
Wypych Handbook of Solvents
.pdf322 |
V V Tereshatov, V Yu. Senichev, E Ya Denisyuk |
ture as a uniform liquid with parameters χ123 and V12 variable in composition. The calculated ratios of components of mixtures, at which the extreme swelling of elastomers is expected, are given in Table 6.2.2.
Table 6.2.2. Position of a maximum on the swelling curve of crosslinked elastomers in binary mixtures. [Adapted, by permission, from V. V. Tereshatov, M. I. Balashova, A. I. Gemuev, Prediction and regulating of properties of polymeric materials, Ural Branch of AS USSR Press, Sverdlovsk, 1989, p. 3.]
|
|
Components ratio, wt% |
||
Elastomer |
Binary mixture |
|
|
|
Calculation |
Experiment |
|||
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
toluene-acetone |
90/10 |
90/10 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PEU |
cyclohexanone-acetone |
40/60 |
50/50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
heptane-acetone |
30/70 |
25/25 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
decane-DBP |
30/70 |
30/70 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
PBU |
TO-DBP |
40/60 |
40/60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DOS-DBP |
60/40 |
50/50 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
ethyl acetate-1,4-dioxane |
- |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SCN-26 |
ethyl acetate-acetone |
70/30 |
70/30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
toluene-acetone |
70/30 |
70/30 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Results of calculation of the liquid phase composition at maximum swelling of elastomer correlate with the experimental data (see Table 6.2.2). The approach predicts the existence of an extremum on the swelling curve. This increases the forecasting efficiency of the prediction.
The application of “approximation of the uniform liquid” (AUL) for prediction of extreme swelling of crosslinked elastomers is proven under condition of coincidence of composition of a two-component solvent in a liquid phase and in the swollen elastomer. Results of study of total and selective sorption by crosslinked elastomers of components of SLs are given below.3
Crosslinked PBU [(ve/V0) = 0.20 kmol/m3] and crosslinked elastomer of buta- diene-nitrile rubber SCN-26 [(ve/V0) = 0.07 kmol/m3] were used in this study. The tests were carried out at 25±0.10oC in the following mixtures: n-nonane-tributyl phosphate (TBP), n-hexane-dibutyl phthalate (DBP), n-hexane-dibutyl maleate (DBM), and dioctyl sebacate (DOS)-diethyl phthalate (DEP). A crosslinked elastomer SCN-26 was immersed to equilibrate in amyl acetate-dimethyl phthalate mixture. Liquid phase composition was in range of 5 to 10%. A sol-fraction of samples (plates of 0.9×10-2 m diameter and in 0.3×10-2 m thickness) was preliminary extracted with toluene.
For the high accuracy of the analysis of binary solvent composition, a volatile solvent, hexane, was used as a component of SL in most experiments. Following the attainment of equilibrium swelling, the samples were taken out of SL and held in air until the full evaporation of hexane, that was controlled by constant mass of sample. A content of a nonvolatile component of SL in elastomer was determined by the difference between the amount of liq-

V V Tereshatov, V Yu. Senichev, E Ya Denisyuk
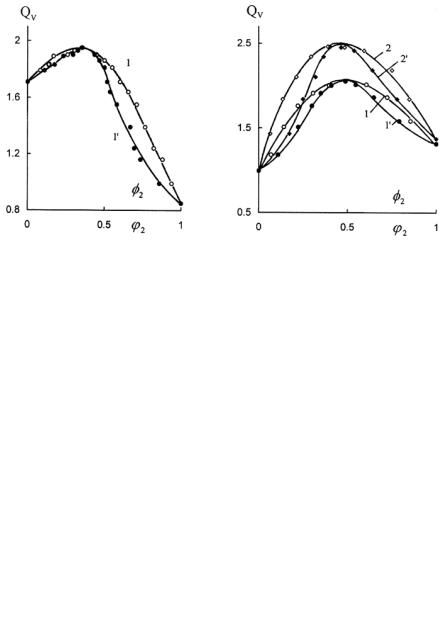
Figure 6.2.8. Dependence of equilibrium swelling of crosslinked elastomer SCN-26 on the ϕ 2 value for DMP in the liquid phase ( 1) and the φ2 value in the gel (1'), swollen in the mixture: amyl acetate-DMP.
