
- •Contents
- •Send Us Your Comments
- •Preface
- •Audience
- •Organization
- •Related Documentation
- •Conventions
- •Documentation Accessibility
- •1 Introduction to the Oracle Server
- •Database Structure and Space Management Overview
- •Logical Database Structures
- •Physical Database Structures
- •Data Dictionary Overview
- •Data Access Overview
- •SQL Overview
- •Objects Overview
- •PL/SQL Overview
- •Java Overview
- •XML Overview
- •Transactions Overview
- •Data Integrity Overview
- •SQL*Plus Overview
- •Memory Structure and Processes Overview
- •An Oracle Instance
- •Memory Structures
- •Process Architecture
- •The Program Interface Mechanism
- •An Example of How Oracle Works
- •Application Architecture Overview
- •Client/Server Architecture
- •Multitier Architecture: Application Servers
- •Distributed Databases Overview
- •Replication Overview
- •Streams Overview
- •Advanced Queuing Overview
- •Heterogeneous Services Overview
- •Data Concurrency and Consistency Overview
- •Concurrency
- •Read Consistency
- •Locking Mechanisms
- •Quiesce Database
- •Database Security Overview
- •Security Mechanisms
- •Database Administration Overview
- •Enterprise Manager Overview
- •Database Backup and Recovery Overview
- •Data Warehousing Overview
- •Differences Between Data Warehouse and OLTP Systems
- •Data Warehouse Architecture
- •Materialized Views
- •OLAP Overview
- •Change Data Capture Overview
- •High Availability Overview
- •Transparent Application Failover
- •Online Reorganization Architecture
- •Data Guard Overview
- •LogMiner Overview
- •Real Application Clusters
- •Real Application Clusters Guard
- •Content Management Overview
- •Oracle Internet File System Overview
- •2 Data Blocks, Extents, and Segments
- •Introduction to Data Blocks, Extents, and Segments
- •Data Blocks Overview
- •Data Block Format
- •Free Space Management
- •Extents Overview
- •When Extents Are Allocated
- •Determine the Number and Size of Extents
- •How Extents Are Allocated
- •When Extents Are Deallocated
- •Segments Overview
- •Introduction to Data Segments
- •Introduction to Index Segments
- •Introduction to Temporary Segments
- •Automatic Undo Management
- •3 Tablespaces, Datafiles, and Control Files
- •Introduction to Tablespaces, Datafiles, and Control Files
- •Oracle-Managed Files
- •Allocate More Space for a Database
- •Tablespaces Overview
- •The SYSTEM Tablespace
- •Undo Tablespaces
- •Default Temporary Tablespace
- •Using Multiple Tablespaces
- •Managing Space in Tablespaces
- •Multiple Block Sizes
- •Online and Offline Tablespaces
- •Read-Only Tablespaces
- •Temporary Tablespaces for Sort Operations
- •Transport of Tablespaces Between Databases
- •Datafiles Overview
- •Datafile Contents
- •Size of Datafiles
- •Offline Datafiles
- •Temporary Datafiles
- •Control Files Overview
- •Control File Contents
- •Multiplexed Control Files
- •4 The Data Dictionary
- •Introduction to the Data Dictionary
- •Structure of the Data Dictionary
- •SYS, Owner of the Data Dictionary
- •How the Data Dictionary Is Used
- •How Oracle Uses the Data Dictionary
- •How to Use the Data Dictionary
- •Dynamic Performance Tables
- •Database Object Metadata
- •Introduction to an Oracle Instance
- •The Instance and the Database
- •Connection with Administrator Privileges
- •Initialization Parameter Files
- •Instance and Database Startup
- •How an Instance Is Started
- •How a Database Is Mounted
- •What Happens When You Open a Database
- •Database and Instance Shutdown
- •Close a Database
- •Unmount a Database
- •Shut Down an Instance
- •6 Application Architecture
- •Client/Server Architecture
- •Multitier Architecture
- •Clients
- •Application Servers
- •Database Servers
- •Oracle Net Services
- •How Oracle Net Services Works
- •The Listener
- •7 Memory Architecture
- •Introduction to Oracle Memory Structures
- •System Global Area (SGA) Overview
- •Dynamic SGA
- •Database Buffer Cache
- •Redo Log Buffer
- •Shared Pool
- •Large Pool
- •Control of the SGA’s Use of Memory
- •Other SGA Initialization Parameters
- •Program Global Areas (PGA) Overview
- •Content of the PGA
- •SQL Work Areas
- •PGA Memory Management for Dedicated Mode
- •Dedicated and Shared Servers
- •Software Code Areas
