
- •Contents
- •Send Us Your Comments
- •Preface
- •What’s New in SQL Reference?
- •1 Introduction to Oracle SQL
- •History of SQL
- •SQL Standards
- •Embedded SQL
- •Lexical Conventions
- •Tools Support
- •2 Basic Elements of Oracle SQL
- •Datatypes
- •Oracle Built-in Datatypes
- •ANSI, DB2, and SQL/DS Datatypes
- •Oracle-Supplied Types
- •"Any" Types
- •XML Types
- •Spatial Type
- •Media Types
- •Datatype Comparison Rules
- •Data Conversion
- •Literals
- •Text Literals
- •Integer Literals
- •Number Literals
- •Interval Literals
- •Format Models
- •Number Format Models
- •Date Format Models
- •String-to-Date Conversion Rules
- •XML Format Model
- •Nulls
- •Nulls in SQL Functions
- •Nulls with Comparison Conditions
- •Nulls in Conditions
- •Pseudocolumns
- •CURRVAL and NEXTVAL
- •LEVEL
- •ROWID
- •ROWNUM
- •XMLDATA
- •Comments
- •Comments Within SQL Statements
- •Comments on Schema Objects
- •Hints
- •Database Objects
- •Schema Objects
- •Nonschema Objects
- •Parts of Schema Objects
- •Schema Object Names and Qualifiers
- •Schema Object Naming Rules
- •Schema Object Naming Examples
- •Schema Object Naming Guidelines
- •Syntax for Schema Objects and Parts in SQL Statements
- •How Oracle Resolves Schema Object References
- •Referring to Objects in Other Schemas
- •Referring to Objects in Remote Databases
- •Referencing Object Type Attributes and Methods
- •3 Operators
- •About SQL Operators
- •Unary and Binary Operators
- •Operator Precedence
- •Arithmetic Operators
- •Concatenation Operator
- •Set Operators
- •4 Expressions
- •About SQL Expressions
- •Simple Expressions
- •Compound Expressions
- •CASE Expressions
- •CURSOR Expressions
- •Datetime Expressions
- •Function Expressions
- •INTERVAL Expressions
- •Object Access Expressions
- •Scalar Subquery Expressions
- •Type Constructor Expressions
- •Variable Expressions
- •Expression Lists
- •5 Conditions
- •About SQL Conditions
- •Condition Precedence
- •Comparison Conditions
- •Simple Comparison Conditions
- •Group Comparison Conditions
- •Logical Conditions
- •Membership Conditions
- •Range Conditions
- •Null Conditions
- •EQUALS_PATH
- •EXISTS Conditions
- •LIKE Conditions
- •IS OF type Conditions
- •UNDER_PATH
- •Compound Conditions
- •6 Functions
- •SQL Functions
- •Single-Row Functions
- •Aggregate Functions
- •Analytic Functions
- •Object Reference Functions
- •Alphabetical Listing of SQL Functions
- •ACOS
- •ADD_MONTHS
- •ASCII
- •ASCIISTR
- •ASIN
- •ATAN
- •ATAN2
- •BFILENAME
- •BITAND
- •CAST
- •CEIL
- •CHARTOROWID
- •COALESCE
- •COMPOSE
- •CONCAT
- •CONVERT
- •CORR
- •COSH
- •COUNT
- •COVAR_POP
- •COVAR_SAMP
- •CUME_DIST
- •CURRENT_DATE
- •CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
- •DBTIMEZONE
- •DECODE
- •DECOMPOSE
- •DENSE_RANK
- •DEPTH
- •DEREF
- •DUMP