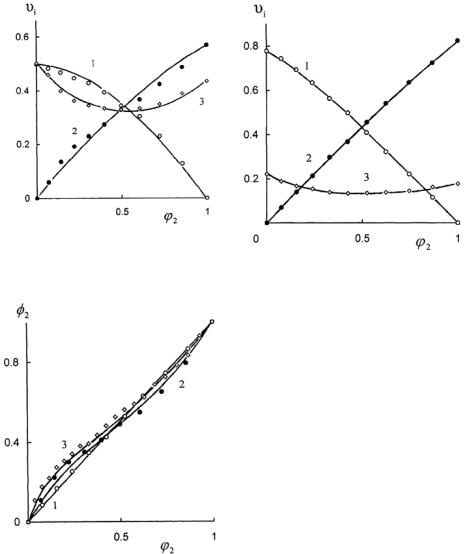
fraction ϕ2 of component 2 in a liquid phase and on the volume fraction φ2 of component 2 of SL that is a part of the swollen gel. The data vividly show that extremum swelling of crosslinked elastomers in SL can be observed in all investigated cases. At the maximum value of QV, the compositions of SL in the liquid phase and in the swollen elastomer practically coincide (ϕ2 ≈ φ2 ).
The total sorption can be determined by the total content of the mixed solvent in the swollen skin9 or in the swollen elastic network (these results). The dependencies of QV on ϕ2 (Figures 6.2.5-6.2.8) reveal the influence of liquid phase composition on the total sorption. The total sorption of the binary solvent by polymer can also be measured by the value of the volume fraction of polymer in the swollen gel9 because the value of υ3 is unequally related to the volume fraction of the absorbed liquid,
υ3 = 1− (υ1 + υ2 ). At the fixed total sorption (QV or υ3 = const) the preferential sorption, ε, can be found from the following equation:
ε = φ1 − ϕ1 = ϕ2 − φ2

6.2 Equilibrium swelling in binary solvents |
325 |
At the same values of Qv difference between coordinates on the abscissa axes of points of the curves 1-1', 2-2' (Figures 6.2.5-6.2.8) are equal ε (Figure 6.2.9).
As expected,10 preferential sorption was observed, with the essential distinction of molar volumes V1 and V2 of components of the mixed solvent (hexane-DBP, DOS-DEP). For swelling of the crosslinked elastomer SCN-26 in the mixture of components, having similar molar volumes V1 and V2 (e.g., amyl acetate-dimethyl phthalate) the preferential sorption of components of SL is practically absent. Influence of V1 and V2 and the influence of double interaction parameters on the sorption of binary liquids by crosslinked elastomers was examined by the method of mathematical experiment. Therewith the set of equations describing swelling of crosslinked elastomers in binary mixture, similar to the equations obtained by Bristow6 from the Flory-Rehner theory11 and from the work of Schulz and Flory,12 were used:
ln ϕ1 + (1− l)ϕ2 + χ12 ϕ22 = ln υ1 + (1− l)υ2 + υ3 + χ12 υ22 + χ12 υ23 +
|
|
|
|
1/ 3 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
+(χ12 |
+ χ13 |
− lχ |
23 )υ2 υ3 + (νe / V3 )V1 |
υ3 |
− |
|
|
υ3 |
|
|
|
|
|
[6.2.6] |
|
f |
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
ln ϕ2 + (1− l −1 )ϕ1 + l −1χ12 ϕ12 = ln υ2 + (1− l −1 )υ1 + υ3 + l −1 |
|
||||||||||||||
χ12 υ1 |
+ lχ23 |
υ3 + |
(χ12 + lχ23 − χ13 )υ1υ3 + (νe /V3 )V2 |
|
υ3 |
|
− |
2 |
υ3 |
|
[6.2.7] |
||||
2 |
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
1/3 |
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
f |
|
|
|
where:
l=V1/V2
ffunctionality of a network
The analysis of calculations from Eqs. [6.2.6] and [6.2.7] has shown that if V1 <V2, the preferential sorption is promoted by difference in parameters of interaction, when χ12 > χ13. The greater is χ12 value at V1 ≠ V2 the more likely preferential sorption takes place with all other parameters being equal. The same applies to the diluted polymer solutions.
