
- •Энергетика
- •Источники энергии
- •Возобновляемые источники энергии
- •Доля ВИЭ в энергопотреблении стран ЕЭС - 2005
- •Percentage of renewables in primary energy consumption of EU-member states in 2005
- •Мировой энергетический баланс
- •Условное топливо
- •Структура генерирующих мощностей
- •Франция - Энергетический баланс - 2006
- •Energy in Norway
- •Net Generation by Energy Source USA 2007
- •Россия - Генерирующие мощности и их структура
- •Топливно-энергетический баланс России
- •Экология
- •Экология в теплоэнергетике
- •Экология в теплоэнергетике 1
- •Экология в теплоэнергетике 2
- •Global fossil carbon emission
- •Киотский протокол
- •Participation in the Kyoto Protocol:
- •Мировые выбросы СО2, %
- •Гидроэнергетика - ГЭС
- •Саяно-Шушинская ГЭС
- •Авария 17 августа 2009 года
- •Перспективы гидроэнергетики
- •Country
- •Countries with the most hydro-electric capacity
- •The Three Gorges Dam, the largest hydro- electric power station in the world
- •The Three Gorges Dam
- •Three Gorges Dam – Main information
- •Альтернативная энергетика
- •Hydroelectric-pumped-storage station
- •Power distribution, over a day, of a pumped-storage hydroelectricity facility.
- •Nuclear weapon
- •Ядерная энергетика - АЭС
- •First steps
- •The first nuclear-powered submarine, USS Nautilus (SSN-571)
- •Атомная энергетика - Перспективы
- •Nuclear power
- •Nuclear power in the world
- •The Nuclear Fuel Cycle begins when uranium is mined, enriched, and manufactured into
- •History of the use nuclear power and the number of active nuclear power
- •Accidents at NPP
- •РБМК (Реактор Большой Мощности Канальный)
- •Технические характеристики РБМК-1000
- •Схема энергоблока АЭС с реактором типа РБМК
- •Схема АЭС
- •Схема АЭС с реактором РБМК-1000
- •Атомные электростанции России
- •АЭС - Энергетическая стратегия России
- •Термоядерный реактор
- •Управляемый термоядерный синтез
- •Термоядерный синтез
- •Термоядерный реактор
- •Возобновляемые источники энергии
- •Ресурсы ВИЭ в сравнении с потреблением энергии во всём мире
- •Геотермальная энергетика - ГеоТЭС
- •Схема ГеоТЭС
- •ГеоТЭС в России и в мире
- •Геотермические ресурсы Европы
- •Hot Dry Rock
- •Hot Dry Rock
- •Hot Dry Rock
- •Ветроэнергетика
- •Ветряные мельницы в Ла Манче (Испания)
- •Ветроэнергетика (ВЭС)
- •Средняя скорость ветра
- •Ветроэнергетика - нюансы
- •Оффшорная ветряная ферма под Копенгагеном
- •Оффшорные ВЭС
- •Суммарные установленные мощности, МВт
- •Рост установленных мощностей ВЭУ
- •Ветроэнергетика –
- •Перспективы
- •Flying Electric Generator
- •Flying Electric Generator
- •Ветроэнергетика России
- •Экономические аспекты
- •Экологические аспекты
- •Солнце
- •Карта солнечного излучения
- •Энергия солнца, поступающая на Землю
- •Ежедневная солнечная активность
- •Способы получения электричества и тепла из солнечного излучения
- •Солнечная энергетика
- •Солнечная энергетика
- •Достоинства и недостатки солнечной энергетики
- •Технические проблемы
- •Экологические проблемы
- •Установки солнечного теплоснабжения
- •Системы солнечного теплоснабжения
- •Это интересно …
- •CIS Tower - Manchester
- •Солнечные батареи на крыше здания Академии наук России
- •Прачечная, использующая для работы
- •«Солнечный» автомобиль
- •Беспилотный самолёт Helios с фотоэлементами на крыльях
- •Приливные электростанции (ПЭС)
- •Приливные электростанции (ПЭС)
- •Крупнейшая в мире приливная электростанция Ля Ранс, Франция – 240 МВт
- •Энергия морских и океанских волн
- •Pelamis Wave Energy Converter
- •Pelamis wave power generator
- •Pelamis Wave Power
- •Малая гидроэнергетика (МГЭС)
- •Биотопливо
- •Топливные гранулы
- •Энергетический лес
- •Машина для переработки древесной биомассы в щепу
- •Бытовой пеллетный камин
- •Биогаз
- •Метантанк биогазовой установки
- •Водород – энергоноситель будущего
- •Получение водорода
- •Сжиженный водород LH2
- •LH2 как автомобильное топливо
- •LH2 как авиационное топливо
- •ТУ-155 на жидком водороде
- •Водород – энергоноситель будущего
- •Теплоэнергетика
- •Топливные ресурсы России
- •Природный газ
- •Крупнейшие газовые месторождения
- •Мировые запасы газа (млрд. м3) - 2006
- •Нефть
- •НЕФТЬ
- •Нефть - Мировые запасы
- •Добыча нефти
- •Нефть – проблемы!!!
- •Катар
- •Уголь
- •Запасы угля
- •Канско-Ачинский бассейн
- •Кузнецкий бассейн
- •Кузбасс
- •Характеристики угля
- •Теплоэнергетика
- •Схема котельной установки
- •Спасибо за внимание!