- •8 Process Architecture
- •Introduction to Processes
- •Multiple-Process Oracle Systems
- •Types of Processes
- •User Processes Overview
- •Connections and Sessions
- •Oracle Processes Overview
- •Server Processes
- •Background Processes
- •Trace Files and the Alert Log
- •Shared Server Architecture
- •Scalability
- •Dispatcher Request and Response Queues
- •Shared Server Processes (Snnn)
- •Restricted Operations of the Shared Server
- •Dedicated Server Configuration
- •The Program Interface
- •Program Interface Structure
- •Program Interface Drivers
- •Communications Software for the Operating System
- •9 Database Resource Management
- •Introduction to the Database Resource Manager
- •Database Resource Manager Overview
- •Example of a Simple Resource Plan
- •How the Database Resource Manager Works
- •Resource Control
- •Database Integration
- •Performance Overhead
- •Resource Plans and Resource Consumer Groups
- •Activation of a Resource Plan
- •Groups of Resource Plans
- •Resource Allocation Methods and Resource Plan Directives
- •Resource Plan Directives
- •CPU Resource Allocation
- •Interaction with Operating-System Resource Control
- •Dynamic Reconfiguration
- •10 Schema Objects
- •Introduction to Schema Objects
- •Tables
- •How Table Data Is Stored
- •Nulls Indicate Absence of Value
- •Default Values for Columns
- •Partitioned Tables
- •Nested Tables
- •Temporary Tables
- •External Tables
- •Views
- •How Views are Stored
- •How Views Are Used
- •Mechanics of Views
- •Dependencies and Views
- •Updatable Join Views
- •Object Views
- •Inline Views
- •Materialized Views
- •Define Constraints on Views
- •Refresh Materialized Views
- •Materialized View Logs
- •Dimensions
- •The Sequence Generator
- •Synonyms
- •Indexes
- •Unique and Nonunique Indexes
- •Composite Indexes
- •Indexes and Keys
- •Indexes and Nulls
- •Function-Based Indexes
- •How Indexes Are Stored
- •How Indexes Are Searched
- •Key Compression
- •Reverse Key Indexes
- •Bitmap Indexes
- •Bitmap Join Indexes
- •Index-Organized Tables
- •Benefits of Index-Organized Tables
- •Index-Organized Tables with Row Overflow Area
- •Secondary Indexes on Index-Organized Tables
- •Bitmap Indexes on Index-Organized Tables
- •Partitioned Index-Organized Tables
- •Index-Organized Table Applications
- •Application Domain Indexes
- •Clusters
- •Hash Clusters
- •Introduction to Partitioning
- •Partition Key
- •Partitioned Tables
- •Partitioned Index-Organized Tables
- •Partitioning Methods
- •Range Partitioning
- •List Partitioning
- •Hash Partitioning
- •Composite Partitioning
- •When to Partition a Table
- •Partitioned Indexes
- •Local Partitioned Indexes
- •Global Partitioned Indexes
- •Global Nonpartitioned Indexes
- •Partitioned Index Examples
- •Miscellaneous Information about Creating Indexes on Partitioned Tables
- •Using Partitioned Indexes in OLTP Applications
- •Using Partitioned Indexes in Data Warehousing and DSS Applications
- •Partitioned Indexes on Composite Partitions
- •Partitioning to Improve Performance
- •Partition Pruning
- •Partition-wise Joins
- •Parallel DML
- •Introduction to Oracle Datatypes
- •Character Datatypes
- •CHAR Datatype
- •VARCHAR2 and VARCHAR Datatypes
- •Length Semantics for Character Datatypes
- •NCHAR and NVARCHAR2 Datatypes
- •Use of Unicode Data in an Oracle Database
- •LOB Character Datatypes
- •LONG Datatype
- •NUMBER Datatype
- •Internal Numeric Format
- •DATE Datatype
- •Use of Julian Dates
- •Date Arithmetic
- •Centuries and the Year 2000
- •Daylight Savings Support
- •Time Zones
- •LOB Datatypes
- •BLOB Datatype
- •CLOB and NCLOB Datatypes
- •BFILE Datatype
- •RAW and LONG RAW Datatypes
- •ROWID and UROWID Datatypes
- •The ROWID Pseudocolumn
- •Physical Rowids
- •Logical Rowids
- •Rowids in Non-Oracle Databases
- •ANSI, DB2, and SQL/DS Datatypes
- •XML Datatypes
- •XMLType Datatype
- •URI Datatypes
- •Data Conversion
- •13 Object Datatypes and Object Views
- •Introduction to Object Datatypes
- •Complex Data Models
- •Multimedia Datatypes
- •Object Datatype Categories
- •Object Types
- •Collection Types
- •Type Inheritance
- •FINAL and NOT FINAL Types
- •NOT INSTANTIABLE Types and Methods
- •User-Defined Aggregate Functions
- •Why Have User-Defined Aggregate Functions?