To improve calculations of the preferential sorption in the diluted solutions of polymers, the correction of Flory’s theory is given in works9,13-15 by introduction of the parameter of three-component interaction, χT, into the expression for free energy of mixing, and substitution of χT by qT.14 This approach is an essential advancement in the analysis of a sorption of two-component liquids by polymer. On the other hand, the increase in the number of experimental parameters complicates the task of prediction of the preferential sorption.
In swelling crosslinked elastomers, the preferential sorption corresponds to the maximum QV value and compositions in a swollen polymer and a liquid phase practically coincide (Figures 6.2.5-6.2.8). This observation can be successfully used for an approximate evaluation of the preferential sorption.
Assuming that ϕ1 = φ1 and ϕ2 = φ2 at extremum of the total sorption (φ3 = φmin3 ), AUL5 can be used to calculate the effective value of χ12e from the expression for χ123:16
χ12e = |
χ13 |
+ |
χ 23V1 |
− |
χ123m V1 |
|
[6.2.8] |
ϕ2m |
|
V12m ϕ1m ϕ |
|
||||
|
|
ϕ1mV2 |
2m |
||||
6.3 Swelling data |
327 |
sorption of SL by polymer. Thus it is necessary to account for proximity of the compositions of solvent in the swollen gel and the liquid phase.
REFERENCES
1A Horta, Makromol. Chem., 182, 1705 (1981).
2V V Tereshatov, V Yu Senichev, A I Gemuev, Vysokomol. Soedin., 32B, 422 (1990).
3V V Tereshatov, M I Balashova, A I Gemuev, Prediction and regulating of properties of polymeric materials, Ural Branch. of AS USSR Press, Sverdlovsk, 1989, p. 3.
4A A Askadsky, Yu I Matveev, Chemical structure and physical properties of polymers, Chemistry, Moscow, 1983.
5R L Scott, J. Chem. Phys., 17, 268 (1949).
6C M Bristow, Trans. Faraday Soc., 55, 1246 (1959).
7A Dondos, D Patterson, J. Polym. Sci., A-2, 5, 230 (1967).
8 L N Mizerovsky, L N Vasnyatskaya, G M Smurova, Vysokomol. Soedin., 29A, 1512 (1987).
9J Pouchly, A Zivny, J. Polym. Sci., 10, 1481 (1972).
10W R Krigbaum, D K Carpenter, J. Polym. Sci., 14, 241 (1954).
11P J Flory, J Rehner, J. Chem. Phys., 11, 521 (1943).
12A R Shulz, P J Flory, J. Polym. Sci., 15, 231 (1955).
13J Pouchly, A Zivny, J. Polym. Sci., 23, 245 (1968).
14J Pouchly, A Zivny, Makromol. Chem., 183, 3019 (1982).
15R M Msegosa, M R Comez-Anton, A Horta, Makromol. Chem., 187, 163 (1986).
16J Scanlan, J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 9, 241 (1965).
6.3SWELLING DATA ON CROSSLINKED POLYMERS IN SOLVENTS
Vasiliy V. Tereshatov, Valery Yu. Senichev
Institute of Technical Chemistry Ural Branch of Russian Academy of Sciences, Perm, Russia
Data on equilibrium swelling of selected crosslinked elastomers in different solvents are presented in Table 6.3.2. All data were obtained in the author’s laboratory during the last 5 years. The network density values for these elastomers are given in Table 6.3.1.
The data can be used for the quantitative evaluation of thermodynamic compatibility of solvents with elastomers and for calculation of Z, the thermodynamic interaction parameter. These data can be recalculated to the network density distinguished by the network density value, given in Table 6.3.1, using Eq. [4.2.9]. Network density values can be used for the calculation of the interaction parameter. It should be noted that each rubber has specific ratio for the equilibrium swelling values in various solvents. This can help to identify rubber in polymeric material.
Temperature influences swelling (see Subchapter 4.2). Equilibrium swelling data at four different temperatures are given in Table 6.3.3.
