
- •Contents
- •Send Us Your Comments
- •Preface
- •What’s New in SQL Reference?
- •1 Introduction to Oracle SQL
- •History of SQL
- •SQL Standards
- •Embedded SQL
- •Lexical Conventions
- •Tools Support
- •2 Basic Elements of Oracle SQL
- •Datatypes
- •Oracle Built-in Datatypes
- •ANSI, DB2, and SQL/DS Datatypes
- •Oracle-Supplied Types
- •"Any" Types
- •XML Types
- •Spatial Type
- •Media Types
- •Datatype Comparison Rules
- •Data Conversion
- •Literals
- •Text Literals
- •Integer Literals
- •Number Literals
- •Interval Literals
- •Format Models
- •Number Format Models
- •Date Format Models
- •String-to-Date Conversion Rules
- •XML Format Model
- •Nulls
- •Nulls in SQL Functions
- •Nulls with Comparison Conditions
- •Nulls in Conditions
- •Pseudocolumns
- •CURRVAL and NEXTVAL
- •LEVEL
- •ROWID
- •ROWNUM
- •XMLDATA
- •Comments
- •Comments Within SQL Statements
- •Comments on Schema Objects
- •Hints
- •Database Objects
- •Schema Objects
- •Nonschema Objects
- •Parts of Schema Objects
- •Schema Object Names and Qualifiers
- •Schema Object Naming Rules
- •Schema Object Naming Examples
- •Schema Object Naming Guidelines
- •Syntax for Schema Objects and Parts in SQL Statements
- •How Oracle Resolves Schema Object References
- •Referring to Objects in Other Schemas
- •Referring to Objects in Remote Databases
- •Referencing Object Type Attributes and Methods
- •3 Operators
- •About SQL Operators
- •Unary and Binary Operators
- •Operator Precedence
- •Arithmetic Operators
- •Concatenation Operator
- •Set Operators
- •4 Expressions
- •About SQL Expressions
- •Simple Expressions
- •Compound Expressions
- •CASE Expressions
- •CURSOR Expressions
- •Datetime Expressions
- •Function Expressions
- •INTERVAL Expressions
- •Object Access Expressions
- •Scalar Subquery Expressions
- •Type Constructor Expressions
- •Variable Expressions
- •Expression Lists
- •5 Conditions
- •About SQL Conditions
- •Condition Precedence
- •Comparison Conditions
- •Simple Comparison Conditions
- •Group Comparison Conditions
- •Logical Conditions
- •Membership Conditions
- •Range Conditions
- •Null Conditions
- •EQUALS_PATH
- •EXISTS Conditions
- •LIKE Conditions
- •IS OF type Conditions
- •UNDER_PATH
- •Compound Conditions
- •6 Functions
- •SQL Functions
- •Single-Row Functions
- •Aggregate Functions
- •Analytic Functions
- •Object Reference Functions
- •Alphabetical Listing of SQL Functions
- •ACOS
- •ADD_MONTHS
- •ASCII
- •ASCIISTR
- •ASIN
- •ATAN
- •ATAN2
- •BFILENAME
- •BITAND
- •CAST
- •CEIL
- •CHARTOROWID
- •COALESCE
- •COMPOSE
- •CONCAT
- •CONVERT
- •CORR
- •COSH
- •COUNT
- •COVAR_POP
- •COVAR_SAMP
- •CUME_DIST
- •CURRENT_DATE
- •CURRENT_TIMESTAMP
- •DBTIMEZONE
- •DECODE
- •DECOMPOSE
- •DENSE_RANK
- •DEPTH
- •DEREF
- •DUMP
- •EMPTY_BLOB, EMPTY_CLOB
- •EXISTSNODE
- •EXTRACT (datetime)
- •EXTRACT (XML)
- •EXTRACTVALUE
- •FIRST
- •FIRST_VALUE
- •FLOOR
- •FROM_TZ
- •GREATEST
