
- •Contents
- •Send Us Your Comments
- •Preface
- •What’s New in SQL Reference?
- •1 Introduction to Oracle SQL
- •History of SQL
- •SQL Standards
- •Embedded SQL
- •Lexical Conventions
- •Tools Support
- •2 Basic Elements of Oracle SQL
- •Datatypes
- •Oracle Built-in Datatypes
- •ANSI, DB2, and SQL/DS Datatypes
- •Oracle-Supplied Types
- •"Any" Types
- •XML Types
- •Spatial Type
- •Media Types
- •Datatype Comparison Rules
- •Data Conversion
- •Literals
- •Text Literals
- •Integer Literals
- •Number Literals
- •Interval Literals
- •Format Models
- •Number Format Models
- •Date Format Models
- •String-to-Date Conversion Rules
- •XML Format Model
- •Nulls
- •Nulls in SQL Functions
- •Nulls with Comparison Conditions
- •Nulls in Conditions
- •Pseudocolumns
- •CURRVAL and NEXTVAL
- •LEVEL
- •ROWID
- •ROWNUM
- •XMLDATA
- •Comments
- •Comments Within SQL Statements
- •Comments on Schema Objects
- •Hints
- •Database Objects
- •Schema Objects
- •Nonschema Objects
- •Parts of Schema Objects
- •Schema Object Names and Qualifiers
- •Schema Object Naming Rules
- •Schema Object Naming Examples
- •Schema Object Naming Guidelines
- •Syntax for Schema Objects and Parts in SQL Statements
- •How Oracle Resolves Schema Object References
- •Referring to Objects in Other Schemas
- •Referring to Objects in Remote Databases
- •Referencing Object Type Attributes and Methods
- •3 Operators
- •About SQL Operators
- •Unary and Binary Operators
- •Operator Precedence
- •Arithmetic Operators
- •Concatenation Operator
- •Set Operators
- •4 Expressions
- •About SQL Expressions
- •Simple Expressions
- •Compound Expressions
- •CASE Expressions
- •CURSOR Expressions
- •Datetime Expressions
- •Function Expressions
- •INTERVAL Expressions
- •Object Access Expressions
- •Scalar Subquery Expressions
- •Type Constructor Expressions
- •Variable Expressions
- •Expression Lists
- •5 Conditions
- •About SQL Conditions
- •Condition Precedence
- •Comparison Conditions
- •Simple Comparison Conditions
- •Group Comparison Conditions
- •Logical Conditions
- •Membership Conditions
- •Range Conditions
- •Null Conditions
- •EQUALS_PATH
- •EXISTS Conditions
- •LIKE Conditions
- •IS OF type Conditions
- •UNDER_PATH
- •Compound Conditions
- •6 Functions
- •SQL Functions
- •Single-Row Functions
- •Aggregate Functions
- •Analytic Functions
- •Object Reference Functions
- •Alphabetical Listing of SQL Functions
- •ACOS
- •ADD_MONTHS
- •ASCII
- •ASCIISTR
- •ASIN
- •ATAN
- •ATAN2
- •BFILENAME
- •BITAND
- •CAST
- •CEIL
- •CHARTOROWID
- •COALESCE
- •COMPOSE
- •CONCAT
- •CONVERT
- •CORR
- •COSH
- •COUNT
- •COVAR_POP
- •COVAR_SAMP
- •CUME_DIST
- •CURRENT_DATE
- •CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
- •DBTIMEZONE
- •DECODE
- •DECOMPOSE
- •DENSE_RANK
- •DEPTH
- •DEREF
- •DUMP
- •EMPTY_BLOB, EMPTY_CLOB
- •EXISTSNODE
- •EXTRACT (datetime)
- •EXTRACT (XML)
- •EXTRACTVALUE
- •FIRST
- •FIRST_VALUE
- •FLOOR
- •FROM_TZ
- •GREATEST
- •GROUP_ID
- •GROUPING
- •GROUPING_ID
- •HEXTORAW
- •INITCAP
- •INSTR
- •LAST
- •LAST_DAY
- •LAST_VALUE
- •LEAD
- •LEAST
- •LENGTH
- •LOCALTIMESTAMP
- •LOWER
- •LPAD