Polymer samples were made from industrial rubbers. The following polyols were used for preparation of polyurethanes: butadiene diol (M~2000) for PBU, polyoxybutylene glycol (M~1000) for SCU-PFL, polyoxypropylene triol (M~5000) for Laprol 5003, polydiethylene glycol adipate (M~2000) for P-9A and polydiethylene glycol adipate (M~800) for PDA. Polyurethanes from these polyols were synthesized by reaction with 2,4-toluylene diisocyanate with addition of crosslinking agent - trimetylol propane, PDUE, synthesized by reaction of oligobutadiene isoprene diol (M~4500) with double excess of 2,4-toluylene diisocyanate, followed by the reaction with glycidol.
328 |
Vasiliy V. Tereshatov, Valery Yu. Senichev |
Table 6.3.1. Network density values for tested elastomers (data obtained from the elasticity modulus of samples swollen in good solvents)
Elastomer |
|
|
|
Trade mark |
|
Network density, (kmol/m3)×102 |
|||||||||||
Silicone rubber |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SCT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Butyl rubber |
|
|
|
|
|
|
BR |
|
|
|
|
|
|
8.9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Polybutadiene rubber |
|
|
|
|
SCDL |
|
|
|
|
|
|
40.5 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ethylene-propylene rubber |
|
|
|
SCEPT |
|
|
|
|
2.7 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Isoprene rubber |
|
|
|
|
|
|
SCI-NL |
|
|
|
|
8.9 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Butadiene-nitrile rubber |
|
|
|
|
SCN-26 |
|
|
|
|
5.1 |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Polydiene-urethane-epoxide |
|
|
|
PDUE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
16.0 |
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Polybutadiene urethane |
|
|
|
|
PBU |
|
|
|
|
|
|
20.8 |
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Polyoxybutylene glycol urethane |
|
|
PFU |
|
|
|
|
|
|
10.0 |
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Polyoxypropylene glycol urethane |
|
|
Laprol 5003 |
|
|
|
|
43.0 |
|
|
|||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Polydiethylene glycol adipate urethane |
|
P-9A |
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.4 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Polydiethylene glycol adipate urethane |
|
PDA |
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.6 |
|
|
||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Table 6.3.2 Equilibrium swelling data (wt%) at 25oC |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Solvent\elastomer |
SCT |
|
BR |
SCDL |
SCEPT |
SCI |
SCN |
|
PDUE |
PBU |
SCU |
|
Laprol |
P-9A |
PDA |
||
|
-NL |
-26 |
|
-PFL |
|
||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hydrocarbons |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pentane |
355 |
|
|
75 |
|
|
214 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hexane |
380 |
|
305 |
105 |
586 |
|
300 |
|
|
122 |
78 |
16 |
|
44 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Heptane |
367 |
|
357 |
|
881 |
|
|
10 |
|
137 |
84 |
16 |
|
42 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Isooctane |
380 |
|
341 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
101 |
|
|
|
32 |
0 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Decane |
|
|
391 |
|
1020 |
|
7 |
|
139 |
|
|
|
28 |
1 |
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cyclohexane |
|
|
677 |
|
|
|
|
155 |
|
315 |
|
39 |
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Transformer oil |
47 |
|
|
230 |
1580 |
600 |
24 |
|
238 |
|
3 |
|
53 |
4 |
0.5 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
Toluene |
|
|
384 |
|
1294 |
|
435 |
|
492 |
356 |
134 |
|
315 |
77 |
31 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Benzene |
|
|
233 |
|
511 |
|
|
506 |
|
479 |
359 |
158 |
|
340 |
175 |
73 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
o-Xylene |
|
|
515 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
496 |
356 |
122 |
|
288 |
53 |
42 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ethers |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diamyl |
310 |
|
|
220 |
889 |
|
584 |
20 |
|
248 |
|
|
|
87 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.3 Swelling data |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
329 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Solvent\elastomer |
|
SCT |
BR |
SCDL |
SCEPT |
SCI |
SCN |
PDUE |
PBU |
SCU |
Laprol |
P-9A |
PDA |
|
-NL |
-26 |
-PFL |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diisoamyl |
|
333 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
33 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Didecyl |
|
|
|
|
791 |
|
7 |
168 |
|
|
22 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dioctyl |
|
120 |
428 |
180 |
896 |
702 |
11 |
203 |
|
6 |
41 |
0.1 |
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diethyl of |
|
85 |
|
156 |
|
242 |
|
|
|
|
251 |
|
54 |
diethylene glycol |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1,4-Dioxane |
|
|
23 |
|
|
|
|
|
264 |
178 |
|
782 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tetrahydrofuran |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
48 |
192 |
|
848 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Esters of monoacids |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Heptyl propionate |
|
260 |
236 |
304 |
382 |
|
287 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ethyl acetate |
