
- •Table of Contents
- •Dedication
- •Foreword
- •Introduction
- •What Is FreeBSD?
- •How Did FreeBSD Get Here?
- •The BSD License: BSD Goes Public
- •The Birth of Modern FreeBSD
- •FreeBSD Development
- •Committers
- •Contributors
- •Users
- •Other BSDs
- •NetBSD
- •OpenBSD
- •Other UNIXes
- •Solaris
- •Linux
- •IRIX, HPUX, etc.
- •FreeBSD's Strengths
- •Portability
- •Power
- •Simplified Software Management
- •Optimized Upgrade Process
- •Filesystem
- •Who Should Use FreeBSD
- •FreeBSD as Your Desktop
- •Who Should Run Another BSD
- •Who Should Run a Proprietary Operating System
- •How to Read This Book
- •What Must You Know?
- •How to Think About UNIX
- •Channels of Communication
- •Working with Channels
- •The Command Line
- •Chapter 1: Installation
- •FreeBSD Hardware
- •Processor
- •Memory (RAM)
- •Hard Drives
- •Downloading FreeBSD
- •Installing by FTP
- •Other FTP Install Information
- •Hardware Setup
- •Actually Installing FreeBSD
- •Configuring the Kernel for ISA Cards
- •Sysinstall: The Ugly FreeBSD Installer
- •Disk Usage
- •Partitioning
- •Root
- •Swap Space
- •Swap Splitting
- •/var, /usr, and /home
- •A Second Hard Drive
- •Soft Updates
- •Block Size
- •What to Install
- •Installation Media
- •Committing
- •Root Password
- •Adding Users
- •Time Zone
- •Mouse
- •Configuring Network Cards
- •Xfree86
- •Software
- •Restart
- •A Note on Editors
- •Chapter 2: Getting More Help
- •Why Not Mail First?
- •The FreeBSD Attitude
- •Man Pages
- •The FreeBSD Manual
- •Man Page Headings
- •The FreeBSD Documentation
- •The Mailing List Archives
- •Other Web Sites
- •Checking the Handbook/FAQ
- •Checking the Man Pages
- •Checking the Mailing List Archives
- •Using Your Answer
- •Mailing for Help
- •Chapter 3: Read This Before You Break Something Else! (Backup and Recovery)
- •Overview
- •System Backups
- •Tape Devices
- •How to Read Dmesg.boot
- •Controlling Your Tape Drive
- •Device Nodes
- •Using the TAPE Variable
- •The mt Command
- •Backup Programs
- •Dump/Restore
- •Restoring from an Archive
- •Checking the Contents of an Archive
- •Extracting Data from an Archive
- •Restoring Interactively
- •Recording What Happened
- •Revision Control
- •Getting Older Versions
- •Breaking Locks
- •Viewing Log Messages
- •Reviewing a File's Revision History
- •Ident and ident Strings
- •Going Further
- •The Fixit Disk
- •Chapter 4: Kernel Games
- •Overview
- •What Is the Kernel?
- •Configuring Your Kernel
- •Sysctl
- •Changing Sysctls
- •Setting Sysctls at Boot
- •Kernel Configuration with Loader.conf
- •Manually Configuring the Loader
- •Viewing Loaded Modules
- •Loading and Unloading Modules
- •Customizing the Kernel
- •Preparation
- •Your Backup Kernel
- •Editing Kernel Files
- •Basic Options
- •Multiple Processors
- •Device Entries
- •Building Your Kernel
- •Troubleshooting Kernel Builds
- •Booting an Alternate Kernel
- •Adding to the Kernel
- •LINT
- •Fixing Errors with Options
- •Tweaking Kernel Performance
- •Sharing Kernels
- •Chapter 5: Networking
- •Overview
- •Network Layers
- •The Physical Layer
- •The Physical Protocol Layer
- •The Logical Protocol Layer
- •The Application Layer
- •The Network in Practice
- •Mbufs
- •What Is a Bit?
- •Ethernet
- •Broadcasting
- •Address Resolution
- •Hubs and Switches
- •Netmasks
- •Netmask Tricks
- •Hexadecimal Netmasks
- •Unusable IP Addresses
- •Routing
- •Network Ports
- •Connecting to an Ethernet Network
- •Multiple IP Addresses on One Interface
- •Using Netstat
- •Chapter 6: Upgrading FreeBSD
- •Overview
- •FreeBSD Versions
- •Release
- •Snapshots
- •Security Updates
- •Which Release Should You Use?