- •EMPTY_BLOB, EMPTY_CLOB
- •EXISTSNODE
- •EXTRACT (datetime)
- •EXTRACT (XML)
- •EXTRACTVALUE
- •FIRST
- •FIRST_VALUE
- •FLOOR
- •FROM_TZ
- •GREATEST
- •GROUP_ID
- •GROUPING
- •GROUPING_ID
- •HEXTORAW
- •INITCAP
- •INSTR
- •LAST
- •LAST_DAY
- •LAST_VALUE
- •LEAD
- •LEAST
- •LENGTH
- •LOCALTIMESTAMP
- •LOWER
- •LPAD
- •LTRIM
- •MAKE_REF
- •MONTHS_BETWEEN
- •NCHR
- •NEW_TIME
- •NEXT_DAY
- •NLS_CHARSET_DECL_LEN
- •NLS_CHARSET_ID
- •NLS_CHARSET_NAME
- •NLS_INITCAP
- •NLS_LOWER
- •NLSSORT
- •NLS_UPPER
- •NTILE
- •NULLIF
- •NUMTODSINTERVAL
- •NUMTOYMINTERVAL
- •PATH
- •PERCENT_RANK
- •PERCENTILE_CONT
- •PERCENTILE_DISC
- •POWER
- •RANK
- •RATIO_TO_REPORT
- •RAWTOHEX
- •RAWTONHEX
- •REFTOHEX
- •REGR_ (Linear Regression) Functions
- •REPLACE
- •ROUND (number)
- •ROUND (date)
- •ROW_NUMBER
- •ROWIDTOCHAR
- •ROWIDTONCHAR
- •RPAD
- •RTRIM
- •SESSIONTIMEZONE
- •SIGN
- •SINH
- •SOUNDEX
- •SQRT
- •STDDEV
- •STDDEV_POP
- •STDDEV_SAMP
- •SUBSTR
- •SYS_CONNECT_BY_PATH
- •SYS_CONTEXT
- •SYS_DBURIGEN
- •SYS_EXTRACT_UTC
- •SYS_GUID
- •SYS_TYPEID
- •SYS_XMLAGG
- •SYS_XMLGEN
- •SYSDATE
- •SYSTIMESTAMP
- •TANH
- •TO_CHAR (character)
- •TO_CHAR (datetime)
- •TO_CHAR (number)
- •TO_CLOB
- •TO_DATE
- •TO_DSINTERVAL
- •TO_MULTI_BYTE
- •TO_NCHAR (character)
- •TO_NCHAR (datetime)
- •TO_NCHAR (number)
- •TO_NCLOB
- •TO_NUMBER
- •TO_SINGLE_BYTE
- •TO_TIMESTAMP
- •TO_TIMESTAMP_TZ
- •TO_YMINTERVAL
- •TRANSLATE
- •TRANSLATE ... USING
- •TREAT
- •TRIM
- •TRUNC (number)
- •TRUNC (date)
- •TZ_OFFSET
- •UNISTR
- •UPDATEXML
- •UPPER
- •USER
- •USERENV
- •VALUE
- •VAR_SAMP
- •VARIANCE
- •VSIZE
- •WIDTH_BUCKET
- •XMLAGG
- •XMLCOLATTVAL
- •XMLCONCAT
- •XMLELEMENT
- •XMLFOREST
- •XMLSEQUENCE
- •XMLTRANSFORM
- •ROUND and TRUNC Date Functions
- •User-Defined Functions
- •Prerequisites
- •Name Precedence
- •7 Common SQL DDL Clauses
- •allocate_extent_clause
- •constraints
- •deallocate_unused_clause
- •file_specification
- •logging_clause
- •parallel_clause
- •physical_attributes_clause
- •storage_clause
- •8 SQL Queries and Subqueries
- •About Queries and Subqueries
- •Creating Simple Queries
- •Hierarchical Queries
- •The UNION [ALL], INTERSECT, MINUS Operators
- •Sorting Query Results
- •Joins
- •Using Subqueries
- •Unnesting of Nested Subqueries
- •Selecting from the DUAL Table
- •Distributed Queries
- •9 SQL Statements: ALTER CLUSTER to ALTER SEQUENCE
- •Types of SQL Statements
- •Organization of SQL Statements
- •ALTER CLUSTER
- •ALTER DATABASE
- •ALTER DIMENSION
- •ALTER FUNCTION
- •ALTER INDEX
- •ALTER INDEXTYPE
- •ALTER JAVA
- •ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW
- •ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG
- •ALTER OPERATOR
- •ALTER OUTLINE
- •ALTER PACKAGE
- •ALTER PROCEDURE
- •ALTER PROFILE
- •ALTER RESOURCE COST
- •ALTER ROLE
- •ALTER ROLLBACK SEGMENT
