
2_kurs_4_semestr
.pdf3.Please call me if you … (need) any help.
4.… Sarah … (be) angry if we don‘t go to her party?
5.Cathy will be able to go on holiday if she … (save) enough money.
6.Unless it … (rain) we‘ll go for a walk.
7.If you … (work) hard you may be promoted.
8.… you … (give) me a call if you have time tomorrow?
9.If you don‘t do your homework I … (not/let) you watch TV.
10.Mary won‘t go to Australia unless I … (pay) for her tickets.
11.If he … (arrive) on time we‘ll have dinner before we go out.
4. Finish the following sentences.
1.I shall go shopping if …
2.We shall spend two days in the country if …
3.He will show you his stamps if …
4.You will enjoy the concert if …
5.We shall go sightseeing if …
6.If you devote all your time to studying foreign languages …
7.If I were you …
8.If you see him …
9.If I give you my book …
10.If your parents let you come to the party …
5. Answer the questions.
1.What will you say if your mother sees you smoking in the yard?
2.What will your teacher do if you miss a lesson?
3.What will you do if you come earlier?
4.What will your family do if your TV-set is broken?
5.What will you do if you loose your passport?
21
UNIT 4
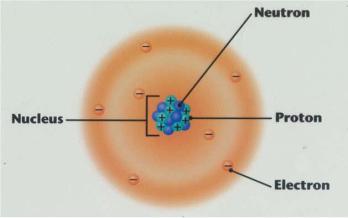
The Structure of Nuclei
Read the text and be ready to discuss the given information.
The term nucleus is from Latin nucleus (―kernel‖), derived from nux (―nut‖). In 1844, Michael Faraday used the term to refer to the ―central point of an atom‖. The modern atomic meaning was proposed by Ernest Rutherford in 1912.
The adoption of the term ―nucleus‖ to atomic theory, however, was not immediate. In 1916, for example, Gilbert N. Lewis stated, in his famous article
The Atom and the Molecule, that ―the atom is composed of the kernel and an outer atom or shell‖.
The nucleus of an atom consists of nucleons (protons and neutrons – two types of baryons) bound by the nuclear force (also known as the residual strong force). These baryons are further composed of subatomic fundamental particles known as quarks bound by the strong interaction. Almost all of the mass in an atom is made up from the protons and neutrons in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the orbiting electrons. It was discovered in 1911, as a result of Ernest Rutherford‘s interpretation of the famous 1909 Rutherford experiment performed by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden, under the direction of Rutherford.
The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 1.6 fm (1.6×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 15 fm for the heaviest
22
atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electronic cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).
The branch of physics concerned with studying and understanding the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics. Understanding the structure of the atomic nucleus is one of the central challenges in nuclear physics. There are many different historical models of the atomic nucleus, to this day none of which completely alone explain experimental data on nuclear structure. A useful review of 37 known models of the atomic nucleus is provided by Cook.
Discussion Question.
Suppose the entire universe was in a (very large) cereal box, and the nutritional labeling was supposed to tell a godlike consumer what percentage of the contents was nuclei. Roughly what would the percentage be like if the labeling was according to mass? What if it was by volume?
Translate the following sentences into English.
1.Атомне ядро – центральна частина атома.
2.Атомні ядра вивчає ядерна фізика.
3.Атомне ядро складається з нуклонів – позитивно заряджених протонів і нейтральних нейтронів, які повʼязані між собою за допомогою сильної взаємодії.
4.Атомне ядро, що розглядається як клас частинок з визначеним числом протонів і нейтронів, прийнято називати нуклідом.
5.Ядра з однаковою кількістю протонів і різною кількістю нейтронів називаються ізотопами.
23
Phrase Match.
1.The proton is
2.The proton is found in the nucleus of each atom, along with neutrons,
3.The neutron is a subatomic particle
4.The nuclei of most atoms consist of protons and neutrons,
5.The proton is composed of three fundamental particles:
6.The two up quarks and one down quark of the proton are held together by the strong force,
7.The number of protons in a nucleus is
8.The number of neutrons
9.Almost all of the mass in an atom is made up
10.The adoption of the term
―nucleus‖ to atomic theory
a.with no net electric charge and a mass slightly larger than that of a proton.
b.two up quarks and one down quark.
c.mediated by gluons.
d.from the protons and neutrons in the nucleus.
e.the atomic number and defines the type of element the atom forms.
f.a subatomic particle with an electric charge of +1 elementary charge.
g.was not immediate.
h.but is also stable by itself and has
asecond identity as the hydrogen ion, H+.
i.is the neutron number and determines the isotope of an element.
j.which are therefore collectively referred to as nucleons.
24
GRAMMAR
2 Conditional. Practice.
EXERCISES
1. What would you do in each situation? Write unreal present conditionals.
1) You found a fly in your soup.
If I found a fly in my soup, I would complain to the manager.
2)You see a burglar breaking into your house.
3)You see a mouse in your kitchen.
4)Your car runs out of petrol.
5)You see an accident.
6)You see a ghost in your room.
2. Choose one of the prompts from the list to say what you would do in each of the situations below.
order a pizza, complain to the manager, light some candles, go to hospital, call the police, stay in bed
1) You see someone robbing a bank.
If I saw someone robbing a bank, I would call the police.
2)A shop assistant is rude to you.
3)You fall over and break your arm.
4)You burn your dinner.
5)There is a power cut in your house.