Nuclear power
•As of 2005, nuclear power provided 2.1 % of the world's energy and 15 % of the world's electricity, with the U.S., France, and Japan together accounting for 56.5 % of nuclear generated electricity.
•Despite concerns about safety and radioactive waste management there are 439 nuclear power reactors in operation in the world, operating in 31 countries.
•In 2007, nuclear power's share of global electricity generation dropped to
14 %. According to the International Atomic Energy Agency, the main reason for this was an earthquake in western Japan on 16 July 2007,
which shut down all seven reactors at the Kashiwazaki-Kariwa NPP. There were also several other "unusual outages" experienced in Korea
and Germany.

Nuclear power in the world
•The United States produces the most nuclear energy, with nuclear power providing 19 % of the electricity it consumes, while France produces the highest percentage of its electrical energy from nuclear reactors – 78 % as of 2006.
•In the European Union as a whole, nuclear energy provides 30 % of the electricity. Nuclear energy policy differs between European Union countries, and some, such as Austria, Estonia, and Ireland, have no active nuclear power stations. In comparison, France has a large number of these plants, with 16 multi-unit stations in current use.
•Many military and some civilian ships (such as some icebreakers) use nuclear marine propulsion. A few space vehicles have been launched using full-fledged nuclear reactors: the Soviet RORSAT series and the American SNAP-10A.

The Nuclear Fuel Cycle begins when uranium is mined, enriched, and manufactured into nuclear fuel (1), which is delivered to a nuclear power plant. After usage in the power plant, the spent fuel is delivered to a reprocessing plant (2) or to a final repository (3) for geological disposition. In reprocessing 95 % of spent fuel can be recycled to be returned to usage in a power plant (4).
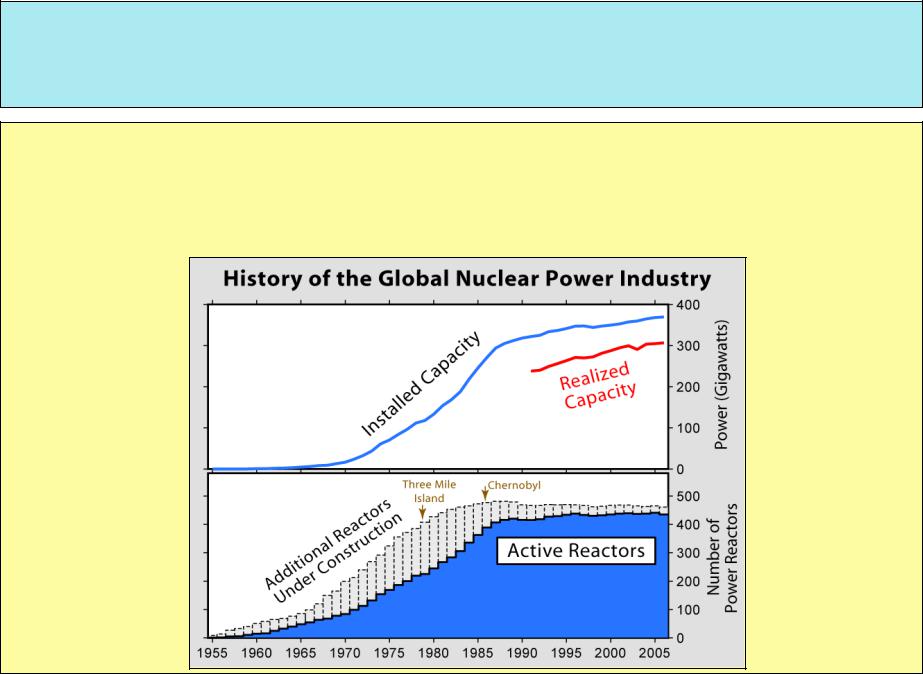
History of the use nuclear power and the number of active nuclear power plants
•Installed nuclear capacity initially rose relatively quickly, rising from less than 1 GW in 1960 to 100 GW in the late 1970s, and 300 GW in the late 1980s. Since the late 1980s worldwide capacity has risen much more slowly, reaching 366 GW in 2005.
•In 2005, around 25 GW of new capacity was planned. More than two-thirds of all nuclear plants ordered after January 1970 were eventually cancelled.

Accidents at NPP
•The 1979 accident at Three Mile Island and the 1986 Chernobyl disaster played a part in stopping new plant construction in many countries.
•Unlike the Three Mile Island accident, the much more serious Chernobyl
accident did not increase regulations affecting Western reactors since the Chernobyl reactors were of the problematic RBMK (High Power Channel-type Reactor) design only used in the Soviet Union.
•Many of these reactors are still in use today. However, changes were made in both the reactors themselves (use of low enriched uranium) and in the control system (prevention of disabling safety systems) to reduce the possibility of a duplicate accident.

РБМК (Реактор Большой Мощности Канальный)

Технические характеристики РБМК-1000
Тепловая мощность реактора – 3000 МВт Электрическая мощность блока – 1000 МВт КПД блока – 31,3 % Давление пара – 65 атм Температура пара – 280 °С Размеры активной зоны:
высота – 7 м, диаметр – 11,8 м Загрузка урана – 192 т

Схема энергоблока АЭС с реактором типа РБМК

Схема АЭС

