •Allowing IPsec Traffic
- •NAT and IPsec Passthrough
- •Configuring the Firewall on the Openswan Host
- •Firewalling and KLIPS
- •Firewalling and NETKEY
- •Packet Size
- •Summary
- •Microsoft Windows
- •Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol (L2TP)
- •Assigning an IP for VPN Access
- •L2TP Properties
- •Pure IPsec versus L2TP/IPsec
- •Client and Server Configurations for L2TP/IPsec
- •The L2TP Openswan Server
- •Configuring Openswan for L2TP/IPsec
- •Linux Kernel Runtime Parameters for L2TP/IPsec
- •Protecting the L2TP Daemon with IPsec using iptables
- •Choosing an L2TP Daemon
- •Configuring L2TPD
- •Configuring User Authentication for pppd
- •Microsoft Windows XP L2TP Configuration
- •Microsoft Windows 2000 L2TP Configuration
- •Apple Mac OS X L2TP Configuration
- •Server Configuration for X.509 IPsec without L2TP
- •Openswan Configuration for X.509 without L2TP
- •Client Configuration for X.509 IPsec without L2TP
- •Microsoft's IKE Daemon
- •Microsoft's Certificate Store
- •Clients using Microsoft Native IPsec Implementation
- •The ipsec.exe Wrapper
- •The Linsys IPsec Tool (lsipsectool)
- •Securepoint IPsec Client
- •TauVPN (iVPN)
- •The WaveSEC Client
- •Third-Party Replacement Clients for Windows
- •The GreenBow VPN Client
- •Astaro Secure Client
- •Mac OS X IPSecuritas
- •VPNtracker
- •Manual Racoon Configuration
- •Importing X.509 Certificates into Windows
- •Importing X.509 Certificates on Mac OS X (Tiger)
- •Summary
- •Openswan as a Client to an Appliance
- •Preparing the Interop
- •The Human Factor
- •Terminology
- •Preparation
- •IPsec Passthrough
- •Tunnel Limitations
- •Anticipate Known Problems
- •Update the Firmware
- •GUI Issues
- •Keepalives
- •ISP Filtering
- •Frequently used VPN Gateways
- •Webmin with Openswan
- •Cisco VPN 3000
- •Cisco PIX Concentrator
- •Nortel Contivity
- •Checkpoint
- •WatchGuard Firebox
- •Symantec
- •Frequently used VPN Client Appliances
- •ZyXEL
- •DrayTek Vigor
- •The Vigor Web Interface
- •Windows Logon Issues
- •Other Vigorisms
- •Unresolved Issues
- •NetScreen
- •Known Issues
- •SonicWALL
- •BinTec
- •LANCOM
- •Linksys
- •Lucent Brick
- •NETGEAR
- •KAME/Racoon
- •Aftercare
- •Summary
- •Methods of Encryption
- •Host-to-Host Mesh
- •Host-to-Gateway Setup
- •Single IP Extrusiautomation or L2TP
- •Opportunistic Encryption in the LAN
- •Non-OE-Capable Machines
- •Designing a Solution for Encrypting the LAN
- •Design Goals
- •Separation of WiFi and Crypto
- •Link Layer Protection
- •The Logical Choice: IPsec
- •Hotspot
- •WaveSEC
- •Full WaveSEC
- •Catch 22 Traffic
- •Building a WaveSEC Server
- •DHCP Server Setup
- •DNS Server Setup
- •Openswan Server Setup
- •Catch 22 Traffic Setup
- •Building a WaveSEC Client
- •DH Client Setup
- •Openswan Setup
- •Testing the WaveSEC
- •Starting the WaveSEC Connection
- •Known Issues with WaveSEC
- •WaveSEC for Windows
- •Design Limitations
- •Building a WaveSEC for Windows Server
- •Obtaining the Certificate and Client Software
- •Our Prototype Experiences
- •Openswan Issues
- •Windows Kernel Issues
- •Summary
- •Cipher Performance
- •Handling Thousands of Tunnels
- •Managing Large Configuration Files
- •Standard Naming Convention
- •The also= Parameter
- •The include Parameter
- •Openswan Startup Time
- •Limitations of the Random Device
- •Other Performance-Enhancing Factors
- •Logging to Disk
- •Disable Dead Peer Detection
- •Reducing the Number of Tunnels
- •OSPF Setup
- •BGPv4 Setup
- •High Availability
- •Heartbeat
- •Xen Migration
- •Using Anycast
- •Summary
- •Do Not Lock Yourself Out!
