
МЕТ_1к_1ч
.pdf5.How can a student avoid a last-minute rush or late-night sitting before an exam? What do you think about "surge study"?
6.Judging from your experience as a learner, how important is the encouraging tone of an examiner?
7.What is your attitude to the common practice of "cramming" before an examination?
25.This summer in England you have got acquainted with new friends. One of them is a student from Oxford University. His name is John and he is the second-year-student. You are a student of the NTUU "KPI". Ask each other about the life at your Universities. Role play the conversation. Use role and cue cards (Appendix 3). You may use some information from this unit.
26.Read some information from the texts "THE BRITISH HIGHER EDUCATION" and "AMERICANS AND HIGHER EDUCATION". Then in pairs ask and answer questions about higher education in Great Britain and America (see the EXTRA READING section to Unit 1) based on the suggested texts.
27.Work in pairs. You are talking with your friend about Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT). Make up a dialogue which starts with the suggested question (use some information from the EXTRA READING section to Unit 1). Act out the conversation.
A:Is Massachusetts Institute of Technology a private institution?
B:___________________________________________________
A:___________________________________________________
B:___________________________________________________
A:___________________________________________________
B:___________________________________________________
21

A:___________________________________________________
B:___________________________________________________
28.A. Comment on the pictures using linking words: firstly / first of all, secondly, thirdly, after this / that, then, next, finally. Use only the Present Simple.
Useful words and phrases:
early childhood education; primary education; secondary education; higher / tertiary education at university; college; to provide the necessary minimum knowledge; generally; to obtain the qualification; to culminate in the receipt of certificates / diplomas / academic degrees; bachelor's / master's degree
B. Answer the following question.
What do you think education should aim to do?
e.g.
prepare students to pass exams,
teach students "life skills",
help students to develop their intellectual abilities.
22

29. Describe the picture. Use the Present Simple and the Present Continuous.
Useful verbs:
to write; to discuss; to solve; to think over; to analyse; to practice; to prove; to
make a decision
30.Look at the list below. Decide which of the factors you think contribute most to a good university education. Explain your reasons.
small groups; modern text books; strict discipline; labs with new equipment; computers; motivated highly qualified teachers; modern buildings; a lot of practice; individual approach; flexible schedule; distance learning
31.You are particularly interested in information (history of foundation, faculties, specialties etc.) about the Institute of Physics and Technology. Find information about your institute and be ready to tell your groupmates.
23
32.Find the Ukrainian equivalents of the following proverbs. Choose two of them and express your opinion.
1.A fool man can ask more questions in an hour than a wise man can answer in seven years.
2.Don’t teach a fish to swim.
3.Repetition is the mother of learning.
4.No pains – no gains.
5.Live and learn.
6.It’s never too late to learn.
7.Knowledge is power.
8.Better untaught than ill-taught.
9.All things are difficult before they are easy.
10.Money spent on the brain is never spent in vain.
11.One good head is better than a hundred strong hands.
12.To teach the dog to bark.
13.Too much knowledge makes the head bald.
LISTENING
14.To know everything is to know nothing.
15.Zeal without knowledge is a runway horse.
16.Where there is a will there is a way.
17.Nothing is impossible to a willing heart.
18.What we do willingly is easy.
19.First think then speak.
20.There is no rule without an exception.
21.Soon learnt – soon forgotten.
22.Little knowledge is a dangerous thing.
23.Like teacher, like pupil.
24.He, who makes no mistakes, makes nothing.
25.He that knows nothing doubts nothing.
You are going to listen to some information about studies and degrees in Great Britain. Be ready to do the following tasks below.
33.Before you listen, check if you know the meaning of the following words and phrases: to concentrate, to offer, the remainder, to extend, to require, to be awarded, vary, to combine, tutorials, seminars, lectures.
34.Answer the questions.
1.How old are the Universities of Oxford and Cambridge?
2.How many students in percentage are taking scientific and technological studies?
3.What is the term of studying at Britain’s Universities?
4.What kind of work does academic staff devote time to?
24
35.Choose the correct item.
1.The number of Britain’s Universities is .......................... .
a)about a hundred
b)forty
c)fifty
d)forty-five
2.Most of the universities in Great Britain were founded .......................... .
a)in the twelfth century
b)in the fifteenth century
c)in the seventeenth century
d)in the nineteenth century
3.About half of all the students of full-time universities in Britain are taking courses .......................... .
a)in medicine
b)in arts and social studies
c)in agriculture forestry, architecture, veterinary
d)science and technology
36.Complete the phrases.
1.Courses in sciences are offered ..............… .
2. |
The Universities concentrate on technology although they .........… . |
3. |
Further study or research is required at the modern universities |
|
for …................. . |
4. |
University’s teaching combines …................ . |
WRITING
37.Refer to Exercise 32. Choose a proverb and comment on it (50−60 words). Use some phrases from Appendix 9 to start your comment.
25