6)You catch a bad cold.
25
3. Put the verbs in brackets into the correct tense to make correct type 2
conditional sentences.
1)If I …were… (be) you, I …would study… (study) for the exams.
2)If we … (have) a car, we … (go) for a drive in the country.
3)Kim … (buy) some new clothes if she … (have) enough money.
4)If cameras … (not/cost) so much, we … (buy) one.
5)John … (lend) you some money if you … (ask) him.
6)He … (open) the door if he … (have) the key.
7)We … (paint) the house if we … (have) the time.
8)If she … (get) good grades, she … (go) to university.
9)If I … (be) rich, I … (never/work) again.
10)Helen … (post) the letters if she … (have) some stamps.
4. Advise Jenny what to do in each situation.
1)J: I can‘t see a thing.
Y:If I were you, I’d clean my glasses!
2)J: I‘m tired.
3)J: I‘m hungry.
4)J: My skirt is too tight.
5)J: My hair‘s a mess.
6)J: I‘ve got a toothache.
5. Finish the following sentences.
1)My friend would ring me up if …
2)My mother would not leave the door open if …
3)They would not come so late if …
4)If you told me about it earlier …
5)If I were you …
26
UNIT 5
The Nuclear Force
Read the text and translate it into Ukrainian.
The nuclear force is the force between two or more nucleons. It is responsible for binding of protons and neutrons into atomic nuclei.
The nuclear force is now understood as a residual effect of an even more powerful strong force, or strong interaction, which is the attractive force that binds particles called quarks together, to form the nucleons themselves. This more powerful force is mediated by particles called gluons. Gluons hold quarks together with a force like that of electric charge, but of far greater power.
The concept of a nuclear force was first quantitatively constructed in 1934, shortly after the discovery of the neutron revealed that atomic nuclei were made of protons and neutrons, held together by an attractive force. The nuclear force at that time was conceived to be transmitted by particles called mesons, which were predicted in theory before being discovered in 1947. In the 1970‘s, further understanding revealed these mesons to be combinations of quarks and gluons, transmitted between nucleons that themselves were made of quarks and gluons. This new model allowed the strong forces that held nucleons together, to be felt in neighboring nucleons, as residual strong forces.
The nuclear forces arising between nucleons are now seen to be analogous to the forces in chemistry between neutral atoms called van der Waals forces. Such forces between atoms are much weaker than the electrical forces that hold the atoms themselves together, and their range is shorter, because they arise from spontaneous separation of charges inside the atom.
27
Similarly, even though nucleons are made of quarks and gluons that are in combinations which cancel most gluon forces, some combinations of quarks and gluons nevertheless leak away from nucleons, in the form of short-range nuclear force fields that extend from one nucleon to another close by. These nuclear forces are very weak compared to direct gluon forces inside nucleons, and they extend only over a few nuclear diameters, falling exponentially with distance. Nevertheless, they are strong enough to bind neutrons and protons over short distances, and overcome the electrical repulsion between protons in the nucleus.
There are four known fundamental forces of physics:
-gravitational force;
-electromagnetic force;
-strong nuclear force;
-weak nuclear force.
The other forces, such as friction and the normal force, all arise from electromagnetic interactions between atoms, and therefore are not considered to be fundamental forces of physics.
Answer the following questions:
1)What is the nuclear force?
2)What is the nuclear force responsible for?
3)When was the concept of a nuclear force quantitatively constructed?
4)What are atomic nuclei made of?
5)Are van der Waals forces much weaker than the electrical forces?
28
Fill in the blanks with the proper information. Don‟t look at the text!
1)The nuclear force is the force between two or more … .
2)Gluons hold … together with a force like that of electric charge, but of far greater power.
3)The … of a nuclear force was first quantitatively constructed in 1934.
4)Atomic nuclei were made of … and …, held together by an attractive force.
5)There are … known fundamental forces of physics.
Be ready to say a few words about:
1)The strong nuclear force;
2)The weak nuclear force;
3)Gravitational force;
4)Electromagnetic force.
29
GRAMMAR
3 Conditional. Practice.
EXERCISES
1. Write unreal conditionals (3rd type) as in the example.
1) (climb ladder/break his leg)
If he hadn’t climbed the ladder, he wouldn’t have broken his leg.
2)(drive carefully/avoid accident)
3)(John run faster/win the race)
2. |
Match the parts of the sentences. |
|
|
|
|
1. |
If I hadn‘t missed the bus, |
a. he would have gone to university. |
|
|
|
2. |
If she hadn‘t felt ill this morning, |
b. Chris wouldn‘t have given me |
|
|
flowers. |
|
|
|
3. |
If the food hadn‘t been awful, |
c. she would have gone to school. |
|
|
|
4. |
If he had passed his exams, |
d. I would have accepted the job. |
|
|
|
5. |
If the salary had been good, |
e. I wouldn‘t have been late for work. |
|
|
|
6. |
If it hadn‘t been my birthday, |
f. we would have eaten it. |
|
|
|
3. Richard Brooks was very upset yesterday because he missed an important meeting. Look at the prompts and make sentences, as in the example.
e.g. If the airline hadn’t been on strike, his flight wouldn’t have been delayed. If his flight hadn’t been delayed, …
the airline / not be / on strike → his flight / not be / delayed → he / arrive / in New York / on time → he / attend / the meeting → he / sign / the contract → his boss / be / pleased with him → she / give / him / a promotion
30