- •Upgrade Methods
- •Upgrading via Sysinstall
- •Upgrading via CVSup
- •Simplifying the CVSup Upgrade Process
- •Building a Local CVSup Server
- •Controlling Access
- •Authentication
- •Combining Authentication and Access
- •Chapter 7: Securing Your System
- •Overview
- •Who Is the Enemy?
- •Script Kiddies
- •Disaffected Users
- •Skilled Attackers
- •FreeBSD Security Announcements
- •Subscribing
- •What You'll Get
- •Installation Security Profiles
- •Moderate
- •Extreme
- •Root, Groups, and Permissions
- •The root Password
- •Groups of Users
- •Primary Group
- •Some Interesting Default Groups
- •Group Permissions
- •Changing Permissions
- •Changing File Ownership
- •Assigning Permissions
- •File Flags
- •Viewing a File's Flags
- •Setting Flags
- •Securelevels
- •Setting Securelevels
- •Which Securelevel Do You Need?
- •What Won't Securelevel and File Flags Do?
- •Living with Securelevels
- •Programs That Can Be Hacked
- •Putting It All Together
- •Chapter 8: Advanced Security Features
- •Traffic Control
- •Default Accept vs. Default Deny
- •TCP Wrappers
- •Configuring Wrappers
- •Daemon Name
- •The Client List
- •Putting It All Together
- •Packet Filtering
- •IPFilter
- •IPFW
- •Default Accept and Default Deny in Packet Filtering
- •Basic Concepts of Packet Filtering
- •Implementing IPFilter
- •Configuring Your Server to Use Jail
- •Configuring Your Kernel to Use Jail
- •Client Setup
- •Final Jail Setup
- •Starting the Jail
- •Managing Jails
- •Shutting Down a Jail
- •Monitoring System Security
- •If You're Hacked
- •Chapter 9: Too Much Information About /etc
- •Overview
- •Varieties of /etc Files
- •Default Files
- •/etc/defaults/rc.conf
- •/etc/adduser.conf
- •/etc/crontab
- •/etc/dhclient.conf
- •/etc/fstab
- •/etc/hosts.allow
- •/etc/hosts.equiv
- •/etc/hosts.lpd
- •/etc/inetd.conf
- •/etc/locate.rc
- •/etc/login.access
- •/etc/login.conf
- •Specifying Default Environment Settings
- •/etc/mail/mailer.conf
- •/etc/make.conf and /etc/defaults/make.conf
- •/etc/master.passwd
- •/etc/motd
- •/etc/mtree/*
- •/etc/namedb/*
- •/etc/newsyslog.conf
- •/etc/passwd
- •/etc/periodic.conf and /etc/defaults/periodic.conf
- •/etc/printcap
- •Working with Printcap Entries
- •/etc/profile
- •/etc/protocols
- •/etc/rc.conf and /etc/defaults/rc.conf
- •/etc/resolv.conf
- •/etc/security
- •/etc/services
- •/etc/shells
- •/etc/spwd.db
- •/etc/sysctl.conf
- •/etc/syslog.conf
- •Chapter 10: Making Your System Useful
- •Overview
- •Making Software
- •The Pain and Pleasure of Source Code
- •Debugging
- •The Ports and Packages System
- •Ports
- •Finding Software
- •Legal Restrictions
- •Using Packages
- •Installing via FTP
- •What Does a Package Install?
- •Uninstalling Packages
- •Package Information
- •Controlling Pkg_add
- •Package Problems
- •Forcing an Install
- •Using Ports
- •Installing a Port
- •Using Make Install
- •Uninstalling and Reinstalling
- •Cleaning Up with Make Clean
- •Building Packages
- •Changing the Install Path
- •Setting Make Options Permanently
- •Upgrading Ports and Packages
- •Upgrading the Ports Collection
- •Ports Collection Upgrade Issues
- •Checking Software Versions
- •Hints for Upgrading
- •Chapter 11: Advanced Software Management
- •Overview
- •Startup and Shutdown Scripts
- •Typical Startup Script
- •Using Scripts to Manage Running Programs
- •Managing Shared Libraries
- •Ldconfig
- •Running Software from the Wrong OS
- •Recompilation
- •Emulation
- •ABI Implementation
- •Foreign Software Libraries
- •Installing and Enabling Linux Mode
- •Identifying Programs
- •What Is Linux_base?
- •Adding to Linux_base
- •Configuring Linux Shared Libraries
- •Installing Extra Linux Packages as RPMs
- •What Is SMP?