- •LTRIM
- •MAKE_REF
- •MONTHS_BETWEEN
- •NCHR
- •NEW_TIME
- •NEXT_DAY
- •NLS_CHARSET_DECL_LEN
- •NLS_CHARSET_ID
- •NLS_CHARSET_NAME
- •NLS_INITCAP
- •NLS_LOWER
- •NLSSORT
- •NLS_UPPER
- •NTILE
- •NULLIF
- •NUMTODSINTERVAL
- •NUMTOYMINTERVAL
- •PATH
- •PERCENT_RANK
- •PERCENTILE_CONT
- •PERCENTILE_DISC
- •POWER
- •RANK
- •RATIO_TO_REPORT
- •RAWTOHEX
- •RAWTONHEX
- •REFTOHEX
- •REGR_ (Linear Regression) Functions
- •REPLACE
- •ROUND (number)
- •ROUND (date)
- •ROW_NUMBER
- •ROWIDTOCHAR
- •ROWIDTONCHAR
- •RPAD
- •RTRIM
- •SESSIONTIMEZONE
- •SIGN
- •SINH
- •SOUNDEX
- •SQRT
- •STDDEV
- •STDDEV_POP
- •STDDEV_SAMP
- •SUBSTR
- •SYS_CONNECT_BY_PATH
- •SYS_CONTEXT
- •SYS_DBURIGEN
- •SYS_EXTRACT_UTC
- •SYS_GUID
- •SYS_TYPEID
- •SYS_XMLAGG
- •SYS_XMLGEN
- •SYSDATE
- •SYSTIMESTAMP
- •TANH
- •TO_CHAR (character)
- •TO_CHAR (datetime)
- •TO_CHAR (number)
- •TO_CLOB
- •TO_DATE
- •TO_DSINTERVAL
- •TO_MULTI_BYTE
- •TO_NCHAR (character)
- •TO_NCHAR (datetime)
- •TO_NCHAR (number)
- •TO_NCLOB
- •TO_NUMBER
- •TO_SINGLE_BYTE
- •TO_TIMESTAMP
- •TO_TIMESTAMP_TZ
- •TO_YMINTERVAL
- •TRANSLATE
- •TRANSLATE ... USING
- •TREAT
- •TRIM
- •TRUNC (number)
- •TRUNC (date)
- •TZ_OFFSET
- •UNISTR
- •UPDATEXML
- •UPPER
- •USER
- •USERENV
- •VALUE
- •VAR_SAMP
- •VARIANCE
- •VSIZE
- •WIDTH_BUCKET
- •XMLAGG
- •XMLCOLATTVAL
- •XMLCONCAT
- •XMLELEMENT
- •XMLFOREST
- •XMLSEQUENCE
- •XMLTRANSFORM
- •ROUND and TRUNC Date Functions
- •User-Defined Functions
- •Prerequisites
- •Name Precedence
- •7 Common SQL DDL Clauses
- •allocate_extent_clause
- •constraints
- •deallocate_unused_clause
- •file_specification
- •logging_clause
- •parallel_clause
- •physical_attributes_clause
- •storage_clause
- •8 SQL Queries and Subqueries
- •About Queries and Subqueries
- •Creating Simple Queries
- •Hierarchical Queries
- •The UNION [ALL], INTERSECT, MINUS Operators
- •Sorting Query Results
- •Joins
- •Using Subqueries
- •Unnesting of Nested Subqueries
- •Selecting from the DUAL Table
- •Distributed Queries
- •9 SQL Statements: ALTER CLUSTER to ALTER SEQUENCE
- •Types of SQL Statements
- •Organization of SQL Statements
- •ALTER CLUSTER
- •ALTER DATABASE
- •ALTER DIMENSION
- •ALTER FUNCTION
- •ALTER INDEX
- •ALTER INDEXTYPE
- •ALTER JAVA
- •ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW
- •ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG
- •ALTER OPERATOR
- •ALTER OUTLINE
- •ALTER PACKAGE
- •ALTER PROCEDURE
- •ALTER PROFILE
- •ALTER RESOURCE COST
- •ALTER ROLE
- •ALTER ROLLBACK SEGMENT
- •ALTER SEQUENCE
- •10 SQL Statements: ALTER SESSION to ALTER SYSTEM
- •ALTER SESSION
- •ALTER SYSTEM
- •ALTER TABLE
- •ALTER TABLESPACE
- •ALTER TRIGGER
- •ALTER TYPE
- •ALTER USER
- •ALTER VIEW
- •ANALYZE
- •ASSOCIATE STATISTICS
- •AUDIT
- •CALL
- •COMMENT
- •COMMIT
- •13 SQL Statements: CREATE CLUSTER to CREATE JAVA
- •CREATE CLUSTER
- •CREATE CONTEXT
- •CREATE CONTROLFILE
- •CREATE DATABASE
- •CREATE DATABASE LINK
- •CREATE DIMENSION
- •CREATE DIRECTORY
- •CREATE FUNCTION
- •CREATE INDEX
- •CREATE INDEXTYPE
- •CREATE JAVA
- •14 SQL Statements: CREATE LIBRARY to CREATE SPFILE
- •CREATE LIBRARY