- •Creation and Use of UDAGs
- •How Do Aggregate Functions Work?
- •Application Interfaces
- •JPublisher
- •JDBC
- •SQLJ
- •Datatype Evolution
- •Introduction to Object Views
- •Advantages of Object Views
- •How Object Views Are Defined
- •Use of Object Views
- •Updates of Object Views
- •Updates of Nested Table Columns in Views
- •View Hierarchies
- •14 SQL, PL/SQL, and Java
- •SQL Overview
- •SQL Statements
- •Identification of Nonstandard SQL
- •Recursive SQL
- •Cursors
- •Shared SQL
- •Parsing
- •SQL Processing
- •The Optimizer Overview
- •PL/SQL Overview
- •How PL/SQL Runs
- •Language Constructs for PL/SQL
- •PL/SQL Program Units
- •PL/SQL Collections and Records
- •PL/SQL Server Pages
- •Java Overview
- •Java and Object-Oriented Programming Terminology
- •Class Hierarchy
- •Interfaces
- •Polymorphism
- •The Java Virtual Machine (JVM)
- •Why Use Java in Oracle?
- •Oracle’s Java Application Strategy
- •15 Dependencies Among Schema Objects
- •Introduction to Dependency Issues
- •Resolution of Schema Object Dependencies
- •Compilation of Views and PL/SQL Program Units
- •Function-Based Index Dependencies
- •Object Name Resolution
- •Shared SQL Dependency Management
- •Local and Remote Dependency Management
- •Management of Local Dependencies
- •Management of Remote Dependencies
- •16 Transaction Management
- •Introduction to Transactions
- •Statement Execution and Transaction Control
- •Statement-Level Rollback
- •Resumable Space Allocation
- •Transaction Management Overview
- •Commit Transactions
- •Rollback of Transactions
- •Savepoints In Transactions
- •Transaction Naming
- •The Two-Phase Commit Mechanism
- •Discrete Transaction Management
- •Autonomous Transactions
- •Autonomous PL/SQL Blocks
- •Transaction Control Statements in Autonomous Blocks
- •17 Triggers
- •Introduction to Triggers
- •How Triggers Are Used
- •Parts of a Trigger
- •The Triggering Event or Statement
- •Trigger Restriction
- •Trigger Action
- •Types of Triggers
- •Row Triggers and Statement Triggers
- •BEFORE and AFTER Triggers
- •INSTEAD OF Triggers
- •Triggers on System Events and User Events
- •Trigger Execution
- •The Execution Model for Triggers and Integrity Constraint Checking
- •Data Access for Triggers
- •Storage of PL/SQL Triggers
- •Execution of Triggers
- •Dependency Maintenance for Triggers
- •18 Parallel Execution of SQL Statements
- •Introduction to Parallel Execution
- •When to Implement Parallel Execution
- •When Not to Implement Parallel Execution
- •How Parallel Execution Works
- •Parallelized SQL Statements
- •Degree of Parallelism
- •SQL Operations That Can Be Parallelized
- •Parallel Query
- •Parallel DDL
- •Parallel DML
- •SQL*Loader
- •How to Make a Statement Run in Parallel
- •19 Direct-Path INSERT
- •Introduction to Direct-Path INSERT
- •Advantages of Direct-Path INSERT
- •Serial and Parallel Direct-Path INSERT
- •Direct-Path INSERT Into Partitioned and Nonpartitioned Tables
- •Serial Direct-Path INSERT into Partitioned and Nonpartitioned Tables
- •Parallel Direct-Path INSERT into Partitioned Tables
- •Parallel Direct-Path INSERT into Nonpartitioned Tables
- •Direct-Path INSERT and Logging Mode
- •Direct-Path INSERT with Logging
- •Direct-Path INSERT without Logging
- •Additional Considerations for Direct-Path INSERT
- •Index Maintenance with Direct-Path INSERT
- •Space Considerations with Direct-Path INSERT
- •Locking Considerations with Direct-Path INSERT
- •20 Data Concurrency and Consistency
- •Introduction to Data Concurrency and Consistency in a Multiuser Environment
- •Preventable Phenomena and Transaction Isolation Levels
- •Overview of Locking Mechanisms
- •How Oracle Manages Data Concurrency and Consistency
