
- •Introduction
- •Who This Book Is For
- •What This Book Covers
- •How This Book Is Structured
- •What You Need to Use This Book
- •Conventions
- •Source Code
- •Errata
- •p2p.wrox.com
- •What Are Regular Expressions?
- •What Can Regular Expressions Be Used For?
- •Finding Doubled Words
- •Checking Input from Web Forms
- •Changing Date Formats
- •Finding Incorrect Case
- •Adding Links to URLs
- •Regular Expressions You Already Use
- •Search and Replace in Word Processors
- •Directory Listings
- •Online Searching
- •Why Regular Expressions Seem Intimidating
- •Compact, Cryptic Syntax
- •Whitespace Can Significantly Alter the Meaning
- •No Standards Body
- •Differences between Implementations
- •Characters Change Meaning in Different Contexts
- •Regular Expressions Can Be Case Sensitive
- •Case-Sensitive and Case-Insensitive Matching
- •Case and Metacharacters
- •Continual Evolution in Techniques Supported
- •Multiple Solutions for a Single Problem
- •What You Want to Do with a Regular Expression
- •Replacing Text in Quantity
- •Regular Expression Tools
- •findstr
- •Microsoft Word
- •StarOffice Writer/OpenOffice.org Writer
- •Komodo Rx Package
- •PowerGrep
- •Microsoft Excel
- •JavaScript and JScript
- •VBScript
- •Visual Basic.NET
- •Java
- •Perl
- •MySQL
- •SQL Server 2000
- •W3C XML Schema
- •An Analytical Approach to Using Regular Expressions
- •Express and Document What You Want to Do in English
- •Consider the Regular Expression Options Available
- •Consider Sensitivity and Specificity
- •Create Appropriate Regular Expressions
- •Document All but Simple Regular Expressions
- •Document What You Expect the Regular Expression to Do
- •Document What You Want to Match
- •Test the Results of a Regular Expression
- •Matching Single Characters
- •Matching Sequences of Characters That Each Occur Once
- •Introducing Metacharacters
- •Matching Sequences of Different Characters
- •Matching Optional Characters
- •Matching Multiple Optional Characters
- •Other Cardinality Operators
- •The * Quantifier
- •The + Quantifier
- •The Curly-Brace Syntax
- •The {n} Syntax
- •The {n,m} Syntax
- •Exercises
- •Regular Expression Metacharacters
- •Thinking about Characters and Positions
- •The Period (.) Metacharacter
- •Matching Variably Structured Part Numbers
- •Matching a Literal Period
- •The \w Metacharacter
- •The \W Metacharacter
- •Digits and Nondigits
- •The \d Metacharacter
- •Canadian Postal Code Example
- •The \D Metacharacter
- •Alternatives to \d and \D
- •The \s Metacharacter
- •Handling Optional Whitespace
- •The \S Metacharacter
- •The \t Metacharacter
- •The \n Metacharacter
- •Escaped Characters
- •Finding the Backslash
- •Modifiers
- •Global Search
- •Case-Insensitive Search
- •Exercises
- •Introduction to Character Classes
- •Choice between Two Characters
- •Using Quantifiers with Character Classes
- •Using the \b Metacharacter in Character Classes
- •Selecting Literal Square Brackets
- •Using Ranges in Character Classes
- •Alphabetic Ranges
- •Use [A-z] With Care
- •Digit Ranges in Character Classes
- •Hexadecimal Numbers
- •IP Addresses
- •Reverse Ranges in Character Classes
- •A Potential Range Trap
- •Finding HTML Heading Elements
- •Metacharacter Meaning within Character Classes
- •The ^ metacharacter
- •How to Use the - Metacharacter
- •Negated Character Classes
- •Combining Positive and Negative Character Classes
- •POSIX Character Classes
- •The [:alnum:] Character Class
- •Exercises
- •String, Line, and Word Boundaries
- •The ^ Metacharacter
- •The ^ Metacharacter and Multiline Mode
- •The $ Metacharacter
- •The $ Metacharacter in Multiline Mode
- •Using the ^ and $ Metacharacters Together
- •Matching Blank Lines
- •Working with Dollar Amounts
- •Revisiting the IP Address Example
- •What Is a Word?