- •CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW
- •CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG
- •CREATE OPERATOR
- •CREATE OUTLINE
- •CREATE PACKAGE
- •CREATE PACKAGE BODY
- •CREATE PFILE
- •CREATE PROCEDURE
- •CREATE PROFILE
- •CREATE ROLE
- •CREATE ROLLBACK SEGMENT
- •CREATE SCHEMA
- •CREATE SEQUENCE
- •CREATE SPFILE
- •15 SQL Statements: CREATE SYNONYM to CREATE TRIGGER
- •CREATE SYNONYM
- •CREATE TABLE
- •CREATE TABLESPACE
- •CREATE TEMPORARY TABLESPACE
- •CREATE TRIGGER
- •CREATE TYPE
- •CREATE TYPE BODY
- •CREATE USER
- •CREATE VIEW
- •DELETE
- •DISASSOCIATE STATISTICS
- •DROP CLUSTER
- •DROP CONTEXT
- •DROP DATABASE LINK
- •DROP DIMENSION
- •DROP DIRECTORY
- •DROP FUNCTION
- •DROP INDEX
- •DROP INDEXTYPE
- •DROP JAVA
- •DROP LIBRARY
- •DROP MATERIALIZED VIEW
- •DROP MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG
- •DROP OPERATOR
- •DROP OUTLINE
- •DROP PACKAGE
- •DROP PROCEDURE
- •DROP PROFILE
- •DROP ROLE
- •DROP ROLLBACK SEGMENT
- •17 SQL Statements: DROP SEQUENCE to ROLLBACK
- •DROP SEQUENCE
- •DROP SYNONYM
- •DROP TABLE
- •DROP TABLESPACE
- •DROP TRIGGER
- •DROP TYPE
- •DROP TYPE BODY
- •DROP USER
- •DROP VIEW
- •EXPLAIN PLAN
- •GRANT
- •INSERT
- •LOCK TABLE
- •MERGE
- •NOAUDIT
- •RENAME
- •REVOKE
- •ROLLBACK
- •18 SQL Statements: SAVEPOINT to UPDATE
- •SAVEPOINT
- •SELECT
- •SET CONSTRAINT[S]
- •SET ROLE
- •SET TRANSACTION
- •TRUNCATE
- •UPDATE
- •Required Keywords and Parameters
- •Optional Keywords and Parameters
- •Syntax Loops
- •Multipart Diagrams
- •Database Objects
- •ANSI Standards
- •ISO Standards
- •Oracle Compliance
- •FIPS Compliance
- •Oracle Extensions to Standard SQL
- •Character Set Support
- •Using Extensible Indexing
- •Using XML in SQL Statements
- •Index

CREATE TYPE BODY
CREATE TYPE BODY
Purpose
Use the CREATE TYPE BODY to define or implement the member methods defined in the object type specification. You create object types with the CREATE TYPE and the CREATE TYPE BODY statements. The CREATE TYPE statement specifies the name of the object type, its attributes, methods, and other properties. The CREATE TYPE BODY statement contains the code for the methods in the type.
For each method specified in an object type specification for which you did not specify the call_spec, you must specify a corresponding method body in the object type body.
Note: If you create a SQLJ object type, you cannot specify a type body. The implementation of the type is specified as a Java class.
See Also: CREATE TYPE on page 16-3 and ALTER TYPE on page 12-6 for information on creating and modifying a type specification
Prerequisites
Every member declaration in the CREATE TYPE specification for object types must have a corresponding construct in the CREATE TYPE or CREATE TYPE BODY statement.
To create or replace a type body in your own schema, you must have the CREATE TYPE or the CREATE ANY TYPE system privilege. To create an object type in another user’s schema, you must have the CREATE ANY TYPE system privileges. To replace an object type in another user’s schema, you must have the DROP ANY TYPE system privileges.