- •GROUP_ID
- •GROUPING
- •GROUPING_ID
- •HEXTORAW
- •INITCAP
- •INSTR
- •LAST
- •LAST_DAY
- •LAST_VALUE
- •LEAD
- •LEAST
- •LENGTH
- •LOCALTIMESTAMP
- •LOWER
- •LPAD
- •LTRIM
- •MAKE_REF
- •MONTHS_BETWEEN
- •NCHR
- •NEW_TIME
- •NEXT_DAY
- •NLS_CHARSET_DECL_LEN
- •NLS_CHARSET_ID
- •NLS_CHARSET_NAME
- •NLS_INITCAP
- •NLS_LOWER
- •NLSSORT
- •NLS_UPPER
- •NTILE
- •NULLIF
- •NUMTODSINTERVAL
- •NUMTOYMINTERVAL
- •PATH
- •PERCENT_RANK
- •PERCENTILE_CONT
- •PERCENTILE_DISC
- •POWER
- •RANK
- •RATIO_TO_REPORT
- •RAWTOHEX
- •RAWTONHEX
- •REFTOHEX
- •REGR_ (Linear Regression) Functions
- •REPLACE
- •ROUND (number)
- •ROUND (date)
- •ROW_NUMBER
- •ROWIDTOCHAR
- •ROWIDTONCHAR
- •RPAD
- •RTRIM
- •SESSIONTIMEZONE
- •SIGN
- •SINH
- •SOUNDEX
- •SQRT
- •STDDEV
- •STDDEV_POP
- •STDDEV_SAMP
- •SUBSTR
- •SYS_CONNECT_BY_PATH
- •SYS_CONTEXT
- •SYS_DBURIGEN
- •SYS_EXTRACT_UTC
- •SYS_GUID
- •SYS_TYPEID
- •SYS_XMLAGG
- •SYS_XMLGEN
- •SYSDATE
- •SYSTIMESTAMP
- •TANH
- •TO_CHAR (character)
- •TO_CHAR (datetime)
- •TO_CHAR (number)
- •TO_CLOB
- •TO_DATE
- •TO_DSINTERVAL
- •TO_MULTI_BYTE
- •TO_NCHAR (character)
- •TO_NCHAR (datetime)
- •TO_NCHAR (number)
- •TO_NCLOB
- •TO_NUMBER
- •TO_SINGLE_BYTE
- •TO_TIMESTAMP
- •TO_TIMESTAMP_TZ
- •TO_YMINTERVAL
- •TRANSLATE
- •TRANSLATE ... USING
- •TREAT
- •TRIM
- •TRUNC (number)
- •TRUNC (date)
- •TZ_OFFSET
- •UNISTR
- •UPDATEXML
- •UPPER
- •USER
- •USERENV
- •VALUE
- •VAR_SAMP
- •VARIANCE
- •VSIZE
- •WIDTH_BUCKET
- •XMLAGG
- •XMLCOLATTVAL
- •XMLCONCAT
- •XMLELEMENT
- •XMLFOREST
- •XMLSEQUENCE
- •XMLTRANSFORM
- •ROUND and TRUNC Date Functions
- •User-Defined Functions
- •Prerequisites
- •Name Precedence
- •7 Common SQL DDL Clauses
- •allocate_extent_clause
- •constraints
- •deallocate_unused_clause
- •file_specification
- •logging_clause
- •parallel_clause
- •physical_attributes_clause
- •storage_clause
- •8 SQL Queries and Subqueries
- •About Queries and Subqueries
- •Creating Simple Queries
- •Hierarchical Queries
- •The UNION [ALL], INTERSECT, MINUS Operators
- •Sorting Query Results
- •Joins
- •Using Subqueries
- •Unnesting of Nested Subqueries
- •Selecting from the DUAL Table
- •Distributed Queries
- •9 SQL Statements: ALTER CLUSTER to ALTER SEQUENCE
- •Types of SQL Statements
- •Organization of SQL Statements
- •ALTER CLUSTER
- •ALTER DATABASE
- •ALTER DIMENSION
- •ALTER FUNCTION
- •ALTER INDEX
- •ALTER INDEXTYPE
- •ALTER JAVA
- •ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW
- •ALTER MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG
- •ALTER OPERATOR
- •ALTER OUTLINE
- •ALTER PACKAGE
- •ALTER PROCEDURE
- •ALTER PROFILE
- •ALTER RESOURCE COST
- •ALTER ROLE
- •ALTER ROLLBACK SEGMENT
- •ALTER SEQUENCE
- •10 SQL Statements: ALTER SESSION to ALTER SYSTEM
- •ALTER SESSION
- •ALTER SYSTEM
- •ALTER TABLE
- •ALTER TABLESPACE
- •ALTER TRIGGER
- •ALTER TYPE
- •ALTER USER
- •ALTER VIEW
- •ANALYZE
- •ASSOCIATE STATISTICS