- •Identifying Word Boundaries
- •The \< Syntax
- •The \>Syntax
- •The \b Syntax
- •The \B Metacharacter
- •Less-Common Word-Boundary Metacharacters
- •Exercises
- •Grouping Using Parentheses
- •Parentheses and Quantifiers
- •Matching Literal Parentheses
- •U.S. Telephone Number Example
- •Alternation
- •Choosing among Multiple Options
- •Unexpected Alternation Behavior
- •Capturing Parentheses
- •Numbering of Captured Groups
- •Numbering When Using Nested Parentheses
- •Named Groups
- •Non-Capturing Parentheses
- •Back References
- •Exercises
- •Why You Need Lookahead and Lookbehind
- •The (? metacharacters
- •Lookahead
- •Positive Lookahead
- •Negative Lookahead
- •Positive Lookahead Examples
- •Positive Lookahead in the Same Document
- •Inserting an Apostrophe
- •Lookbehind
- •Positive Lookbehind
- •Negative Lookbehind
- •How to Match Positions
- •Adding Commas to Large Numbers
- •Exercises
- •What Are Sensitivity and Specificity?
- •Extreme Sensitivity, Awful Specificity
- •Email Addresses Example
- •Replacing Hyphens Example
- •The Sensitivity/Specificity Trade-Off
- •Sensitivity, Specificity, and Positional Characters
- •Sensitivity, Specificity, and Modes
- •Sensitivity, Specificity, and Lookahead and Lookbehind
- •How Much Should the Regular Expressions Do?
- •Abbreviations
- •Characters from Other Languages
- •Names
- •Sensitivity and How to Achieve It
- •Specificity and How to Maximize It
- •Exercises
- •Documenting Regular Expressions
- •Document the Problem Definition
- •Add Comments to Your Code
- •Making Use of Extended Mode
- •Know Your Data
- •Abbreviations
- •Proper Names
- •Incorrect Spelling
- •Creating Test Cases
- •Debugging Regular Expressions
- •Treacherous Whitespace
- •Backslashes Causing Problems
- •Considering Other Causes
- •The User Interface
- •Metacharacters Available
- •Quantifiers
- •The @ Quantifier
- •The {n,m} Syntax
- •Modes
- •Character Classes
- •Back References
- •Lookahead and Lookbehind
- •Lazy Matching versus Greedy Matching
- •Examples
- •Character Class Examples, Including Ranges
- •Whole Word Searches
- •Search-and-Replace Examples
- •Changing Name Structure Using Back References
- •Manipulating Dates
- •The Star Training Company Example
- •Regular Expressions in Visual Basic for Applications
- •Exercises
- •The User Interface
- •Metacharacters Available
- •Quantifiers
- •Modes
- •Character Classes
- •Alternation
- •Back References
- •Lookahead and Lookbehind
- •Search Example
- •Search-and-Replace Example
- •Online Chats
- •POSIX Character Classes
- •Matching Numeric Digits
- •Exercises
- •Introducing findstr
- •Finding Literal Text
- •Quantifiers
- •Character Classes
- •Command-Line Switch Examples
- •The /v Switch
- •The /a Switch
- •Single File Examples
- •Simple Character Class Example
- •Find Protocols Example
- •Multiple File Example
- •A Filelist Example
- •Exercises
- •The PowerGREP Interface
- •A Simple Find Example
- •The Replace Tab
- •The File Finder Tab
- •Syntax Coloring
- •Other Tabs
- •Numeric Digits and Alphabetic Characters
- •Quantifiers
- •Back References
- •Alternation
- •Line Position Metacharacters
- •Word-Boundary Metacharacters
- •Lookahead and Lookbehind
- •Longer Examples
- •Finding HTML Horizontal Rule Elements
- •Matching Time Example
- •Exercises
- •The Excel Find Interface
- •Escaping Wildcard Characters
- •Using Wildcards in Data Forms
- •Using Wildcards in Filters
- •Exercises
- •Using LIKE with Regular Expressions
- •The % Metacharacter
- •The _ Metacharacter