- •Kernel Assumptions
- •FreeBSD 3.0 SMP
- •FreeBSD 5 SMP
- •Using SMP
- •SMP and Upgrades
- •Chapter 12: Finding Hosts With DNS
- •How DNS Works
- •Basic DNS Tools
- •The Host Command
- •Getting Detailed Information with Dig
- •Looking Up Hostnames with Dig
- •More Dig Options
- •Configuring a DNS Client: The Resolver
- •Domain or Search Keywords
- •The Nameserver List
- •DNS Information Sources
- •The Hosts File
- •The Named Daemon
- •Zone Files
- •A Real Sample Zone
- •named.conf
- •/var/named/master/absolutebsd.com
- •Making Changes Work
- •Starting Named at Boottime
- •Checking DNS
- •Named Configuration Errors
- •Named Security
- •Controlling Information Order
- •More About BIND
- •Chapter 13: Managing Small Network Services
- •Bandwidth Control
- •Configuring IPFW
- •Reviewing IPFW Rules
- •Dummynet Queues
- •Directional Traffic Shaping
- •Certificates
- •Create a Request
- •Being Your Own CA
- •Testing SSH
- •Enabling SSH
- •Basics of SSH
- •Creating Keys
- •Confirming SSH Identity
- •SSH Clients
- •Connecting via SSH
- •Configuring SSH
- •System Time
- •Setting the Time Zone
- •Network Time Protocol
- •Ntpdate
- •Ntpd
- •Inetd
- •/etc/inetd.conf
- •Configuring Programs in Inetd
- •Inetd Security
- •Starting Inetd
- •Changing Inetd's Behavior
- •Chapter 14: Email Services
- •Email Overview
- •Where FreeBSD Fits In
- •The Email Protocol
- •Email Programs
- •Who Needs Sendmail?
- •Replacing Sendmail
- •Installing Postfix
- •Pieces of Postfix
- •Configuring Postfix
- •Email Aliases
- •Email Logging
- •Virtual Domains
- •Postfix Commands
- •Finding the Correct Mail Host
- •Undeliverable Mail
- •Installing POP3
- •Testing POP3
- •POP3 Logging
- •POP3 Modes
- •Qpopper Preconfiguration Questions
- •Default Qpopper Configuration
- •APOP Setup
- •Configuring Pop3ssl
- •Qpopper Security
- •Chapter 15: Web and FTP Services
- •Overview
- •How a Web Server Works
- •The Apache Web Server
- •Apache Configuration Files
- •Configuring Apache
- •Controlling Apache
- •Virtual Hosting
- •Tweaking Virtual Hosts
- •.NET on FreeBSD
- •Installing the SSCLI
- •FTP Security
- •The FTP Client
- •The FTP Server
- •Chapter 16: Filsystems and Disks
- •Device Nodes
- •Hard Disks and Partitions
- •The /etc/fstab File
- •Disk Basics
- •The Fast File System
- •Vnodes
- •FFS Mount Types
- •FFS Mount Options
- •What's Mounted Now?
- •Dirty Disks
- •Fsck
- •Mounting and Unmounting Disks
- •Mounting Standard Filesystems
- •Mounting with Options
- •Mounting All Standard Filesystems
- •Mounting at Nonstandard Locations
- •Unmounting
- •Soft Updates
- •Enabling Soft Updates
- •IDE Write Caching and Soft Updates
- •Virtual Memory Directory Caching
- •Mounting Foreign Filesystems
- •Using Foreign Mounts
- •Foreign Filesystem Types
- •Mount Options and Foreign Filesystems
- •Filesystem Permissions
- •Removable Media and /etc/fstab
- •Creating a Floppy
- •Creating an FFS Filesystem
- •The Basics of SCSI
- •SCSI Types
- •SCSI Adapters
- •SCSI Buses
- •Termination and Cabling
- •SCSI IDs and LUNs
- •FreeBSD and SCSI
- •Wiring Down Devices
- •Adding New Hard Disks
- •Creating Slices
- •Creating Partitions
- •Configuring /etc/fstab
- •Installing Existing Files onto New Disks
- •Temporary Mounts
- •Moving Files
- •Stackable Mounts
- •Chapter 17: RAID
- •Hardware vs. Software RAID
- •RAID Levels
- •Software RAID
- •Vinum Disk Components
- •Vinum Plex Types
- •Preparing Vinum Drives
- •Dedicating Partitions to Vinum
- •Configuring Vinum
- •Concatenated Plex
- •Removing Vinum Configuration
- •Striped Volumes
- •Mirrored Volumes
- •Starting Vinum at Boot
- •Other Vinum Commands
- •Replacing a Failed Mirrored Plex
- •Chapter 18: System Performance
- •Overview
- •Computer Resources
- •Disk Input/Output
- •Network Bandwidth
- •CPU and Memory
- •Using Top
- •Memory Usage
- •Swap Space Usage
- •CPU Usage
- •When Swap Goes Bad
- •Paging
- •Swapping
- •Are You Swapping or Paging?