- •ALTER SEQUENCE
- •10 SQL Statements: ALTER SESSION to ALTER SYSTEM
- •ALTER SESSION
- •ALTER SYSTEM
- •ALTER TABLE
- •ALTER TABLESPACE
- •ALTER TRIGGER
- •ALTER TYPE
- •ALTER USER
- •ALTER VIEW
- •ANALYZE
- •ASSOCIATE STATISTICS
- •AUDIT
- •CALL
- •COMMENT
- •COMMIT
- •13 SQL Statements: CREATE CLUSTER to CREATE JAVA
- •CREATE CLUSTER
- •CREATE CONTEXT
- •CREATE CONTROLFILE
- •CREATE DATABASE
- •CREATE DATABASE LINK
- •CREATE DIMENSION
- •CREATE DIRECTORY
- •CREATE FUNCTION
- •CREATE INDEX
- •CREATE INDEXTYPE
- •CREATE JAVA
- •14 SQL Statements: CREATE LIBRARY to CREATE SPFILE
- •CREATE LIBRARY
- •CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW
- •CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG
- •CREATE OPERATOR
- •CREATE OUTLINE
- •CREATE PACKAGE
- •CREATE PACKAGE BODY
- •CREATE PFILE
- •CREATE PROCEDURE
- •CREATE PROFILE
- •CREATE ROLE
- •CREATE ROLLBACK SEGMENT
- •CREATE SCHEMA
- •CREATE SEQUENCE
- •CREATE SPFILE
- •15 SQL Statements: CREATE SYNONYM to CREATE TRIGGER
- •CREATE SYNONYM
- •CREATE TABLE
- •CREATE TABLESPACE
- •CREATE TEMPORARY TABLESPACE
- •CREATE TRIGGER
- •CREATE TYPE
- •CREATE TYPE BODY
- •CREATE USER
- •CREATE VIEW
- •DELETE
- •DISASSOCIATE STATISTICS
- •DROP CLUSTER
- •DROP CONTEXT
- •DROP DATABASE LINK
- •DROP DIMENSION
- •DROP DIRECTORY
- •DROP FUNCTION
- •DROP INDEX
- •DROP INDEXTYPE
- •DROP JAVA
- •DROP LIBRARY
- •DROP MATERIALIZED VIEW
- •DROP MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG
- •DROP OPERATOR
- •DROP OUTLINE
- •DROP PACKAGE
- •DROP PROCEDURE
- •DROP PROFILE
- •DROP ROLE
- •DROP ROLLBACK SEGMENT
- •17 SQL Statements: DROP SEQUENCE to ROLLBACK
- •DROP SEQUENCE
- •DROP SYNONYM
- •DROP TABLE
- •DROP TABLESPACE
- •DROP TRIGGER
- •DROP TYPE
- •DROP TYPE BODY
- •DROP USER
- •DROP VIEW
- •EXPLAIN PLAN
- •GRANT
- •INSERT
- •LOCK TABLE
- •MERGE
- •NOAUDIT
- •RENAME
- •REVOKE
- •ROLLBACK
- •18 SQL Statements: SAVEPOINT to UPDATE
- •SAVEPOINT
- •SELECT
- •SET CONSTRAINT[S]
- •SET ROLE
- •SET TRANSACTION
- •TRUNCATE
- •UPDATE
- •Required Keywords and Parameters
- •Optional Keywords and Parameters
- •Syntax Loops
- •Multipart Diagrams
- •Database Objects
- •ANSI Standards
- •ISO Standards
- •Oracle Compliance
- •FIPS Compliance
- •Oracle Extensions to Standard SQL
- •Character Set Support
- •Using Extensible Indexing
- •Using XML in SQL Statements
- •Index

CREATE PFILE
CREATE PFILE
Purpose
Use the CREATE PFILE statement to export a binary server parameter file into a text initialization parameter file. Creating a text parameter file is a convenient way to get a listing of the current parameter settings being used by the database, and it lets you edit the file easily in a text editor and then convert it back into a server parameter file using the CREATE SPFILE statement.