- •Character Classes
- •Negated Character Classes
- •Using Full-Text Search
- •Using The CONTAINS Predicate
- •Document Filters on Image Columns
- •Exercises
- •Using the _ and % Metacharacters
- •Testing Matching of Literals: _ and % Metacharacters
- •Using Positional Metacharacters
- •Using Character Classes
- •Quantifiers
- •Social Security Number Example
- •Exercises
- •The Interface to Metacharacters in Microsoft Access
- •Creating a Hard-Wired Query
- •Creating a Parameter Query
- •Using the ? Metacharacter
- •Using the * Metacharacter
- •Using the # Metacharacter
- •Using the # Character with Date/Time Data
- •Using Character Classes in Access
- •Exercises
- •The RegExp Object
- •Attributes of the RegExp Object
- •The Other Properties of the RegExp Object
- •The test() Method of the RegExp Object
- •The exec() Method of the RegExp Object
- •The String Object
- •Metacharacters in JavaScript and JScript
- •SSN Validation Example
- •Exercises
- •The RegExp Object and How to Use It
- •Quantifiers
- •Positional Metacharacters
- •Character Classes
- •Word Boundaries
- •Lookahead
- •Grouping and Nongrouping Parentheses
- •Exercises
- •The System.Text.RegularExpressions namespace
- •A Simple Visual Basic .NET Example
- •The Classes of System.Text.RegularExpressions
- •The Regex Object
- •Using the Match Object and Matches Collection
- •Using the Match.Success Property and Match.NextMatch Method
- •The GroupCollection and Group Classes
- •The CaptureCollection and Capture Class
- •The RegexOptions Enumeration
- •Case-Insensitive Matching: The IgnoreCase Option
- •Multiline Matching: The Effect on the ^ and $ Metacharacters
- •Right to Left Matching: The RightToLeft Option
- •Lookahead and Lookbehind
- •Exercises
- •An Introductory Example
- •The Classes of System.Text.RegularExpressions
- •The Regex Class
- •The Options Property of the Regex Class
- •Regex Class Methods
- •The CompileToAssembly() Method
- •The GetGroupNames() Method
- •The GetGroupNumbers() Method
- •GroupNumberFromName() and GroupNameFromNumber() Methods
- •The IsMatch() Method
- •The Match() Method
- •The Matches() Method
- •The Replace() Method
- •The Split() Method
- •Using the Static Methods of the Regex Class
- •The IsMatch() Method as a Static
- •The Match() Method as a Static
- •The Matches() Method as a Static
- •The Replace() Method as a Static
- •The Split() Method as a Static
- •The Match and Matches Classes
- •The Match Class
- •The GroupCollection and Group Classes
- •The RegexOptions Class
- •The IgnorePatternWhitespace Option
- •Metacharacters Supported in Visual C# .NET
- •Using Named Groups
- •Using Back References
- •Exercise
- •The ereg() Set of Functions
- •The ereg() Function
- •The ereg() Function with Three Arguments
- •The eregi() Function
- •The ereg_replace() Function
- •The eregi_replace() Function
- •The split() Function
- •The spliti() Function
- •The sql_regcase() Function
- •Perl Compatible Regular Expressions
- •Pattern Delimiters in PCRE
- •Escaping Pattern Delimiters
- •Matching Modifiers in PCRE
- •Using the preg_match() Function
- •Using the preg_match_all() Function
- •Using the preg_grep() Function
- •Using the preg_quote() Function
- •Using the preg_replace() Function
- •Using the preg_replace_callback() Function
- •Using the preg_split() Function
- •Supported Metacharacters with ereg()
- •Using POSIX Character Classes with PHP
- •Supported Metacharacters with PCRE
- •Positional Metacharacters
- •Character Classes in PHP