- •Fairness in Benchmarking
- •The Initial Test
- •Using Both CPUs
- •Directory Caching
- •Moving /usr/obj
- •Lessons Learned
- •Chapter 19: Now What's It Doing?
- •Status Mails
- •Forwarding Reports
- •Logging with Syslogd
- •Facilities
- •Levels
- •Syslog.conf
- •Wildcards
- •Rotating Logs with Newsyslog.conf
- •Reporting with SNMP
- •Basics of SNMP
- •MIBs
- •Snmpwalk
- •Specific Snmpwalk Queries
- •Translating Between Numbers and Names
- •Setting Up Snmpd
- •Index Numbers
- •Configuring MRTG
- •Sample mrtg.cfg Entry
- •Testing MRTG
- •Tracking Other System Values
- •Monitoring a Single MIB
- •Customizing MRTG
- •MRTG Index Page
- •Sample MRTG Configurations
- •Chapter 20: System Crashes and Panics
- •What Causes Panics?
- •What Does a Panic Look Like?
- •Responding to a Panic
- •Prerequisites
- •Crash Dump Process
- •The Debugging Kernel
- •kernel.debug
- •Dumpon
- •Savecore
- •Upon a Crash
- •Dumps and Bad Kernels
- •Using the Dump
- •Advanced Kernel Debugging
- •Examining Lines
- •Examining Variables
- •Apparent Gdb Weirdness
- •Results
- •Vmcore and Security
- •Symbols vs. No Symbols
- •Serial Consoles
- •Hardware Serial Console
- •Software Serial Console
- •Changing the Configuration
- •Using a Serial Console
- •Serial Login
- •Emergency Logon Setup
- •Disconnecting the Serial Console
- •Submitting a Problem Report
- •Problem Report System
- •What's in a PR?
- •Filling Out the Form
- •PR Results
- •Chapter 21: Desktop FreeBSD
- •Overview
- •Accessing File Shares
- •Prerequisites
- •Character Sets
- •Kernel Support for CIFS
- •SMB Tools
- •Configuring CIFS
- •Minimum Configuration: Name Resolution
- •Other smbutil Functions
- •Mounting a Share
- •Other mount_smbfs Options
- •Sample nsmb.conf Entries
- •CIFS File Ownership
- •Serving Windows File Shares
- •Accessing Print Servers
- •Running a Local Lpd
- •Printer Testing
- •Local Printers
- •X: A Graphic Interface
- •X Prerequisites
- •X Versions
- •Configuring X
- •Making X Look Decent
- •Desktop Applications
- •Web Browsers
- •Email Readers
- •Office Suites
- •Music
- •Graphics
- •Desk Utilities
- •Games
- •Afterword
- •Overview
- •The Community
- •What Can You Do?
- •Getting Things Done
- •Second Opinions
- •Appendix: Some Useful SYSCTL MIBs
- •List of Figures
- •Chapter 1: Installation
- •Chapter 5: Networking
- •Chapter 6: Upgrading FreeBSD
- •Chapter 19: Now What's It Doing?
- •List of Tables
- •Chapter 4: Kernel Games
- •Chapter 5: Networking
- •Chapter 8: Advanced Security Features
- •Chapter 9: Too Much Information About /etc
- •List of Sidebars
- •Chapter 15: Web and FTP Services

Chapter 5: Networking
Overview
BSD is famous for its network performance. In fact, the TCP/IP network protocol itself was first developed on BSD. Many other operating systems have chosen to use the BSD network stack because of its high performance and liberal licensing.
If you're a system administrator, you must understand how networking works. If you're like most sysadmins, you're probably familiar with some of the basics, but not many people understand how all of that networking stuff hangs together. Knowings what an IP address really is, understanding how a netmask works, and comprehending the symbiotic relationship between IP and TCP is what separates a novice from a professional. We'll cover some of these issues here.
If you know what makes a /31 network mostly useless, you can skip this chapter. Otherwise, read on. There will be a test later–not in this book, but in the real world.
Network Layers
Network layers simplify the networking process. Each layer handles a specific part of the networking process, and information is said to travel down and up through these layers. New users often have trouble understanding this, but we'll go over it in detail. The important thing to remember is that each layer only communicates with the layer directly above it and the layer directly beneath it.
The classic ISO network protocol diagram has seven layers, is exhaustively complete, and covers any situation. The Internet isn't "every situation,"; however, and this isn't a book about networking. Since we'll limit our discussion to the Internet world, we can simplify this diagram somewhat and divide the network into four layers: the application, the logical protocol, the physical protocol, and the physical.