Upon successful execution of this statement, Oracle creates a text parameter file on the server. In a Real Application Clusters environment, it will contain all parameter settings of all instances. It will also contain any comments that appeared on the same line with a parameter setting in the server parameter file.
See Also:
■CREATE SPFILE on page 14-94 for information on server parameter files
■Oracle9i Database Administrator’s Guide for information on pre-Oracle9i text initialization parameter files and Oracle9i binary server parameter files
■Oracle9i Real Application Clusters Administration for information on using server parameter files in a Real Application Clusters environment
Prerequisites
You must have the SYSDBA or the SYSOPER role to execute this statement. You can execute this statement either before or after instance startup.
Syntax
create_pfile::=
|
= |
’ |
pfile_name |
’ |
|
= |
’ |
spfile_name |
’ |
CREATE |
PFILE |
|
|
FROM |
SPFILE |
|
|
|
; |
14-62 Oracle9i SQL Reference

CREATE PFILE
Semantics
pfile_name
Specify the name of the text parameter file you want to create. If you do not specify pfile_name, Oracle uses the platform-specific default initialization parameter file name.
spfile_name
Specify the name of the binary server parameter from which you want to create a text file.
■If you specify spfile_name, the file must exist on the server. If the file does not reside in the default directory for server parameter files on your operating system, you must specify the full path.
■If you do not specify spfile_name, Oracle looks in the default directory for server parameter files on your operating system, for the platform-specific default server parameter file name, and uses that file. If that file does not exist in the expected directory, Oracle returns an error.
See Also: Oracle9i Database Administrator’s Guide for Windows (or other appropriate operating system specific documentation) for default parameter file names
Examples
Creating a Parameter File: Example The following example creates a text parameter file my_init.ora from a binary server parameter file production.ora:
CREATE PFILE = ’my_init.ora’ FROM SPFILE = ’s_params.ora’;
Note: Typically you will need to specify the full path and filename for parameter files on your operating system. Please refer to your Oracle operating system documentation for path information.
SQL Statements: CREATE LIBRARY to CREATE SPFILE 14-63

CREATE PROCEDURE
CREATE PROCEDURE
Purpose
Use the CREATE PROCEDURE statement to create a standalone stored procedure or a call specification.
A procedure is a group of PL/SQL statements that you can call by name. A call specification ("call spec") declares a Java method or a third-generation language (3GL) routine so that it can be called from SQL and PL/SQL. The call spec tells Oracle which Java method to invoke when a call is made. It also tells Oracle what type conversions to make for the arguments and return value.
Stored procedures offer advantages in the areas of development, integrity, security, performance, and memory allocation.
See Also:
■Oracle9i Application Developer’s Guide - Fundamentals for more information on stored procedures, including how to call stored procedures and for information about registering external procedures
■CREATE FUNCTION on page 13-52 for information specific to functions, which are similar to procedures in many ways
■CREATE PACKAGE on page 14-52 for information on creating packages. (The CREATE PROCEDURE statement creates a procedure as a standalone schema object. You can also create a procedure as part of a package.)
■ALTER PROCEDURE on page 9-124 and DROP PROCEDURE on page 16-93 for information on modifying and dropping a standalone procedure
■CREATE LIBRARY on page 14-2 for more information about shared libraries
Prerequisites
Before creating a procedure, the user SYS must run a SQL script commonly called DBMSSTDX.SQL. The exact name and location of this script depends on your operating system.
To create a procedure in your own schema, you must have the CREATE PROCEDURE system privilege. To create a procedure in another user’s schema, you must have
14-64 Oracle9i SQL Reference
CREATE PROCEDURE
CREATE ANY PROCEDURE system privilege. To replace a procedure in another schema, you must have the ALTER ANY PROCEDURE system privilege.
To invoke a call spec, you may need additional privileges (for example, EXECUTE privileges on the C library for a C call spec).
To embed a CREATE PROCEDURE statement inside an Oracle precompiler program, you must terminate the statement with the keyword END-EXEC followed by the embedded SQL statement terminator for the specific language.