- •Documenting PHP Regular Expressions
- •Exercises
- •W3C XML Schema Basics
- •Tools for Using W3C XML Schema
- •Comparing XML Schema and DTDs
- •How Constraints Are Expressed in W3C XML Schema
- •W3C XML Schema Datatypes
- •Derivation by Restriction
- •Unicode and W3C XML Schema
- •Unicode Overview
- •Using Unicode Character Classes
- •Matching Decimal Numbers
- •Mixing Unicode Character Classes with Other Metacharacters
- •Unicode Character Blocks
- •Using Unicode Character Blocks
- •Metacharacters Supported in W3C XML Schema
- •Positional Metacharacters
- •Matching Numeric Digits
- •Alternation
- •Using the \w and \s Metacharacters
- •Escaping Metacharacters
- •Exercises
- •Introduction to the java.util.regex Package
- •Obtaining and Installing Java
- •The Pattern Class
- •Using the matches() Method Statically
- •Two Simple Java Examples
- •The Properties (Fields) of the Pattern Class
- •The CASE_INSENSITIVE Flag
- •Using the COMMENTS Flag
- •The DOTALL Flag
- •The MULTILINE Flag
- •The UNICODE_CASE Flag
- •The UNIX_LINES Flag
- •The Methods of the Pattern Class
- •The compile() Method
- •The flags() Method
- •The matcher() Method
- •The matches() Method
- •The pattern() Method
- •The split() Method
- •The Matcher Class
- •The appendReplacement() Method
- •The appendTail() Method
- •The end() Method
- •The find() Method
- •The group() Method
- •The groupCount() Method
- •The lookingAt() Method
- •The matches() Method
- •The pattern() Method
- •The replaceAll() Method
- •The replaceFirst() Method
- •The reset() Method
- •The start() Method
- •The PatternSyntaxException Class
- •Using the \d Metacharacter
- •Character Classes
- •The POSIX Character Classes in the java.util.regex Package
- •Unicode Character Classes and Character Blocks
- •Using Escaped Characters
- •Using Methods of the String Class
- •Using the matches() Method
- •Using the replaceFirst() Method
- •Using the replaceAll() Method
- •Using the split() Method
- •Exercises
- •Obtaining and Installing Perl
- •Creating a Simple Perl Program
- •Basics of Perl Regular Expression Usage
- •Using the m// Operator
- •Using Other Regular Expression Delimiters
- •Matching Using Variable Substitution
- •Using the s/// Operator
- •Using s/// with the Global Modifier
- •Using s/// with the Default Variable
- •Using the split Operator
- •Using Quantifiers in Perl
- •Using Positional Metacharacters
- •Captured Groups in Perl
- •Using Back References in Perl
- •Using Alternation
- •Using Character Classes in Perl
- •Using Lookahead
- •Using Lookbehind
- •Escaping Metacharacters
- •A Simple Perl Regex Tester
- •Exercises
- •Index
PowerGREP
The overall effect is that if Star occurs before zero or more spaces and then the character sequence Training, it is replaced by the character sequence Moon.
Alternation
Alternation is supported by PowerGREP. An example was shown in the first example in this chapter, using Regex.txt as a sample file.
Line Position Metacharacters
PowerGREP supports both line-end positional metacharacters ^ and $. The ^ metacharacter matches the position before the first character in a line. The $ metacharacter matches the position after the last character in a line.
The test file, LineEndTest.txt, is shown here:
This is here.
Look at this.
This is a theatre.
Theatre is as stimulating as this.
Try It Out |
Line Position Metacharacters |
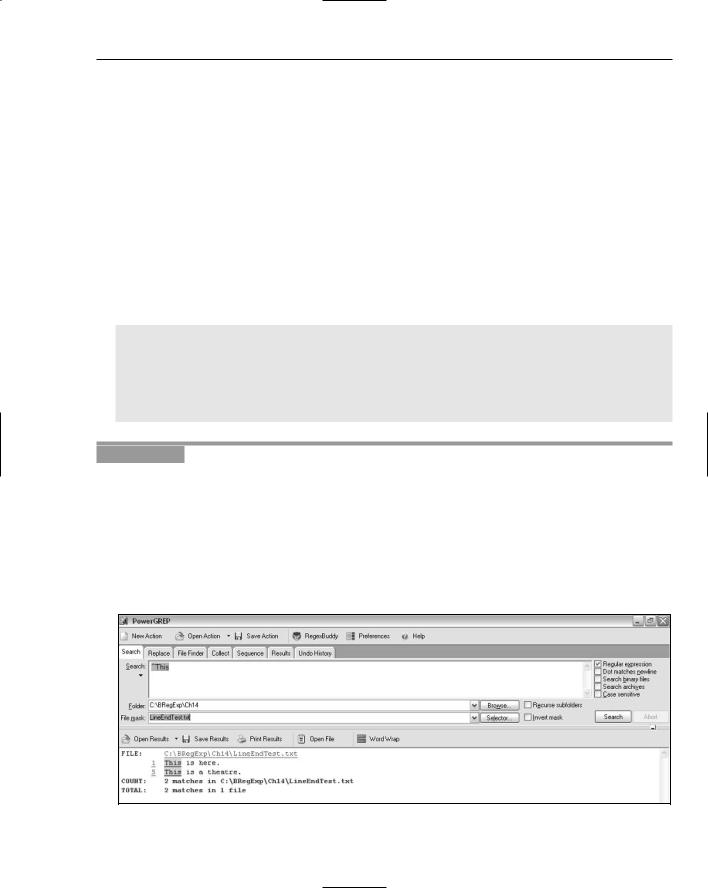
1.Open PowerGREP, and ensure that the Regular Expression check box is checked.