- •AUDIT
- •CALL
- •COMMENT
- •COMMIT
- •13 SQL Statements: CREATE CLUSTER to CREATE JAVA
- •CREATE CLUSTER
- •CREATE CONTEXT
- •CREATE CONTROLFILE
- •CREATE DATABASE
- •CREATE DATABASE LINK
- •CREATE DIMENSION
- •CREATE DIRECTORY
- •CREATE FUNCTION
- •CREATE INDEX
- •CREATE INDEXTYPE
- •CREATE JAVA
- •14 SQL Statements: CREATE LIBRARY to CREATE SPFILE
- •CREATE LIBRARY
- •CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW
- •CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG
- •CREATE OPERATOR
- •CREATE OUTLINE
- •CREATE PACKAGE
- •CREATE PACKAGE BODY
- •CREATE PFILE
- •CREATE PROCEDURE
- •CREATE PROFILE
- •CREATE ROLE
- •CREATE ROLLBACK SEGMENT
- •CREATE SCHEMA
- •CREATE SEQUENCE
- •CREATE SPFILE
- •15 SQL Statements: CREATE SYNONYM to CREATE TRIGGER
- •CREATE SYNONYM
- •CREATE TABLE
- •CREATE TABLESPACE
- •CREATE TEMPORARY TABLESPACE
- •CREATE TRIGGER
- •CREATE TYPE
- •CREATE TYPE BODY
- •CREATE USER
- •CREATE VIEW
- •DELETE
- •DISASSOCIATE STATISTICS
- •DROP CLUSTER
- •DROP CONTEXT
- •DROP DATABASE LINK
- •DROP DIMENSION
- •DROP DIRECTORY
- •DROP FUNCTION
- •DROP INDEX
- •DROP INDEXTYPE
- •DROP JAVA
- •DROP LIBRARY
- •DROP MATERIALIZED VIEW
- •DROP MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG
- •DROP OPERATOR
- •DROP OUTLINE
- •DROP PACKAGE
- •DROP PROCEDURE
- •DROP PROFILE
- •DROP ROLE
- •DROP ROLLBACK SEGMENT
- •17 SQL Statements: DROP SEQUENCE to ROLLBACK
- •DROP SEQUENCE
- •DROP SYNONYM
- •DROP TABLE
- •DROP TABLESPACE
- •DROP TRIGGER
- •DROP TYPE
- •DROP TYPE BODY
- •DROP USER
- •DROP VIEW
- •EXPLAIN PLAN
- •GRANT
- •INSERT
- •LOCK TABLE
- •MERGE
- •NOAUDIT
- •RENAME
- •REVOKE
- •ROLLBACK
- •18 SQL Statements: SAVEPOINT to UPDATE
- •SAVEPOINT
- •SELECT
- •SET CONSTRAINT[S]
- •SET ROLE
- •SET TRANSACTION
- •TRUNCATE
- •UPDATE
- •Required Keywords and Parameters
- •Optional Keywords and Parameters
- •Syntax Loops
- •Multipart Diagrams
- •Database Objects
- •ANSI Standards
- •ISO Standards
- •Oracle Compliance
- •FIPS Compliance
- •Oracle Extensions to Standard SQL
- •Character Set Support
- •Using Extensible Indexing
- •Using XML in SQL Statements
- •Index

14
SQL Statements: CREATE LIBRARY to CREATE SPFILE
This chapter contains the following SQL statements:
■CREATE LIBRARY
■CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW
■CREATE MATERIALIZED VIEW LOG
■CREATE OPERATOR
■CREATE OUTLINE
■CREATE PACKAGE
■CREATE PACKAGE BODY
■CREATE PFILE
■CREATE PROCEDURE
■CREATE PROFILE
■CREATE ROLE
■CREATE ROLLBACK SEGMENT
■CREATE SCHEMA
■CREATE SEQUENCE
■CREATE SPFILE
SQL Statements: CREATE LIBRARY to CREATE SPFILE 14-1
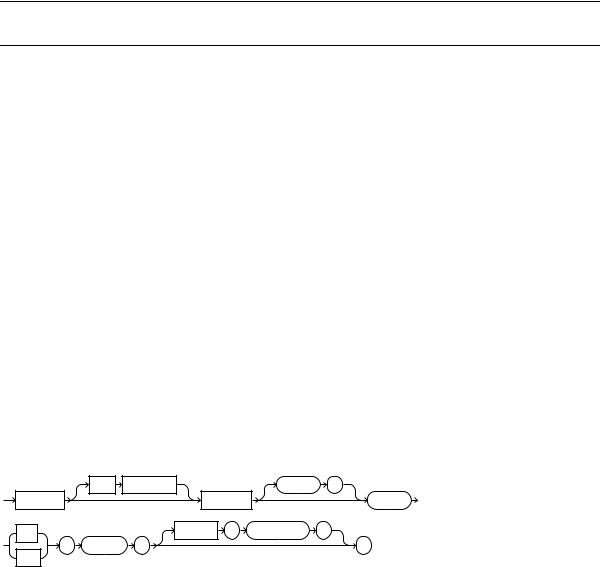
CREATE LIBRARY
CREATE LIBRARY
Purpose
Use the CREATE LIBRARY statement to create a schema object associated with an operating-system shared library. The name of this schema object can then be used in the call_spec of CREATE FUNCTION or CREATE PROCEDURE statements, or when declaring a function or procedure in a package or type, so that SQL and PL/SQL can call to third-generation-language (3GL) functions and procedures.