SQL Statements: CREATE TYPE to DROP ROLLBACK SEGMENT 16-25
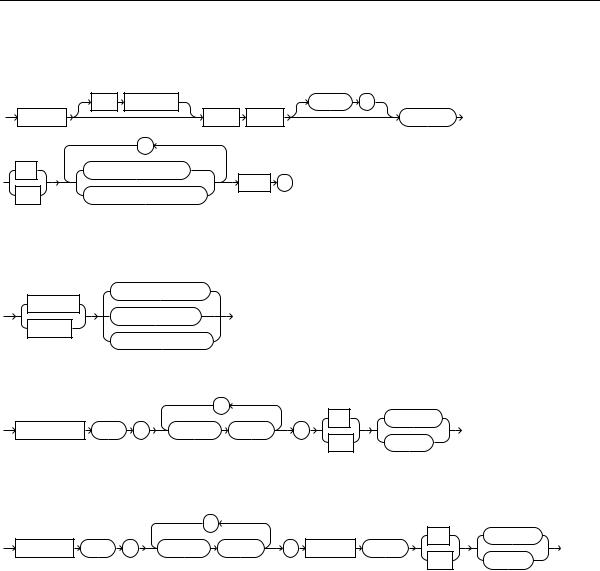
CREATE TYPE BODY
Syntax
create_type_body::=
|
OR |
REPLACE |
|
schema |
. |
CREATE |
|
TYPE |
BODY |
|
type_name |
|
|
; |
|
|
|
IS |
subprogram_declaration |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
END |
; |
|
AS |
map_order_func_declaration |
|
|
|
|
(procedure_declaration::= on page 16-26, function_declaration::= on page 16-26, constructor_declaration::= on page 16-27)
subprogram_declaration::=
procedure_declaration
MEMBER
function_declaration
STATIC
constructor_declaration
procedure_declaration::=
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IS |
pl/sql_block |
PROCEDURE |
name |
( |
parameter |
datatype |
) |
|
|
|
|
|
|
AS |
call_spec |
(call_spec::= on page 16-8) function_declaration::=
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
IS |
pl/sql_block |
FUNCTION |
name |
( |
parameter |
datatype |
) |
RETURN |
datatype |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AS |
call_spec |
(call_spec::= on page 16-8)
16-26 Oracle9i SQL Reference

CREATE TYPE BODY
constructor_declaration::=
FINAL |
|
INSTANTIABLE |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
CONSTRUCTOR |
FUNCTION |
datatype |
|
|
|
SELF |
IN |
OUT |
datatype |
, |
, |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|||||
( |
|
|
|
|
|
parameter |
datatype |
) |
|
|
|
|
IS |
pl/sql_block |
|
|
|
RETURN |
SELF |
AS |
RESULT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
AS |
call_spec |
|
|
|
map_order_func_declaration::=
MAP
MEMBER  function_declaration
function_declaration
ORDER
call_spec::=
Java_declaration
LANGUAGE
C_declaration
Java_declaration::=
JAVA  NAME
NAME  ’
’  string
string  ’
’
C_declaration::=
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
NAME |
name |
|
|
|
AGENT |
IN |
( |
argument |
) |
C |
|
|
LIBRARY |
lib_name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|
|
WITH |
CONTEXT |
PARAMETERS |
( |
parameter |
|
) |
|
|
||
SQL Statements: CREATE TYPE to DROP ROLLBACK SEGMENT 16-27

CREATE TYPE BODY
Semantics
OR REPLACE
Specify OR REPLACE to re-create the type body if it already exists. Use this clause to change the definition of an existing type body without first dropping it.
Users previously granted privileges on the re-created object type body can use and reference the object type body without being granted privileges again.
You can use this clause to add new member subprogram definitions to specifications added with the ALTER TYPE ... REPLACE statement.
schema
Specify the schema to contain the type body. If you omit schema, Oracle creates the type body in your current schema.
type_name
Specify the name of an object type.
IS | AS
MEMBER | STATIC
Specify the type of function or procedure subprogram associated with the object type specification.
You must define a corresponding method name, optional parameter list, and (for functions) a return type in the object type specification for each procedure or function declaration.
procedure_declaration, function_declaration, Declare a procedure or function subprogram.
constructor_declaration Declare a user-defined constructor subprogram. The RETURN clause of a constructor function must be RETURN SELF AS RESULT. This setting indicates that the most specific type of the value returned by the constructor function is the same as the most specific type of the SELF argument that was passed in to the constructor function.