- •Narrowing Down the Problem
- •Host Issues
- •Configuration Problems
- •Connection Names
- •Interoperability
- •Hunting Ghosts
- •Rekey Problems (After an Hour)
- •Openswan Error Messages
- •IKE: Unknown VendorIDs
- •Network Issues
- •Firewalls
- •MTU and Fragmentation Issues
- •Debugging IPsec on Apple Mac OS X
- •Debugging IPsec on Microsoft Windows
- •Oakley Debugging
- •Debugging ipsec.exe
- •Microsoft L2TP Errors
- •You Suddenly Cannot Log in Anymore over the VPN
- •Software Bugs
- •Userland Issues: Assertion Failed or Segmentation Faults
- •Kernel Issues: Crashes and Oopses
- •Memory Issues
- •Common IKE Error Messages
- •Common Kernel-Related Error Messages
- •Common Errors when Upgrading
- •Using tcpdump to Debug IPsec
- •Situation A: No Communication on Port 500
- •Situation B: Failure at Third Exchange
- •Situation C: QUICK Mode Initiates, but Never Completes
- •Situation D: All IKE Messages Occur, but no Traffic Flows
- •A Final tcpdump Example
- •User Mode Linux Testing
- •Preparing the Openswan for the UML Build Process
- •Running the UMLs
- •Writing a UML Test Case
- •Debugging the Kernel with GDB
- •Asking the Openswan Community for Help
- •Internet Relay Chat (IRC)
- •The Openswan Mailing Lists
- •Posting to the Lists
- •Research First, Ask Later
- •Free, as in Beer
- •Do not Anonymize
- •Summary
- •Linux Kernel Developments
- •Kernel API Changes between 2.6.12 and 2.6.14
- •Red Hat Kernel Developments
- •Fedora Kernel Source/Headers Packaging Change
- •MD5 Insecurities
- •Discontinuation of Openswan 1 by the End of 2005
- •Update on UML Testing Suite Installation
- •Openswan GIT Repositories
- •Openswan on Windows and Mac OS X Updates
- •Known Outstanding Bugs
- •Vulnerability Fixes in Openswan 2.4.4
- •The OSI Model and the IP Model
- •No Layers, Just Packets
- •The Protocol
- •IP Network Overview
- •IP Address Management
- •The Old IP Classes
- •Classless IP Networks
- •The Definition of a Subnet
- •Calculating with Subnets: The Subnet Mask
- •The Rest of the Network
- •Linux Networking Commands
- •Routing
- •Routing Decisions
- •Peering
- •Network Address Translation
- •Port Forwarding
- •Openswan Links
- •Community Documentation
- •Generic Linux Distributions Containing Openswan
- •Specialized Linux Distributions Containing Openswan
- •Overview RFCs
- •Basic Protocols
- •Key Management
- •Procedural and Operational RFCs
- •Detailed RFCs on Specific Cryptographic Algorithms and Ciphers
- •Dead Peer Detection RFCs
- •NAT-Traversal and UDP Encapsulation RFCs
- •RFCs for Secure DNS Service, which IPSEC May Use
- •RFCs Related to L2TP, Often Used in Combination with IPsec
- •RFCs on IPsec in Relation to Other Protocols
- •RFCs Not in Use or Implemented across Multiple Vendors
- •Index

Debugging and Troubleshooting
MTU and Fragmentation Issues
MTU issues normally produce intermittent or flow problems. Simple things, such as a ping or an SSH login will work, but more intense tasks, such as an ls -alg / after log in, FTP, HTTP, or Windows file-sharing fails. In general, connections will seem to stall or hang. You can test this by using ping with small or big packet sizes:
#ping -s 500 ip-at-end-of-the-tunnel
#ping -s 2000 ip-at-end-of-the-tunnel
If using KLIPS, you can force a lower MTU for a tunnel with overridemtu=. Values to try are 1400 or even 1000. This option is not available with NETKEY as it does not have separate virtual ipsecX interfaces, but you can set the MTU for a particular route. By setting a route to your remote IPsec endpoint, you can effectively lower the MTU for your inner tunnel. This is done using the ip command:
# ip route replace 1.2.3.4 via x.x.x.x dev eth1 mtu yyyy
Here, 1.2.3.4 is the address of the remote gateway, x.x.x.x is your nexthop gateway, and yyyy is the new MTU for packets destined for the remote IPsec endpoint.