2.In the Search text area, type the pattern ^This.
3.Ensure that the Folder text box contains C:\BRegExp\Ch14 or adapt this path if you downloaded code to a different directory.
4.In the File Mask text box, type LineEndTest.txt; click the Search button; and inspect the results, as shown in Figure 14-14. Remember that the default matching in PowerGREP is case insensitive. Notice that the character sequence This is matched only at the beginning of a line.
Figure 14-14
339
Chapter 14
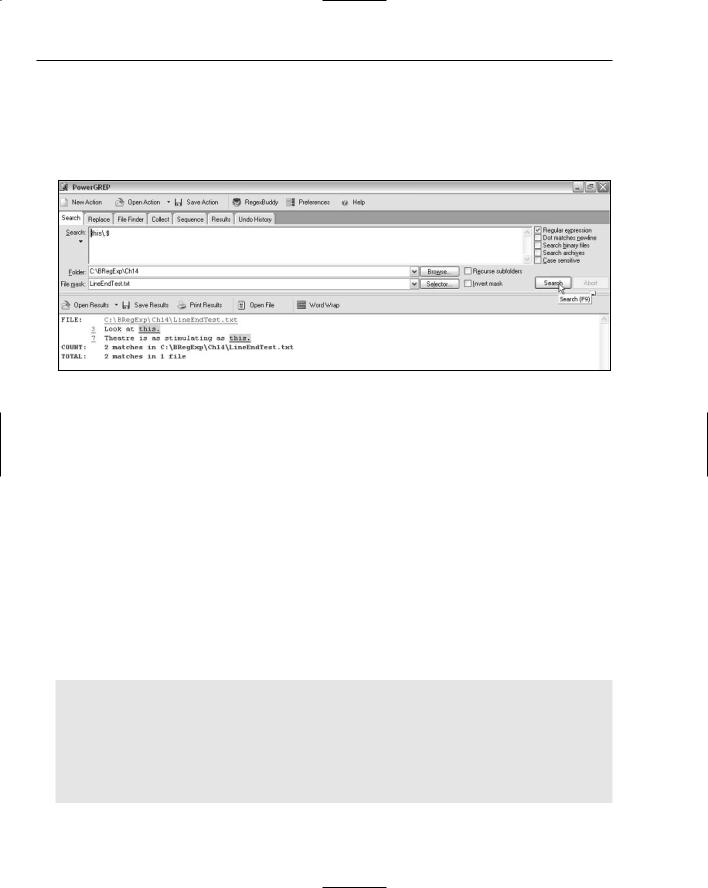
5.Modify the pattern in the Search text area to this\.$. Remember that if the period character is the last character on the line, the pattern this$ will never match with the test text for this example.
6.Click the Search button, and inspect the results, as shown in Figure 14-15. Both of the occurrences of the character sequence this. at the end of a line are matched.
Figure 14-15
How It Works
First, let’s look at matching with the pattern ^This. This matches the position before the first character on a line and then attempts to match the character sequence This. This means that it matches the character sequence This at the beginning of a line.
When the pattern is this\.$, this followed by a period character, followed by the $ metacharacter, the character sequence this followed by a period character is first matched; then an attempt is made to match the end-of-line position. That only succeeds when this. makes up the final five characters on a line.
Word-Boundary Metacharacters
Only the \b word-boundary character is supported in PowerGREP. Neither the \< nor the \> wordboundary metacharacters is supported.
The test text for this example, Cat.txt, is shown here:
Catalonia is a region of Spain.
“Scat,” he said.
A caterpillar later becomes a butterfly.
I love my cat.
The cat sat on the mat.
340

PowerGREP
Try it Out |
Word-Boundary Position Metacharacters |
1.Open PowerGREP, and ensure that the Regular Expression check box is checked.