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
170 |
|
133 |
|
213 |
88 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Butyl acetate |
|
|
55 |
|
55 |
|
562 |
317 |
251 |
121 |
|
64 |
40 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Isobutyl acetate |
|
|
48 |
|
|
|
|
267 |
210 |
|
238 |
48 |
35 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amyl acetate |
|
|
82 |
|
|
|
|
343 |
|
|
249 |
36 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Isoamyl acetate |
|
|
74 |
|
|
|
|
|
236 |
100 |
|
|
22 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Heptyl acetate |
|
|
|
|
213 |
|
|
|
545 |
100 |
|
|
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Methyl capronate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
369 |
285 |
115 |
260 |
36 |
26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Isobutyl isobuturate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
328 |
276 |
64 |
|
6 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Esters of multifunctional acids |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dihexyl oxalate |
|
|
|
|
28 |
|
350 |
|
|
73 |
166 |
11 |
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diethyl phthalate |
|
|
|
|
6 |
|
837 |
47 |
93 |
165 |
272 |
496 |
126 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dibutyl phthalate |
|
|
|
|
9 |
|
767 |
123 |
154 |
121 |
228 |
47 |
20 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dihexyl phthalate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
570 |
|
|
|
187 |
9 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diheptyl phthalate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
37 |
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dioctyl phthalate |
|
8 |
|
|
28 |
|
|
189 |
|
29 |
|
|
1 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dinonyl phthalate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
211 |
181 |
33 |
|
|
1.4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Didecyl phthalate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
23 |
|
|
0.5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diamyl maleate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
425 |
197 |
|
71 |
232 |
19 |
14 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dimethyl adipate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
560 |
|
|
|
246 |
716 |
6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diamyl adipate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
294 |
203 |
88 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dihexyl adipate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
280 |
|
|
|
|
8 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dioctyl adipate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
295 |
199 |
42 |
|
2 |
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dipropyl sebacate |
|
|
|
|
20 |
|
|
|
|
126 |
|
12 |
0.6 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
330 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Vasiliy V. Tereshatov, Valery Yu. Senichev |
||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Solvent\elastomer |
|
SCT |
BR |
|
SCDL |
|
SCEPT |
SCI |
SCN |
|
PDUE |
PBU |
SCU |
Laprol |
|
P-9A |
PDA |
||||
|
|
|
-NL |
-26 |
|
-PFL |
|
||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diamyl sebacate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
70 |
|
|
|
|
2 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diheptyl sebacate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
118 |
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dioctyl sebacate |
|
13 |
|
|
160 |
|
127 |
445 |
39 |
|
261 |
162 |
5.5 |
74 |
|
|
0.4 |
0.7 |
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Triacetyne |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
34 |
|
|
15 |
28 |
|
|
|
489 |
129 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tricresyl phosphate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
800 |
|
45 |
|
|
140 |
|
|
|
|
80 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tributyl phosphate |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
300 |
244 |
238 |
256 |
|
93 |
105 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ketones |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Cyclohexanone |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
577 |
|
|
|
327 |
|
523 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Acetone |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7 |
|
|
|
44 |
|
|
88 |
|
|
|
218 |
99 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Alcohols |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ethanol |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
49 |
|
|
|
|
16 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Butanol |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
25 |
72 |
|
|
|
7 |
12 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pentanol |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
28 |
33 |
66 |
|
|
|
10 |
5 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hexanol |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
46 |
34 |
62 |
|
|
|
9 |
4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Heptanol |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
36 |
67 |
|
|
|
19 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nonanol |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
57 |
|
|
|
|