You can also try to set the MTU of your physical device (ppp0 or ethX) to a lower value, although that would affect all packets on that interface, not just tunneled packets.
Another workaround, discussed at the end of Chapter 7, is TCP MSS clamping. Be aware that this only fixes protocols based on TCP. There is no similar fix for UDP. If you cannot get a Windows Logon working through the VPN, but you can ping, then your MTU issues might be preventing the Kerberos protocol from working properly, as it uses UDP by default. You can try to force Kerberos to using TCP. See the Microsoft Knowledge Base article Q244474, How to force Kerberos to use TCP instead of UDP in Windows Server 2003, in Windows XP, and in Windows 2000. You can also try to set the MTU on Windows, though this might cause you a lot more grief than pleasure. Do not do this lightly. You can find this information in Microsoft Knowledge Base article 826159, HOW TO: Change the Default Maximum Transmission Unit (MTU) Size Settings for PPP Connections or for VPN Connections.
Debugging IPsec on Apple Mac OS X
To view the logs in Internet Connect, select Window | Connection Log. You can also look at the Racoon log file in /private/var/log/system.log. Note that IPSecuritas for Mac OS X places all its Racoon logs in /tmp.
Debugging IPsec on Microsoft Windows
For a detailed overview of how to enable Microsoft Windows debugging, see the Microsoft website. Currently, the following URL works:
http://www.microsoft.com/resources/documentation/windows/xp/all/proddocs/enus/sag_ipsec_tools.mspx
270

Chapter 12
Oakley Debugging
In essence, you want to enable Oakley.log. This is the file where all IKE debugging information will end up. You need to add the following key to the Windows Registry:
HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\System\CurrentControlSet\Services\PolicyAgent\Oakley\Enable
Logging
and set it to the value 1. Then either reboot the machine, or just restart the IPsec IKE daemon using these commands at a command prompt:
net stop policyagent net start policyagent
If you are running Remote Access, you will also need to restart the Remote Access Service.
If you are using Windows XP SP2 or higher, and have installed ipseccmd.exe from the Resource Kit, you can execute the following command to enable debugging:
ipseccmd set logike
To disable logging, you can use:
ipseccmd set dontlogike
The logike and dontlogike commands do not require you to explicitly restart the policy agent.
All IKE debugging information appears in %systemroot%\Debug\Oakley.log. With later updates to 2000 and XP, Oakley.log has become quite readable. Here's a typical excerpt:
[...]