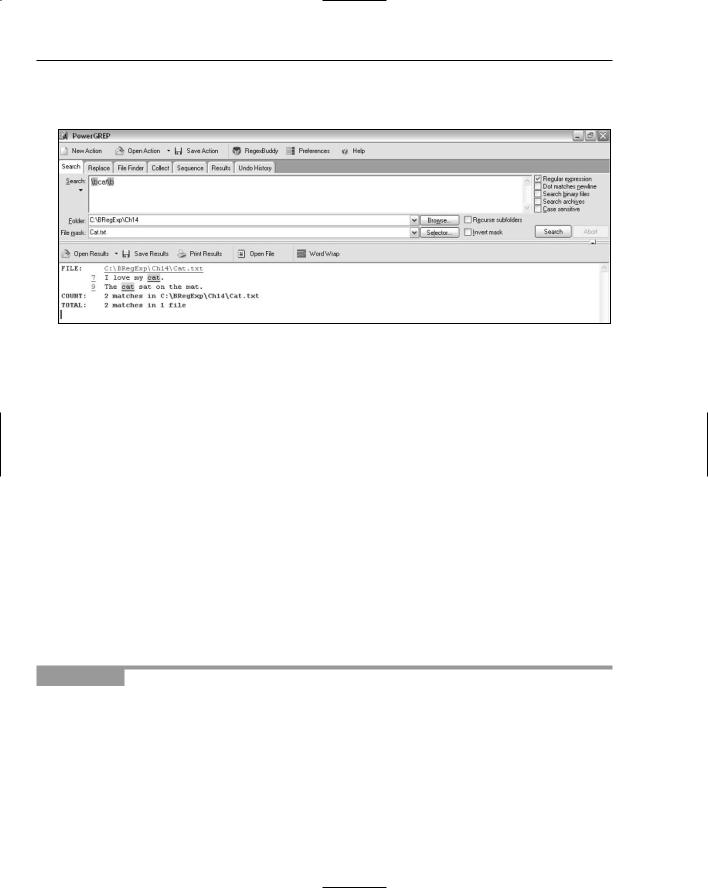
2.In the Search text area, type the pattern \bcat.
3.In the Folder text box, type C:\BRegExp\Ch14, adjusting the folder if you downloaded files to some other location.
4.In the File Mask text box, type Cat.txt; click the Search button; and inspect the results, as shown in Figure 14-16. Notice that the character sequence cat is matched only when it is the first three characters of an alphabetic character sequence — colloquially, a word.
Figure 14-16
5.Modify the pattern in the Search text area to cat\b; click the Search button; and inspect the results, as shown in Figure 14-17. Notice that the character sequence cat is matched only when it is the last three characters of an alphabetic character sequence.
Figure 14-17
341
Chapter 14
6.Modify the pattern in the Search text area to \bcat\b; click the Search button; and inspect the results, as shown in Figure 14-18.
Figure 14-18
How It Works
The pattern \bcat first matches a boundary between nonalphabetic and alphabetic characters. Because the \b metacharacter is followed by a sequence of alphabetic characters, it is, in that context, functioning as a beginning-of-word position metacharacter. Therefore, \bcat matches the three-character sequence of characters cat when it occurs at the beginning of a word.
The pattern cat\b matches the three-character sequence of characters cat when the sequence is followed by a word-boundary position. Therefore, cat\b matches the character sequence when it occurs at the end of a word, as in cat or Scat.
The pattern \bcat\b matches only when there is a word-boundary position before the character sequence cat and immediately after it. In other words, the pattern \bcat\b matches only the word cat.
Lookahead and Lookbehind
Lookahead and lookbehind are supported in PowerGREP.
The following example uses the StarOriginal.txt file, which was used earlier in the chapter.
Try It Out |
Lookahead and Lookbehind |
1.Open PowerGREP, and ensure that the Regular Expression check box is checked.
2.In the Search text area, type the pattern Star(?=.).
3.In the Folder text box, type C:\BRegExp\Ch14 or adapt the path if you downloaded sample files to another location.
4.In the File Mask text box, type StarOriginal.txt; click the Search button; and inspect the results, as shown in Figure 14-19.
5.Edit the pattern in the Search text area to (?<=with )Star, click the Search button, and inspect the results.
342