Note The descriptions in this chapter are necessarily generalizations, and very thick books have been written about this topic. My favorite is Stevens' TCP/IP Illustrated, volumes 1 through 3 (Addison−Wesley).
97
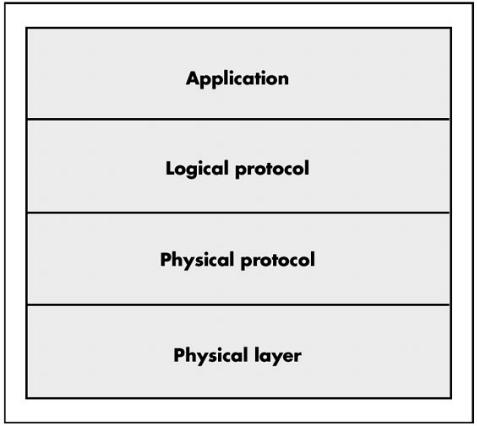
Figure 5.1: 4−layer network diagram
The Physical Layer
The bottom layer is the physical one, encompassing the network card and the wire (or other connection) running out of it. This layer also includes the switch (or network hub) and the wire running to the router, as well as the fiber that carries your packets from your ISP to one of the Internet switching points (network access points, or NAPs) and on to the destination. It may even include radio waves, if you're using wireless. Without this link, you have nothing. The physical protocol is the only thing that needs to recognize how this bottom layer works.
A piece of wire–it's really that simple. If your wire is intact and meets the specifications required by the physical protocol, you're in business. If not, you're hosed.
Some physical protocols have been implemented over many different physical layers and Ethernet has been transmitted over half a dozen different sorts of cable. With minor changes in the device drivers and major changes in the network card, you can change your physical layer and not alter any other layer.
Similarly, a single connection might travel over several different types of wire. One of the functions of Internet routers is to convert one sort of physical layer into another.
The physical layer has no decision−making abilities and no intelligence; everything it does is dictated by the physical protocol.
The Physical Protocol Layer
The physical protocol layer is where things get interesting. The physical protocol talks over the wire. It encodes transmissions in the actual ones and zeroes that are sent over the physical layer in the
98
appropriate manner for that sort of media. For example, Ethernet uses Media Access Control (MAC) addresses and the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP); dial−up uses the Point−to−Point Protocol (PPP, usually used for home connections). The physical protocol has to understand how to speak to these addresses, and to encode and decode messages for them.
Ethernet and PPP are the main physical protocols, though FreeBSD also supports a variety of other physical protocols, such as Asynchronous Transfer Mode (ATM) and Integrated Services Digital Network (ISDN), as well as combinations such as PPP over Ethernet (used by some home−broadband vendors). Each of these protocols has special requirements, and while we'll only discuss Ethernet in some detail, you should understand that other connection protocols exist.
The physical protocol passes information to and from the physical layer and the logical protocol layer.
The Logical Protocol Layer
Logical protocols, such as Internet Protocol (IP) and Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) handle things like IP addresses and port operations by exchanging information with the physical protocol and the application. You can use multiple logical protocols simultaneously.
There are many logical protocols. (See the /etc/protocols file for a mostly complete list.) The protocols we're most concerned with are IP and TCP (both already mentioned), Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP), and User Datagram Protocol (UDP).
Logical protocols can work side by side, and can even depend upon one another. When a packet is transmitted, it includes a flag that identifies which protocol it belongs to.
Internet Protocol
The Internet Protocol (IP) is the baling wire that holds the Internet together, and every device on the Internet is expected to speak IP. IP provides very basic, core functions, such as network addresses and packet routing, as well as the fundamental infrastructure used by other logical protocols. You can live without TCP and other protocols, but if you don't have IP you don't have the Net.
Note In this book, we only discuss IP version 4; IP version 6 is fairly new. While FreeBSD includes excellent IPv6 support, it's not yet widespread enough to cover here. Hopefully, by the time a new edition of this book comes out, IPv6 will be widespread, because it fixes many problems found in IPv4, thus eliminating the gross hacks that have been implemented to work around them.
IP Addresses
An IP address is a 32−bit number, generally divided into four groups of 8 bits each. Translated into English, this means that you'll see four numbers, each from 0 to 255, separated by periods. For example, 192.168.1.87 is a valid IP address, while 192.259.0.87 is not–one of the numbers exceeds 255. 607.322.843.999 is Right Out.
Every device on the Internet has a unique IP address, unless it's using Network Address Translation (NAT) or some other ugly hack.
99