>5-10: 10:00:50:777:1fc entered kill_old_policy_sas 2
>5-10: 10:00:50:777:1fc entered kill_old_policy_sas 2
>5-10: 10:01:07:501:544 Acquire from driver: op=00000006 src=192.168.1.2.0 dst=192.168.2.234.0 proto = 0, SrcMask=255.255.255.255, DstMask=255.255.255.0, Tunnel 1, TunnelEndpt=193.110.157.131 Inbound TunnelEndpt=192.168.1.2
>5-10: 10:01:07:511:1fc Filter to match: Src 202.149.x.x Dst 192.168.1.2
>5-10: 10:01:07:551:1fc MM PolicyName: 2
>5-10: 10:01:07:551:1fc MMPolicy dwFlags 2 SoftSAExpireTime 28800
>5-10: 10:01:07:551:1fc MMOffer[0] LifetimeSec 28800 QMLimit 1 DHGroup 2
>5-10: 10:01:07:561:1fc MMOffer[0] Encrypt: Triple DES CBC Hash: SHA
>5-10: 10:01:07:561:1fc MMOffer[1] LifetimeSec 28800 QMLimit 1 DHGroup 2
>5-10: 10:01:07:561:1fc MMOffer[1] Encrypt: Triple DES CBC Hash: MD5
>5-10: 10:01:07:561:1fc MMOffer[2] LifetimeSec 28800 QMLimit 1 DHGroup 1
>5-10: 10:01:07:561:1fc MMOffer[2] Encrypt: DES CBC Hash: SHA
>5-10: 10:01:07:561:1fc MMOffer[3] LifetimeSec 28800 QMLimit 1 DHGroup 1
>5-10: 10:01:07:561:1fc MMOffer[3] Encrypt: DES CBC Hash: MD5
>5-10: 10:01:07:571:1fc Auth[0]:RSA Sig C=CA, S=Ontario, L=Ottawa, O=Xelerance, OU=IT, CN=Phb, E=phb@xelerance.com AuthFlags 0
>5-10: 10:01:07:571:1fc QM PolicyName: Host-roadwarrior filter action dwFlags 1> 5-10: 10:01:07:571:1fc QMOffer[0] LifetimeKBytes 50000 LifetimeSec 3600
>5-10: 10:01:07:571:1fc QMOffer[0] dwFlags 0 dwPFSGroup -2147483648
>5-10: 10:01:07:571:1fc Algo[0] Operation: ESP Algo: Triple DES CBC HMAC: MD5
>5-10: 10:01:07:571:1fc Starting Negotiation: src = 192.168.1.2.0500, dst = 202.149.x.x.0500, proto = 00, context = 00000006, ProxySrc = 192.168.1.2.0000, ProxyDst = 192.168.2.0.0000 SrcMask = 255.255.255.255 DstMask = 255.255.255.0
>5-10: 10:01:07:571:1fc constructing ISAKMP Header
>5-10: 10:01:07:571:1fc constructing SA (ISAKMP)
>5-10: 10:01:07:571:1fc Constructing Vendor MS NT5 ISAKMPOAKLEY
>5-10: 10:01:07:581:1fc Constructing Vendor FRAGMENTATION
>5-10: 10:01:07:581:1fc Constructing Vendor draft-ietf-ipsec-nat-t-ike-02
>5-10: 10:01:07:581:1fc Constructing Vendor Vid-Initial-Contact
[...]
271

Debugging and Troubleshooting
The most common errors on Windows are wrongly imported certificates and incorrect settings in ipsec.conf when using ipsec.exe. These will usually result in an error in the Openswan log similar to the following:
Jan 24 09:54:45 FenAtHome pluto[16979]: "west-roadwarriors"[1] 193.110.157.131 #1: encrypted Informational Exchange message is invalid because it is for incomplete ISAKMP SA
This is because Windows seems to think the encryption for ISAKMP (Phase 1) already succeeded, while Openswan does not agree. Therefore Windows sends an encrypted packet, and Openswan drops this invalid packet. But the root of this problem is usually that Windows rejects a certificate. You can see the corresponding Windows error in Oakley.log when Openswan sends an unencrypted notification to the Windows machine:
8-30: 15:58:48:865:714 Receive: (get) SA = 0x000fea00 from 193.110.157.131 8-30: 15:58:48:865:714 ISAKMP Header: (V1.0), len = 188
8-30: 15:58:48:865:714 |
I-COOKIE 72db281985c1bc2a |
8-30: 15:58:48:865:714 |
R-COOKIE 1830a6b579ac5c77 |
8-30: 15:58:48:865:714 |
exchange: Oakley Main Mode |
8-30: 15:58:48:865:714 |
flags: 0 |
8-30: 15:58:48:865:714 |
next payload: KE |
8-30: 15:58:48:865:714 |
message ID: 00000000 |
8-30: 15:58:48:865:714 received an unencrypted packet when crypto active 8-30: 15:58:48:865:714 GetPacket failed 35ec
But Openswan does not always blindly send notification messages, because that could result in two systems sending endless ignored notification messages, a so-called notification war.