16-28 Oracle9i SQL Reference

CREATE TYPE BODY
See Also:
■CREATE TYPE on page 16-3 for a list of restrictions on user-defined functions
■PL/SQL User’s Guide and Reference for information about overloading subprogram names within a package
■CREATE PROCEDURE on page 14-64, CREATE FUNCTION on page 13-52, and Oracle9i Application Developer’s Guide - Fundamentals for information on the components of type body
■Oracle9i Application Developer’s Guide - Object-Relational Features for information on and examples of user-defined constructors
pl/sql_block Declare the procedure or function.
See Also: PL/SQL User’s Guide and Reference
call_spec Specify the call specification ("call spec") that maps a Java or C method name, parameter types, and return type to their SQL counterparts.
The Java_declaration, ’string’ identifies the Java implementation of the method.
See Also:
■
■
Oracle9i Java Stored Procedures Developer’s Guide
Oracle9i Application Developer’s Guide - Fundamentals for an explanation of the parameters and semantics of the C_ declaration
map_order_func_declaration
You can declare either one MAP method or one ORDER method, regardless how many MEMBER or STATIC methods you declare. If you declare either a MAP or ORDER method, you can compare object instances in SQL.
If you do not declare either method, you can compare object instances only for equality or inequality. Instances of the same type definition are equal only if each pair of their corresponding attributes is equal.
SQL Statements: CREATE TYPE to DROP ROLLBACK SEGMENT 16-29

CREATE TYPE BODY
MAP MEMBER Clause
Specify MAP MEMBER to declare or implement a member function (MAP method) that returns the relative position of a given instance in the ordering of all instances of the object. A MAP method is called implicitly and specifies an ordering of object instances by mapping them to values of a predefined scalar type. PL/SQL uses the ordering to evaluate Boolean expressions and to perform comparisons.
If the argument to the MAP method is null, the MAP method returns null and the method is not invoked.
An object type body can contain only one MAP method, which must be a function. The MAP function can have no arguments other than the implicit SELF argument.
ORDER MEMBER Clause
Specify ORDER MEMBER to specify a member function (ORDER method) that takes an instance of an object as an explicit argument and the implicit SELF argument and returns either a negative, zero, or positive integer. The negative, positive, or zero indicates that the implicit SELF argument is less than, equal to, or greater than the explicit argument.
If either argument to the ORDER method is null, the ORDER method returns null and the method is not invoked.
When instances of the same object type definition are compared in an ORDER BY clause, Oracle invokes the ORDER MEMBER function_declaration.
An object specification can contain only one ORDER method, which must be a function having the return type NUMBER.
function_declaration Declare a function subprogram.
See Also: CREATE PROCEDURE on page 14-64 and CREATE FUNCTION on page 13-52 for the full syntax with all possible clauses
AS EXTERNAL AS EXTERNAL is an alternative way of declaring a C method. This clause has been deprecated and is supported for backward compatibility only. Oracle Corporation recommends that you use the call_spec syntax with the C_ declaration.
Examples
Several examples of creating type bodies appear in the "Examples" section of CREATE TYPE on page 16-19.
16-30 Oracle9i SQL Reference

CREATE TYPE BODY
Updating a Type Body: Example The following example shows how the type body of the data_typ object type (see "Object Type Examples" on page 16-19) must be modified when an attribute is added to the type (the PL/SQL is shown in italics):
ALTER TYPE data_typ
ADD MEMBER FUNCTION qtr(der_qtr DATE)
RETURN CHAR CASCADE;
CREATE OR REPLACE TYPE BODY data_typ IS
MEMBER FUNCTION prod (invent NUMBER) RETURN NUMBER IS BEGIN
RETURN (year + invent); END;
MEMBER FUNCTION qtr(der_qtr DATE) RETURN CHAR IS BEGIN
IF (der_qtr < TO_DATE(’01-APR’, ’DD-MON’)) THEN RETURN ’FIRST’;
ELSIF (der_qtr < TO_DATE(’01-JUL’, ’DD-MON’)) THEN RETURN ’SECOND’;
ELSIF (der_qtr < TO_DATE(’01-OCT’, ’DD-MON’)) THEN RETURN ’THIRD’;
ELSE
RETURN ’FOURTH’; END IF;
END; END;
/
END;
SQL Statements: CREATE TYPE to DROP ROLLBACK SEGMENT 16-31