38.Read the text "MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY" (see the EXTRA READING section to Unit 1). Write a short summary of the text (50−60 words). Follow these steps:
Read the text.
Make notes of the main points of the text.
Start your piece of writing with one sentence that summarizes the idea of the whole text.
Write your summary, including all the main points. Use your own words.
Check if your summary is clear, complete and it makes sense.
39.Read the text "FROM THE HISTORY OF THE NATIONAL TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY OF UKRAINE "KYIV POLYTECHNIC INSTITUTE"" and
make a mind map to it. Share your mind map with a partner. Explain how
the circles are related to each other.
MIND MAPPING
To make a mind map, use a whole sheet of paper, and write your topic in the middle, with a circle around it. Then put the next idea in a circle above or below your topic, and connect the circles with lines. The lines show that the two ideas are related.
26

40.Write an essay on the topic "Are exams necessary?" (100−120 words).
Follow the structure: introduction, main body, conclusions (see the WRITING HELP section). Use the MINI-DICTIONARY section to Unit 1.
Useful words and phrases:
to be evaluated by their teachers; exam pressure; personal review schemes; continuous assessment; to perform well / badly under exam conditions; to test students' skills; to be abolished; be an efficient way to measure the knowledge; stress and anxiety
41.Work in small groups. Create a crossword on the topic "The National Technical University of Ukraine "Kyiv Polytechnic Institute". Exchange the crosswords and solve them.
PROBLEM-SOLVING
42. Test yourself (see the PROBLEM-SOLVING section to Unit 1).
27
Unit 2: IMPERIAL ENGLISH: THE LANGUAGE OF SCIENCE
Language is the dress of thought.
Samuel Johnson
WARM-UP
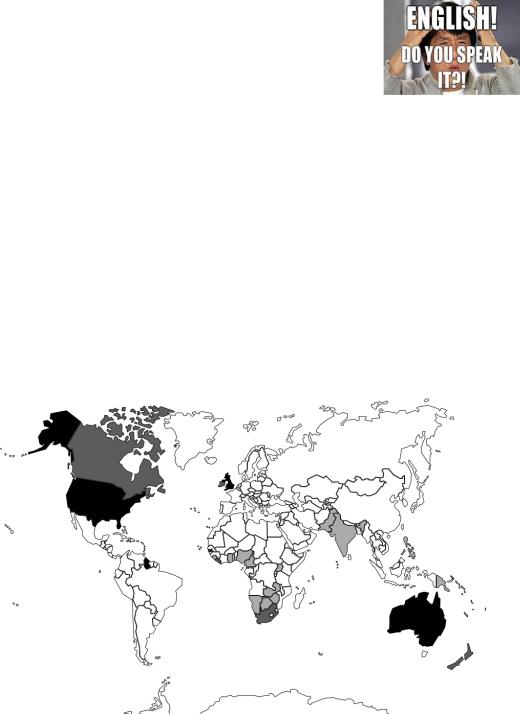
1.Name
countries where English is the first and often the only language of most people (black colour);
countries where besides English as a native language there is at least one more native tongue (dark grey colour);
countries where English is not a native language, the only official language (light grey colour).
ENGLISH LANGUAGE − AROUND THE WORLD
If you have any difficulties, see Appendix 3.
28

2.Look at the picture and read notes. Does this student undestand the importance of knowing the foreign language? Explain your point of view using answers in clouds.
3.Discuss the following quotations. Which quotation is closer to your own ideas?
A."We have too many high sounding words and too few actions that correspond with them."
Abigail Adams
B."If you can speak three languages you're trilingual. If you can speak two languages you're bilingual. If you can speak only one language you're an American."
Unknown
C."The English language is nobody's special property. It is the property of the imagination: it is the property of the language itself."
Derek Walcott
29

D."Words, too, have genuine substance − mass and weight and specific gravity."
Tim O'Brien, Tomcat in Love
E."Language is the means of getting an idea from my brain into yours without surgery."
Mark Amidon
F. "Words want to be free!"
Unknown
G."A word is not a crystal, transparent and unchanged, it is the skin of a living thought and may vary greatly in colour and content according to the circumstances and the time in which it is used."
Oliver Wendell Holmes
4.Discuss the following statements.
English is one of the international languages.
English is the language of science.
English is the language of business.
READING
5.Underline the stressed syllable in each word as in the example. Practise reading.
gradually, monolingual, incompetence, inexorably, immaculate, universal, currency, importance, occasionally, fluctuated, counterpoint, throughout, medium
6.Read the article "IMPERIAL ENGLISH: THE LANGUAGE OF SCIENCE" and match the statements to the paragraphs.
A.Meetings were often held in several languages.
B.Unlike Heisenberg, most American science students only speak English.
30