See Also: PL/SQL User’s Guide and Reference or Oracle9i Java Stored
Procedures Developer’s Guide for more information
Syntax
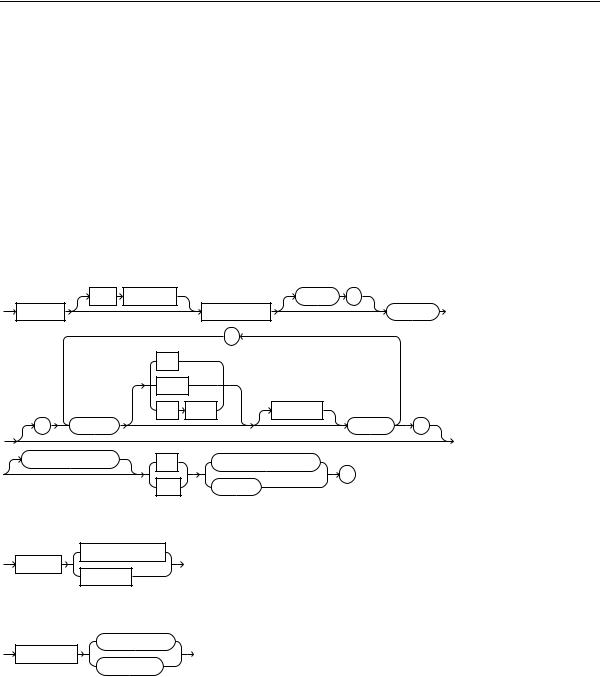
create_procedure::=
|
OR |
REPLACE |
|
schema |
. |
|
CREATE |
|
|
PROCEDURE |
|
procedure |
|
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|
|
IN |
|
|
|
|
|
|
OUT |
|
|
|
|
|
|
IN |
OUT |
NOCOPY |
|
|
( |
argument |
|
|
|
datatype |
) |
invoker_rights_clause |
IS |
|
pl/sql_subprogram_body |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
; |
|
|
|
AS |
|
call_spec |
|
|
invoker_rights_clause::=
CURRENT_USER
AUTHID
DEFINER
call_spec::=
Java_declaration
LANGUAGE
C_declaration
SQL Statements: CREATE LIBRARY to CREATE SPFILE 14-65

CREATE PROCEDURE
Java_declaration::=
JAVA  NAME
NAME  ’
’  string
string  ’
’
C_declaration::=
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
NAME |
name |
|
|
|
AGENT |
IN |
( |
argument |
) |
C |
|
|
LIBRARY |
lib_name |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
, |
|
|
|
|
WITH |
CONTEXT |
PARAMETERS |
( |
parameter |
|
) |
|
|
||
Semantics
OR REPLACE
Specify OR REPLACE to re-create the procedure if it already exists. Use this clause to change the definition of an existing procedure without dropping, re-creating, and regranting object privileges previously granted on it. If you redefine a procedure, Oracle recompiles it.
Users who had previously been granted privileges on a redefined procedure can still access the procedure without being regranted the privileges.
If any function-based indexes depend on the package, Oracle marks the indexes
DISABLED.
See Also: ALTER PROCEDURE on page 9-124 for information on recompiling procedures
schema
Specify the schema to contain the procedure. If you omit schema, Oracle creates the procedure in your current schema.
procedure
Specify the name of the procedure to be created.
If creating the procedure results in compilation errors, Oracle returns an error. You can see the associated compiler error messages with the SQL*Plus command SHOW ERRORS.
14-66 Oracle9i SQL Reference

CREATE PROCEDURE
argument
Specify the name of an argument to the procedure. If the procedure does not accept arguments, you can omit the parentheses following the procedure name.
IN Specify IN to indicate that you must specify a value for the argument when calling the procedure.
OUT Specify OUT to indicate that the procedure passes a value for this argument back to its calling environment after execution.
IN OUT Specify IN OUT to indicate that you must specify a value for the argument when calling the procedure and that the procedure passes a value back to its calling environment after execution.
If you omit IN, OUT, and IN OUT, the argument defaults to IN.
NOCOPY Specify NOCOPY to instruct Oracle to pass this argument as fast as possible. This clause can significantly enhance performance when passing a large value like a record, an index-by table, or a varray to an OUT or IN OUT parameter. (IN parameter values are always passed NOCOPY.)