If Windows gets stuck slightly further into the IPsec SA set-up procedure before it fails, then it will actually send a delete for the ISAKMP SA:
Jan 24 10:15:48 EphemeralTruth pluto[25023]: "west-roadwarriors"[2] 193.110.157.131 #4: received Delete SA payload: deleting ISAKMP State #4
This happens either because of a wrong DN, or because the Root CA or X.509 Certificate is not found. See Chapter 8 to properly generate and import certificates on Windows. These problems can also be seen in the Oakley.log file on Windows.
8-13: 02:28:36:250:d20 Looking for any cert
8-13: 02:28:36:250:d20 failed to get chain 80092004
8-13: 02:28:36:250:d20 ProcessFailure: sa:000D9EC0 centry:00000000 status:35ee 8-13: 02:28:36:250:d20 isadb_set_status sa:000D9EC0 centry:00000000 status 35ee 8-13: 02:28:36:250:d20 Key Exchange Mode (Main Mode)
8-13: 02:28:36:250:d20 Source IP Address 192.168.13.13 Source IP Address Mask 255.255.255.255 Destination IP Address 193.110.157.131 Destination IP Address Mask 255.255.255.255 Protocol 0 Source Port 0 Destination Port 0 IKE Local Addr IKE Peer Addr
8-13: 02:28:36:250:d20 Certificate based Identity. Peer IP Address: 193.110.157.131
8-13: 02:28:36:250:d20 Me
8-13: 02:28:36:250:d20 IKE failed to find valid machine certificate 8-13: 02:28:36:250:d20 0x80092004 0x0
8-13: 02:28:36:250:d20 ProcessFailure: sa:000D9EC0 centry:00000000 status:35ee
8-13: 02:28:36:250:d20 constructing ISAKMP Header
8-13: 02:28:36:250:d20 constructing HASH (null)
8-13: 02:28:36:250:d20 constructing NOTIFY 28
8-13: 02:28:36:250:d20 constructing HASH (Notify/Delete)
Note the line saying "IKE failed to find valid machine certificate". The certimport.exe tool can help here; you can find it on the Openswan website or FTP site.
272
Chapter 12
If you cannot start the policy agent, and get this error:
Windows cannot start the policyagent
Could not start the IPSEC Services service on Local Computer
Error 123: The filename, directory name, or volume label syntax is incorrect
then your Windows machine cannot start the IKE daemon, lsass.exe. Go to the IPSEC Services service in Administrative Tools and view the properties window to verify the path to executable. If it starts with \SystemRoot\C:\Windows, then you need to remove the \systemRoot\ part.
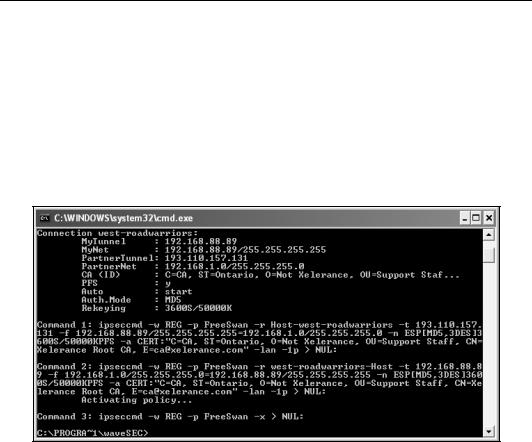
Debugging ipsec.exe
If using the e.bootis VPN client (aka ipsec.exe), you can also run the command in debug mode to see exactly what it will do.
Be aware that Windows will only start IKE negotiation when it receives traffic destined for the other end of the VPN connection, so you should run a ping first. Often, that one ping command, which sends three consecutive ping packets, is enough to trigger the VPN to establish, but those three ping packets are almost always lost. Always issue the ping command at least twice to see the response packets confirming your IPsec connection has come up. If your ping commands do not even trigger the message "Negotiating IP security", then you might have accidentally used auto=add instead of auto=start in your Window's ipsec.conf file. To fix this, run
ipsec --delete, edit the file, and rerun ipsec.exe.
If ipsec.exe on Windows XP gives you the error:
Error converting policy: 0x7b
then the Windows IKE daemon could not start for some reason. This could be because another VPN client is running (such as Cisco, or Nortel).
You can also run the IPsec monitor through MMC to see these loaded policies. See Chapter 8 for how to enable the IPsec monitor.
273