See Also: CREATE FUNCTION on page 13-52 and PL/SQL User’s Guide and Reference for more information on functions and procedures
Prerequisites
To create a library in your own schema, you must have the CREATE LIBRARY system privilege. To create a library in another user’s schema, you must have the CREATE ANY LIBRARY system privilege. To use the procedures and functions stored in the library, you must have EXECUTE object privileges on the library.
The CREATE LIBRARY statement is valid only on platforms that support shared libraries and dynamic linking.
Syntax
create_library::=
|
OR |
REPLACE |
|
|
schema |
. |
CREATE |
|
|
LIBRARY |
|
libname |
|
IS |
|
|
AGENT |
’ |
agent_dblink |
’ |
’ |
filename |
’ |
|
|
|
; |
AS |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Semantics
OR REPLACE
Specify OR REPLACE to re-create the library if it already exists. Use this clause to change the definition of an existing library without dropping, re-creating, and regranting schema object privileges granted on it.
14-2 Oracle9i SQL Reference

CREATE LIBRARY
Users who had previously been granted privileges on a redefined library can still access the library without being regranted the privileges.
libname
Specify the name you wish to represent this library when declaring a function or procedure with a call_spec.
’filename’
Specify a string literal, enclosed in single quotes. This string should be the path or filename your operating system recognizes as naming the shared library.
The ’filename’ is not interpreted during execution of the CREATE LIBRARY statement. The existence of the library file is not checked until an attempt is made to execute a routine from it.
AGENT Clause
Specify the AGENT clause if you want external procedures to be run from a database link other than the server. Oracle will use the database link specified by agent_ dblink to run external procedures. If you omit this clause, the default agent on the server (extproc) will run external procedures.
Examples
Creating a Library: Examples The following statement creates library ext_lib:
CREATE LIBRARY ext_lib AS ’/OR/lib/ext_lib.so’;
/
The following statement re-creates library ext_lib:
CREATE OR REPLACE LIBRARY ext_lib IS ’/OR/newlib/ext_lib.so’;
/
Specifying an External Procedure Agent: Example The following example creates a library app_lib and specifies that external procedures will be run from the public database sales.hq.acme.com:
CREATE LIBRARY app_lib as ’${ORACLE_HOME}/lib/app_lib.so’ AGENT ’sales.hq.acme.com’;
/
SQL Statements: CREATE LIBRARY to CREATE SPFILE 14-3

CREATE LIBRARY
See Also: "Defining a Public Database Link: Example" on page 13-41 for information on creating database links
14-4 Oracle9i SQL Reference