■When you specify NOCOPY, assignments made to a package variable may show immediately in this parameter (or assignments made to this parameter may show immediately in a package variable) if the package variable is passed as the actual assignment corresponding to this parameter.
■Similarly, changes made either to this parameter or to another parameter may be visible immediately through both names if the same variable is passed to both.
■If the procedure is exited with an unhandled exception, any assignment made to this parameter may be visible in the caller’s variable.
These effects may or may not occur on any particular call. You should use NOCOPY only when these effects would not matter.
datatype Specify the datatype of the argument. An argument can have any datatype supported by PL/SQL.
Datatypes cannot specify length, precision, or scale. For example, VARCHAR2(10) is not valid, but VARCHAR2 is valid. Oracle derives the length, precision, and scale of an argument from the environment from which the procedure is called.
SQL Statements: CREATE LIBRARY to CREATE SPFILE 14-67

CREATE PROCEDURE
invoker_rights_clause
The invoker_rights_clause lets you specify whether the procedure executes with the privileges and in the schema of the user who owns it or with the privileges and in the schema of CURRENT_USER.
This clause also determines how Oracle resolves external names in queries, DML operations, and dynamic SQL statements in the procedure.
AUTHID CURRENT_USER
Specify CURRENT_USER to indicate that the procedure executes with the privileges of CURRENT_USER. This clause creates an invoker-rights procedure.
This clause also specifies that external names in queries, DML operations, and dynamic SQL statements resolve in the schema of CURRENT_USER. External names in all other statements resolve in the schema in which the procedure resides.
AUTHID DEFINER
Specify DEFINER to indicate that the procedure executes with the privileges of the owner of the schema in which the procedure resides, and that external names resolve in the schema where the procedure resides. This is the default and creates a definer-rights procedure.
See Also:
■
■
PL/SQL User’s Guide and Reference
Oracle9i Database Concepts and Oracle9i Application Developer’s Guide - Fundamentals for information on how CURRENT_USER is determined
IS | AS Clause
pl/sql_subprogram_body
Declare the procedure in a PL/SQL subprogram body.
See Also: Oracle9i Application Developer’s Guide - Fundamentals for more information on PL/SQL subprograms
call_spec
Use the call_spec to map a Java or C method name, parameter types, and return type to their SQL counterparts.
14-68 Oracle9i SQL Reference

CREATE PROCEDURE
In Java_declaration, ’string’ identifies the Java implementation of the method.
See Also:
■
■
Oracle9i Java Stored Procedures Developer’s Guide for an explanation of the parameters and semantics of the Java_ declaration
Oracle9i Application Developer’s Guide - Fundamentals for an explanation of the parameters and semantics of the C_ declaration
AS EXTERNAL The AS EXTERNAL clause is an alternative way of declaring a C method. This clause has been deprecated and is supported for backward compatibility only. Oracle Corporation recommends that you use the AS LANGUAGE C syntax.
Examples
Creating a Procedure: Example The following statement creates the procedure remove_emp in the schema hr (PL/SQL is shown in italics):
CREATE PROCEDURE remove_emp (employee_id NUMBER) AS tot_emps NUMBER;
BEGIN
DELETE FROM employees
WHERE employees.employee_id = remove_emp.employee_id; tot_emps := tot_emps - 1;
END;
/
The remove_emp procedure removes a specified employee. When you call the procedure, you must specify the employee_id of the employee to be removed. The argument’s datatype is NUMBER.
The procedure uses a DELETE statement to remove from the employees table the row of employee_id.
See Also: "Creating a Package Body: Example" on page 14-59 to see how to incorporate this procedure into a package
SQL Statements: CREATE LIBRARY to CREATE SPFILE 14-69

CREATE PROCEDURE
In the following example, external procedure c_find_root expects a pointer as a parameter. Procedure find_root passes the parameter by reference using the BY REFERENCE phrase (PL/SQL is shown in italics):
CREATE PROCEDURE find_root ( x IN REAL )
IS LANGUAGE C
NAME c_find_root
LIBRARY c_utils
PARAMETERS ( x BY REFERENCE );
14-70 Oracle9i SQL Reference