- •Multiversion Concurrency Control
- •Statement-Level Read Consistency
- •Transaction-Level Read Consistency
- •Read Consistency with Real Application Clusters
- •Oracle Isolation Levels
- •Comparison of Read Committed and Serializable Isolation
- •Choice of Isolation Level
- •How Oracle Locks Data
- •Transactions and Data Concurrency
- •Deadlocks
- •Types of Locks
- •DML Locks
- •DDL Locks
- •Latches and Internal Locks
- •Explicit (Manual) Data Locking
- •Oracle Lock Management Services
- •Flashback Query
- •Flashback Query Benefits
- •Some Uses of Flashback Query
- •21 Data Integrity
- •Introduction to Data Integrity
- •Types of Data Integrity
- •How Oracle Enforces Data Integrity
- •Introduction to Integrity Constraints
- •Advantages of Integrity Constraints
- •The Performance Cost of Integrity Constraints
- •Types of Integrity Constraints
- •NOT NULL Integrity Constraints
- •UNIQUE Key Integrity Constraints
- •PRIMARY KEY Integrity Constraints
- •Referential Integrity Constraints
- •CHECK Integrity Constraints
- •The Mechanisms of Constraint Checking
- •Default Column Values and Integrity Constraint Checking
- •Deferred Constraint Checking
- •Constraint Attributes
- •SET CONSTRAINTS Mode
- •Unique Constraints and Indexes
- •Constraint States
- •Constraint State Modification
- •22 Controlling Database Access
- •Introduction to Database Security
- •Schemas, Database Users, and Security Domains
- •User Authentication
- •Authentication by the Operating System
- •Authentication by the Network
- •Authentication by the Oracle Database
- •Multitier Authentication and Authorization
- •Authentication by the Secure Socket Layer Protocol
- •Authentication of Database Administrators
- •Oracle Internet Directory
- •User Tablespace Settings and Quotas
- •Default Tablespace Option
- •Temporary Tablespace Option
- •Tablespace Access and Quotas
- •The User Group PUBLIC
- •User Resource Limits and Profiles
- •Types of System Resources and Limits
- •Profiles
- •23 Privileges, Roles, and Security Policies
- •Introduction to Privileges
- •System Privileges
- •Schema Object Privileges
- •Table Security
- •View Security
- •Procedure Security
- •Type Security
- •Introduction to Roles
- •Common Uses for Roles
- •The Mechanisms of Roles
- •Grant and Revoke Roles
- •Who Can Grant or Revoke Roles?
- •Role Names
- •Security Domains of Roles and Users
- •PL/SQL Blocks and Roles
- •Data Definition Language Statements and Roles
- •Predefined Roles
- •The Operating System and Roles
- •Roles in a Distributed Environment
- •Fine-Grained Access Control
- •Dynamic Predicates
- •Application Context
- •Secure Application Roles
- •Creation of Secure Application Roles
- •24 Auditing
- •Introduction to Auditing
- •Features of Auditing
- •Mechanisms for Auditing
- •Statement Auditing
- •Privilege Auditing
- •Schema Object Auditing
- •Schema Object Audit Options for Views and Procedures
- •Fine-Grained Auditing
- •Focus Statement, Privilege, and Schema Object Auditing
- •Successful and Unsuccessful Statement Executions Auditing
- •BY SESSION and BY ACCESS Clauses of Audit Statement
- •Audit By User
- •Audit in a Multitier Environment
- •Allocating Extents in Dictionary Managed Tablespaces
- •Introduction to Rollback Segments
- •PCTFREE, PCTUSED, and Row Chaining
- •Glossary
- •Index

User Authentication
Security Issues for Middle-Tier Applications
There are a number of security issues for middle-tier applications:
Accountability: The database server must be able to distinguish between the actions of a client and the actions an application takes on behalf of a client. It must be possible to audit both kinds of actions.