3 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Halogen compounds |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CCl4 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2830 |
|
284 |
|
999 |
|
|
|
584 |
|
66 |
|
|
Chlorobenzene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
234 |
|
|
|
277 |
114 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chloroform |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
1565 |
572 |
|
|
|
|
616 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Fluorobenzene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
205 |
|
|
|
|
113 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nitrogen compounds |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Diethyl aniline |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
336 |
120 |
|
|
|
|
34 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Dimethylformamide |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
52 |
|
|
|
|
918 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Nitrobenzene |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
277 |
298 |
242 |
377 |
|
799 |
241 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Capronitrile |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
769 |
|
142 |
|
|
115 |
|
|
|
84 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Acetonitrile |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
47 |
|
69 |
16 |
|
|
|
|
323 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Aniline |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
317 |
|
|
|
|
423 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||
Table 6.3.3 Equilibrium swelling data (wt%) at -35,-10, 25, and 50oC |
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
Solvent\Elastomer |
|
|
Laprol* |
|
|
|
SCU-PFL |
|
P-9A |
|
|
PBU |
|
|
|
SCN-26 |
|||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||||||||
Isopropanol |
|
8,12,37,305 |
|
|
|
8,19,72,- |
|
8,10,18,28 |
|
3,5,18,28 |
|
|
20,23,26,41 |
||||||||
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.4 Influence of structure on equilibrium swelling |
|
|
331 |
||
|
|
|
|
|
|
Solvent\Elastomer |
Laprol* |
SCU-PFL |
P-9A |
PBU |
SCN-26 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Pentanol |
27,34,80,119 |
16,25,78,104 |
7,9,10,18 |
8,9,33,52 |
31,37,49,60 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Acetone |
80,366,381,- |
80,122,132,- |
48,73,218,- |
56,321,347,- |
162,254,269,382 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Ethyl acetate |
214,230,288,314 |
113,114,133,138 |
209,210,210,213 |
165,171,187,257 |
324,343,395,407 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Butyl acetate |
294,304,309,469 |
119,122,123,125 |
41,44,64,80 |
288,293,307,473 |
404,426,518,536 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Isobutyl acetate |
259,259,288,- |
89,92,100,105 |
23,28,48,57 |
210,212,223,348 |
309,326,357,362 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Amyl acetate |
315,309,315,426 |
124,136,144,155 |
16,18,36,44 |
285,297,298,364 |
343,347,358,359 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Tetrahydrofuran |
91,96,97,119 |
119,177,192,- |
838,840,848,859 |
45,51,57,80 |
145,150,166,- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
o-Xylene |
363,368,389,471 |
117,121,122,137 |
24,25,53,60 |
328,357,369,375 |
428,440,405,406 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Chlorobenzene |
522,537,562,- |
241,242,242,246 |
238,244,277,333 |
517,528,559,698 |
967,973,985,1256 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Acetonitrile |
19,21,28,33 |
23,26,39,41 |
254,263,323,362 |
6,10,16,27 |
47,47,47,82 |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Hexane |
50,52,61,75 |
2,3,9,14 |
4,4,4,28 |
51,56,63,80 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Toluene |
360,366,380, 397 |
120,122,134,149 |
50,57,77,85 |
331,339,372,415 |
- |
|
|
|
|
|
|
*(ve/V) = 0.149 kmol/m3. Network density values for other elastomers correspond to Table 6.3.2
6.4 INFLUENCE OF STRUCTURE ON EQUILIBRIUM SWELLING
Vasiliy V. Tereshatov, Valery Yu. Senichev
Institute of Technical Chemistry Ural Branch of Russian Academy of Sciences, Perm, Russia
Swelling of single-phase elastomers is, other parameters being equal, limited by the chemical network. Microphase separation of hard and soft blocks can essentially influence swelling of block-copolymers. Hard domains formed in this process are knots of physical network, which can be resistant to action of solvents.1-4 Swelling of polyurethane block-co- polymers with urethane-urea hard segments is investigated. The maximum values of swelling, Qmax, of segmented polyurethane (prepolymer of oligopropylene diol with functional isocyanate groups) cured by 4,4'-methylene-bis-o-chloroaniline (MOCA) are given in Tables 6.4.1 and 6.4.2. The prepolymer Vibratane B 600 was obtained by the reaction of oligopropylene diol with 2,4-toluylene diisocyanate. The swelling experiments were carried out in four groups of solvents of different polarity and chemical structure.5 The effective molecular mass of elastically active chains, Mc, between network crosslinks was estimated from the Flory-Rehner equation.6 The interaction parameter of solvent with polymer was determined by calculation.
In the first variant of calculation, a classical method based on the solubility parameter concept, was used with application of Bristow and Watson’s semi-empirical relationship for χ1:7