Differentiation: The database server must be able to distinguish between a web server transaction, a web server transaction on behalf of a browser client, and a client accessing the database directly.
Least privilege: Users and middle tiers should be given the fewest privileges necessary to do their jobs.
Identity Issues in a Multitier Environment
Multitier authentication maintains the identify of the client through all tiers of the connection. This is necessary because if the identity of the originating client is lost, it is not possible to maintain useful audit records. In addition, it is not possible to distinguish operations performed by the application server on behalf of the client from those done by the application server for itself.
Restricted Privileges in a Multitier Environment
Privileges in a multitier environment are limited to what is necessary to perform the requested operation.
Client Privileges Client privileges are as limited as possible in a multitier environment. Operations are performed on behalf of the client by the application server.
Application Server Privileges Application server privileges in a multitier environment are limited so that the application server cannot perform unwanted or unneeded operations while performing a client operation.
See Also: Oracle9i Database Administrator’s Guide for more information about multitier authentication
Authentication by the Secure Socket Layer Protocol
The Secure Socket Layer (SSL) protocol is an application layer protocol. It can be used for user authentication to a database, independent of global user management in Oracle Internet Directory. That is, users can use SSL to authenticate to the database without implying anything about their directory access. However, if you
22-12 Oracle9i Database Concepts
User Authentication
wish to use the enterprise user functionality to manage users and their privileges in a directory, the user must use SSL to authenticate to the database. A parameter in the initialization file governs which use of SSL is expected.
Authentication of Database Administrators
Database administrators perform special operations (such as shutting down or starting up a database) that should not be performed by normal database users. Oracle provides a more secure authentication scheme for database administrator usernames.
You can choose between operating system authentication or password files to authenticate database administrators.
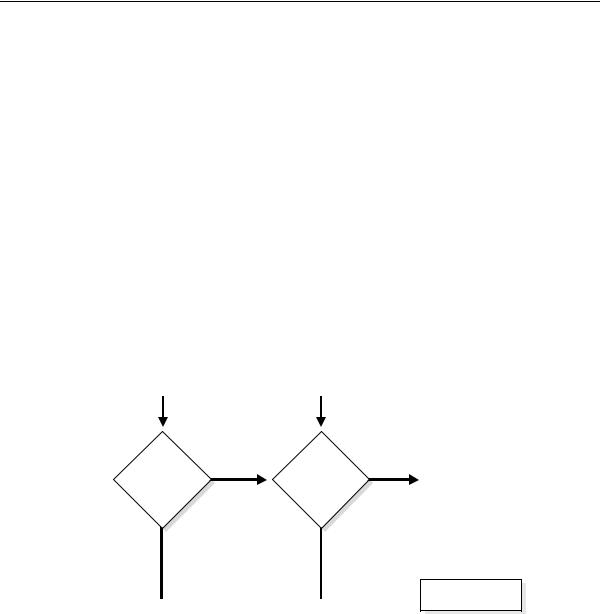
Figure 22–3 illustrates the choices you have for database administrator authentication schemes, depending on whether you administer your database locally (on the same machine on which the database resides) or if you administer many different database machines from a single remote client.
Figure 22–3 Database Administrator Authentication Methods
Remote Database |
Local Database |
|
|
|
|
Administration |
|
Administration |
|
|
|
Do you |
Yes |
Do you |
Yes |
|
|
have a secure |
|
want to use OS |
|
|
Use OS |
connection? |
|
authentication? |
|
|
authentication |
No |
|
No |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
||
 Use a password file
Use a password file
On most operating systems, operating system authentication for database administrators involves placing the operating system username of the database administrator in a special group (on UNIX systems, this is the dba group) or giving that operating system username a special process right.
Controlling Database Access 22-13
